Inicio rápido: Compilación de una aplicación Immersive Reader
Lector inmersivo es una herramienta diseñada de manera inclusiva que implementa técnicas demostradas para mejorar la comprensión lectora de nuevos lectores, estudiantes de idiomas y personas con dificultades de aprendizaje, como la dislexia. Puede usar Lector inmersivo en sus aplicaciones para aislar el texto con el fin de mejorar la concentración, mostrar imágenes para palabras de uso frecuente, resaltar partes del texto, leer texto seleccionado en voz alta, traducir palabras y frases en tiempo real y mucho más.
En esta guía de inicio rápido, creará una aplicación web desde cero mediante C# e integrará Immersive Reader mediante la biblioteca cliente. Hay disponible un ejemplo funcional completo de esta guía de inicio rápido en GitHub.
Requisitos previos
- Suscripción a Azure. Puede crear una de forma gratuita.
- Un recurso del Lector inmersivo configurado para la autenticación de Microsoft Entra. Siga estas instrucciones para realizar la configuración. Guarde la salida de la sesión en un archivo de texto para que pueda configurar las propiedades del entorno.
- Visual Studio 2022.
Creación de un proyecto de aplicación web
Cree un proyecto en Visual Studio mediante la plantilla de aplicación web de ASP.NET Core con Modelo-Vista-Controlador integrado y ASP.NET Core 6. Asigne al proyecto el nombre QuickstartSampleWebApp.
Configuración de la autenticación
Haga clic con el botón derecho en el proyecto en el Explorador de soluciones y elija Administrar secretos de usuario. Se abre un archivo denominado secrets.json. Este archivo no está protegido bajo control de código fuente. Para obtener más información, consulte Almacenamiento seguro de secretos de aplicaciones. Reemplace el contenido de secrets. json con lo siguiente, y proporcione los valores especificados al crear el recurso del Lector inmersivo.
Importante
Recuerde no publicar nunca secretos públicamente. En el caso de producción, use una forma segura de almacenar sus credenciales y acceder a ellas, como Azure Key Vault.
{
"TenantId": "YOUR_TENANT_ID",
"ClientId": "YOUR_CLIENT_ID",
"ClientSecret": "YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET",
"Subdomain": "YOUR_SUBDOMAIN"
}
Instalación del paquete NuGet de Identity Client
El código siguiente usa objetos del paquete NuGet Microsoft.Identity.Client, por lo que debe agregar una referencia a ese paquete en el proyecto.
Importante
El paquete Microsoft.IdentityModel.Clients.ActiveDirectory NuGet y la Biblioteca de autenticación (ADAL) de Azure AD han quedado obsoletos. No se han agregado nuevas características desde el 30 de junio de 2020. Le recomendamos encarecidamente que haga una actualización. Para más información, consulte la guía de migración.
Abra la consola del administrador de paquetes NuGet en Herramientas ->Administrador de paquetes NuGet ->Consola del administrador de paquetes y ejecute el siguiente comando:
Install-Package Microsoft.Identity.Client -Version 4.59.0
Actualización del controlador para adquirir el token
Abra Controllers\HomeController.cs y agregue el código siguiente después de las instrucciones using en la parte superior del archivo.
using Microsoft.Identity.Client;
Configure el controlador para obtener los valores de Microsoft Entra ID de secrets.json. En la parte superior de la clase HomeController, después de public class HomeController : Controller { agregue el código siguiente.
private readonly string TenantId; // Azure subscription TenantId
private readonly string ClientId; // Microsoft Entra ApplicationId
private readonly string ClientSecret; // Microsoft Entra Application Service Principal password
private readonly string Subdomain; // Immersive Reader resource subdomain (resource 'Name' if the resource was created in the Azure portal, or 'CustomSubDomain' option if the resource was created with Azure CLI PowerShell. Check the Azure portal for the subdomain on the Endpoint in the resource Overview page, for example, 'https://[SUBDOMAIN].cognitiveservices.azure.com/')
private IConfidentialClientApplication _confidentialClientApplication;
private IConfidentialClientApplication ConfidentialClientApplication
{
get {
if (_confidentialClientApplication == null) {
_confidentialClientApplication = ConfidentialClientApplicationBuilder.Create(ClientId)
.WithClientSecret(ClientSecret)
.WithAuthority($"https://login.windows.net/{TenantId}")
.Build();
}
return _confidentialClientApplication;
}
}
public HomeController(Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration.IConfiguration configuration)
{
TenantId = configuration["TenantId"];
ClientId = configuration["ClientId"];
ClientSecret = configuration["ClientSecret"];
Subdomain = configuration["Subdomain"];
if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(TenantId))
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("TenantId is null! Did you add that info to secrets.json?");
}
if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(ClientId))
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("ClientId is null! Did you add that info to secrets.json?");
}
if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(ClientSecret))
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("ClientSecret is null! Did you add that info to secrets.json?");
}
if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(Subdomain))
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("Subdomain is null! Did you add that info to secrets.json?");
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Get a Microsoft Entra ID authentication token
/// </summary>
public async Task<string> GetTokenAsync()
{
const string resource = "https://cognitiveservices.azure.com/";
var authResult = await ConfidentialClientApplication.AcquireTokenForClient(
new[] { $"{resource}/.default" })
.ExecuteAsync()
.ConfigureAwait(false);
return authResult.AccessToken;
}
[HttpGet]
public async Task<JsonResult> GetTokenAndSubdomain()
{
try
{
string tokenResult = await GetTokenAsync();
return new JsonResult(new { token = tokenResult, subdomain = Subdomain });
}
catch (Exception e)
{
string message = "Unable to acquire Microsoft Entra token. Check the console for more information.";
Debug.WriteLine(message, e);
return new JsonResult(new { error = message });
}
}
Adición de contenido de ejemplo
En primer lugar, abra Views\Shared\Layout.cshtml. Antes de la línea </head>, agregue el código siguiente:
@RenderSection("Styles", required: false)
Ahora, agregue contenido de muestra a esta aplicación web. Abra Views\Home\Index.cshtml y reemplace el código generado automáticamente por este ejemplo:
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Immersive Reader C# Quickstart";
}
@section Styles {
<style type="text/css">
.immersive-reader-button {
background-color: white;
margin-top: 5px;
border: 1px solid black;
float: right;
}
</style>
}
<div class="container">
<button class="immersive-reader-button" data-button-style="iconAndText" data-locale="en"></button>
<h1 id="ir-title">About Immersive Reader</h1>
<div id="ir-content" lang="en-us">
<p>
Immersive Reader is a tool that implements proven techniques to improve reading comprehension for emerging readers, language learners, and people with learning differences.
The Immersive Reader is designed to make reading more accessible for everyone. The Immersive Reader
<ul>
<li>
Shows content in a minimal reading view
</li>
<li>
Displays pictures of commonly used words
</li>
<li>
Highlights nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs
</li>
<li>
Reads your content out loud to you
</li>
<li>
Translates your content into another language
</li>
<li>
Breaks down words into syllables
</li>
</ul>
</p>
<h3>
The Immersive Reader is available in many languages.
</h3>
<p lang="es-es">
El Lector inmersivo está disponible en varios idiomas.
</p>
<p lang="zh-cn">
沉浸式阅读器支持许多语言
</p>
<p lang="de-de">
Der plastische Reader ist in vielen Sprachen verfügbar.
</p>
<p lang="ar-eg" dir="rtl" style="text-align:right">
يتوفر \"القارئ الشامل\" في العديد من اللغات.
</p>
</div>
</div>
Tenga en cuenta que todo el texto tiene un atributo lang que describe los idiomas del texto. Este atributo ayuda al Lector inmersivo a proporcionar características de idioma y gramática pertinentes.
Incorporación de JavaScript para administrar el inicio del Lector inmersivo
La biblioteca del Lector inmersivo proporciona funcionalidades como el inicio del Lector inmersivo y la representación de sus botones. Para obtener más información, consulte la referencia del SDK de JavaScript.
En la parte inferior de Views\Home\Index.cshtml, agregue el siguiente código:
@section Scripts
{
<script src="https://ircdname.azureedge.net/immersivereadersdk/immersive-reader-sdk.1.4.0.js"></script>
<script>
function getTokenAndSubdomainAsync() {
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
$.ajax({
url: "@Url.Action("GetTokenAndSubdomain", "Home")",
type: "GET",
success: function (data) {
if (data.error) {
reject(data.error);
} else {
resolve(data);
}
},
error: function (err) {
reject(err);
}
});
});
}
$(".immersive-reader-button").click(function () {
handleLaunchImmersiveReader();
});
function handleLaunchImmersiveReader() {
getTokenAndSubdomainAsync()
.then(function (response) {
const token = response["token"];
const subdomain = response["subdomain"];
// Learn more about chunk usage and supported MIME types https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/ai-services/immersive-reader/reference#chunk
const data = {
title: $("#ir-title").text(),
chunks: [{
content: $("#ir-content").html(),
mimeType: "text/html"
}]
};
// Learn more about options https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/ai-services/immersive-reader/reference#options
const options = {
"onExit": exitCallback,
"uiZIndex": 2000
};
ImmersiveReader.launchAsync(token, subdomain, data, options)
.catch(function (error) {
alert("Error in launching the Immersive Reader. Check the console.");
console.log(error);
});
})
.catch(function (error) {
alert("Error in getting the Immersive Reader token and subdomain. Check the console.");
console.log(error);
});
}
function exitCallback() {
console.log("This is the callback function. It is executed when the Immersive Reader closes.");
}
</script>
}
Compilación y ejecución de la aplicación
En la barra de menús, seleccione Depurar > Iniciar depuración o presione F5 para iniciar la aplicación.
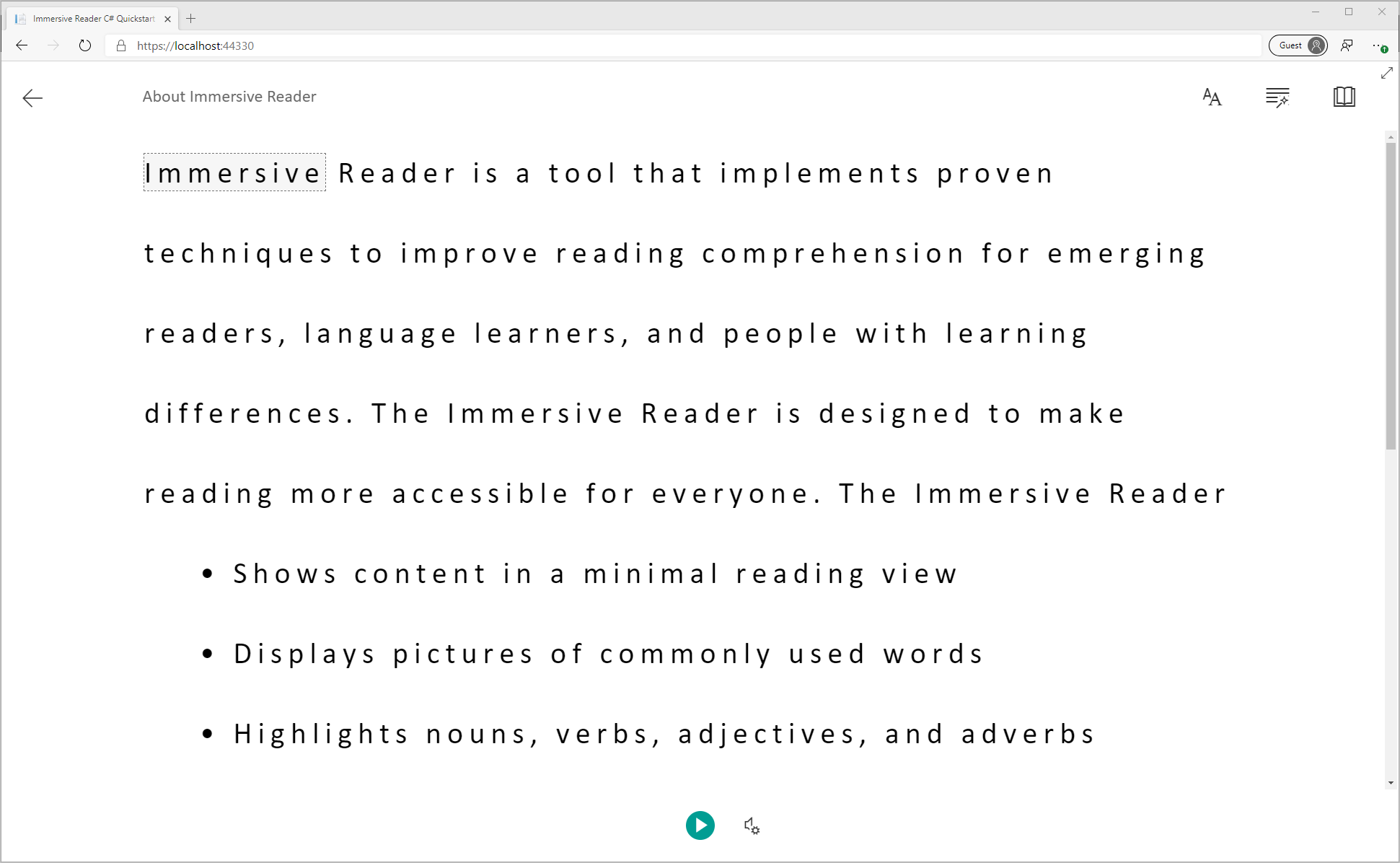
En el explorador, verá:
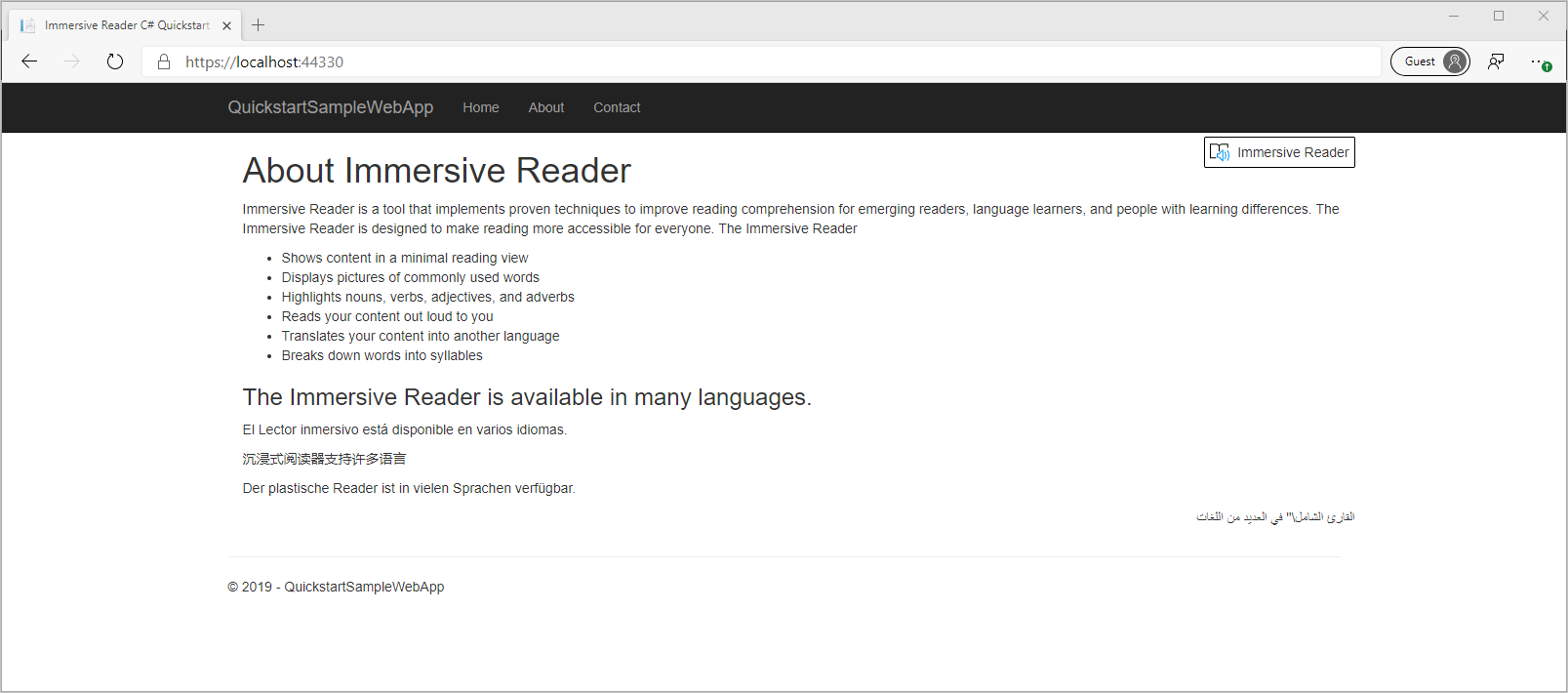
Inicio del Lector inmersivo
Al seleccionar el botón Immersive Reader, Immersive Reader se inicia con el contenido de la página.
Paso siguiente
En este inicio rápido, se va a crear una aplicación web desde cero y se integrará el Lector inmersivo mediante la biblioteca cliente de esta herramienta. Hay disponible un ejemplo funcional completo de esta guía de inicio rápido en GitHub.
Requisitos previos
- Suscripción a Azure. Puede crear una de forma gratuita.
- Un recurso del Lector inmersivo configurado para la autenticación de Microsoft Entra. Siga estas instrucciones para realizar la configuración. Guarde la salida de la sesión en un archivo de texto para que pueda configurar las propiedades del entorno.
- Un IDE como Visual Studio Code.
Crear una aplicación web de Node.js con Express
Cree una aplicación web Node.js mediante la herramienta express-generator.
npm install express-generator -g
express --view=pug quickstart-nodejs
cd quickstart-nodejs
Instale las dependencias de yarn y agregue las dependencias request y dotenv.
yarn
yarn add request
yarn add dotenv
Instale las bibliotecas axios y qs.
npm install axios qs
Configuración de la autenticación
Cree un nuevo archivo denominado . env en la raíz del proyecto. Pegue en él el siguiente código, y proporcione los valores especificados al crear el recurso del Lector inmersivo. No incluya comillas ni los caracteres { y }.
Importante
Recuerde no publicar nunca secretos públicamente. En el caso de producción, use una forma segura de almacenar sus credenciales y acceder a ellas, como Azure Key Vault.
TENANT_ID={YOUR_TENANT_ID}
CLIENT_ID={YOUR_CLIENT_ID}
CLIENT_SECRET={YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET}
SUBDOMAIN={YOUR_SUBDOMAIN}
Asegúrese de no confirmar este archivo en el control de código fuente, ya que contiene secretos que no deben hacerse públicos.
A continuación, abra app.js y agregue el código siguiente a la parte superior del archivo. Esto carga las propiedades definidas en el archivo .env como variables de entorno en el nodo.
require('dotenv').config();
Actualización del enrutador para adquirir el token
Abra el archivo routes\index.jsy reemplace el código generado automáticamente por el código siguiente.
Este código crea un punto de conexión de API que adquiere un token de autenticación de Microsoft Entra ID mediante la contraseña de la entidad de servicio. También recupera el subdominio. Luego, devuelve un objeto que contiene el token y el subdominio.
var axios = require('axios');
var express = require('express');
var router = express.Router();
var qs = require('qs');
/* GET home page. */
router.get('/', function(req, res, next) {
res.render('index', { title: 'Express' });
});
router.get('/GetTokenAndSubdomain', function(req, res) {
try {
var config ={
headers: {
'content-type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'
}
}
var data = {
grant_type: 'client_credentials',
client_id: process.env.CLIENT_ID,
client_secret: process.env.CLIENT_SECRET,
resource: 'https://cognitiveservices.azure.com/'
};
var url = `https://login.windows.net/${process.env.TENANT_ID}/oauth2/token`
console.log(qs.stringify(data));
axios.post(url, qs.stringify(data), config)
.then(function (response) {
var token = response.data.access_token;
var subdomain = process.env.SUBDOMAIN;
return res.send({token, subdomain});
})
.catch(function (response) {
if (response.status !== 200) {
return res.send({error : "Unable to acquire Microsoft Entra token. Check the debugger for more information."})
}
});
} catch (error) {
console.log(error);
return res.status(500).send('CogSvcs IssueToken error');
}
});
module.exports = router;
El punto de conexión de la API GetTokenAndSubdomain debe estar protegido mediante algún tipo de autenticación, como OAuth, para evitar que usuarios no autorizados obtengan tokens y los utilicen en el servicio Immersive Reader y su facturación; este trabajo queda fuera del ámbito de este inicio rápido.
Adición de contenido de ejemplo
Ahora, agregue contenido de muestra a esta aplicación web. Abra views\index.pug y reemplace el código generado automáticamente por este ejemplo:
doctype html
html
head
title Immersive Reader Quickstart Node.js
link(rel='icon', href='data:;base64,iVBORw0KGgo=')
link(rel='stylesheet', href='https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/3.4.1/css/bootstrap.min.css')
// A polyfill for Promise is needed for IE11 support.
script(src='https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/promise-polyfill@8/dist/polyfill.min.js')
script(src='https://ircdname.azureedge.net/immersivereadersdk/immersive-reader-sdk.1.4.0.js')
script(src='https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.3.1.min.js')
style(type="text/css").
.immersive-reader-button {
background-color: white;
margin-top: 5px;
border: 1px solid black;
float: right;
}
body
div(class="container")
button(class="immersive-reader-button" data-button-style="iconAndText" data-locale="en")
h1(id="ir-title") About Immersive Reader
div(id="ir-content" lang="en-us")
p Immersive Reader is a tool that implements proven techniques to improve reading comprehension for emerging readers, language learners, and people with learning differences. The Immersive Reader is designed to make reading more accessible for everyone. The Immersive Reader
ul
li Shows content in a minimal reading view
li Displays pictures of commonly used words
li Highlights nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs
li Reads your content out loud to you
li Translates your content into another language
li Breaks down words into syllables
h3 The Immersive Reader is available in many languages.
p(lang="es-es") El Lector inmersivo está disponible en varios idiomas.
p(lang="zh-cn") 沉浸式阅读器支持许多语言
p(lang="de-de") Der plastische Reader ist in vielen Sprachen verfügbar.
p(lang="ar-eg" dir="rtl" style="text-align:right") يتوفر \"القارئ الشامل\" في العديد من اللغات.
script(type="text/javascript").
function getTokenAndSubdomainAsync() {
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
$.ajax({
url: "/GetTokenAndSubdomain",
type: "GET",
success: function (data) {
if (data.error) {
reject(data.error);
} else {
resolve(data);
}
},
error: function (err) {
reject(err);
}
});
});
}
$(".immersive-reader-button").click(function () {
handleLaunchImmersiveReader();
});
function handleLaunchImmersiveReader() {
getTokenAndSubdomainAsync()
.then(function (response) {
const token = response["token"];
const subdomain = response["subdomain"];
// Learn more about chunk usage and supported MIME types https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/ai-services/immersive-reader/reference#chunk
const data = {
title: $("#ir-title").text(),
chunks: [{
content: $("#ir-content").html(),
mimeType: "text/html"
}]
};
// Learn more about options https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/ai-services/immersive-reader/reference#options
const options = {
"onExit": exitCallback,
"uiZIndex": 2000
};
ImmersiveReader.launchAsync(token, subdomain, data, options)
.catch(function (error) {
alert("Error in launching the Immersive Reader. Check the console.");
console.log(error);
});
})
.catch(function (error) {
alert("Error in getting the Immersive Reader token and subdomain. Check the console.");
console.log(error);
});
}
function exitCallback() {
console.log("This is the callback function. It is executed when the Immersive Reader closes.");
}
Tenga en cuenta que todo el texto tiene un atributo lang que describe los idiomas del texto. Este atributo ayuda al Lector inmersivo a proporcionar características de idioma y gramática pertinentes.
Compilación y ejecución de la aplicación
Nuestra aplicación web ya está lista. Inicie la aplicación; para ello, ejecute:
npm start
Abra el explorador web y vaya a http://localhost:3000. Debería ver lo siguiente:
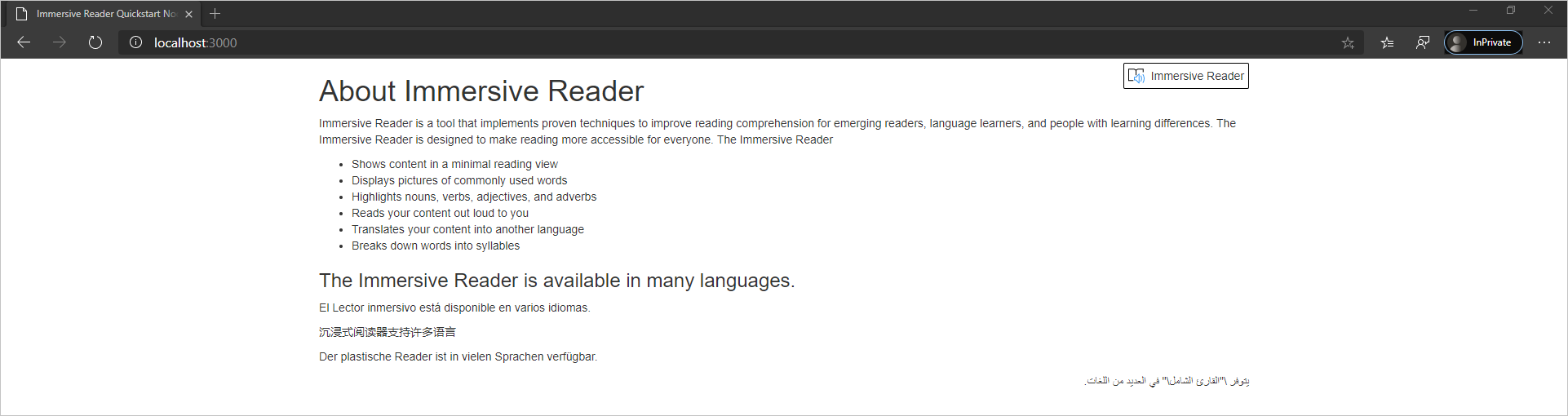
Inicio del Lector inmersivo
Al seleccionar el botón Immersive Reader, Immersive Reader se inicia con el contenido de la página.
Paso siguiente
En este inicio rápido, creará una aplicación Android desde cero e integrará el Lector inmersivo. Hay disponible un ejemplo funcional completo de esta guía de inicio rápido en GitHub.
Requisitos previos
- Suscripción a Azure. Puede crear una de forma gratuita.
- Un recurso del Lector inmersivo configurado para la autenticación de Microsoft Entra. Siga estas instrucciones para realizar la configuración. Guarde la salida de la sesión en un archivo de texto para que pueda configurar las propiedades del entorno.
- Git.
- Android Studio.
Creación de un proyecto de Android
Inicie un nuevo proyecto en Android Studio.
En la ventana Plantillas, seleccione Actividad de vistas vacías y, a continuación, seleccione Siguiente.
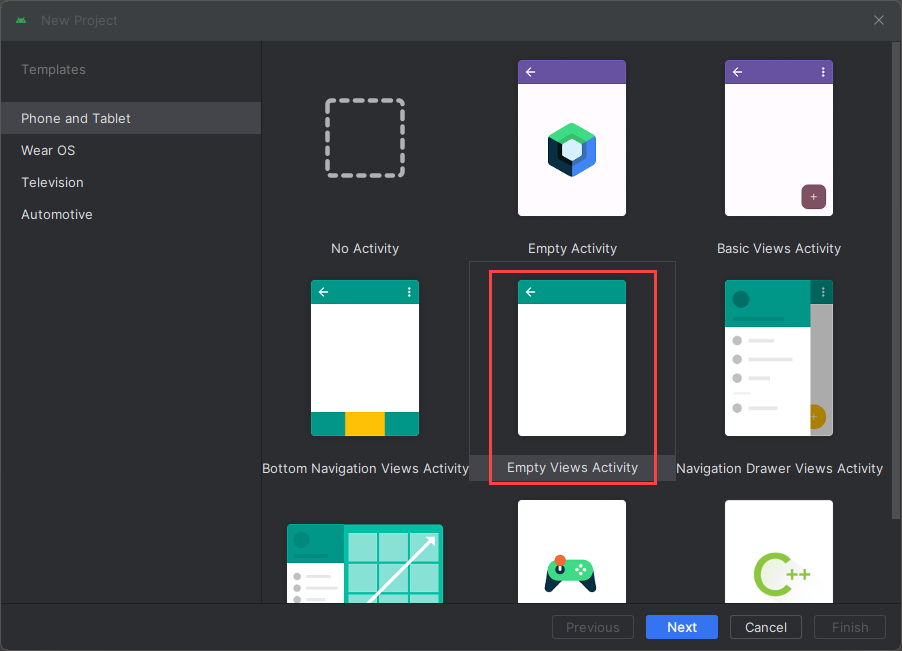
Configuración del proyecto
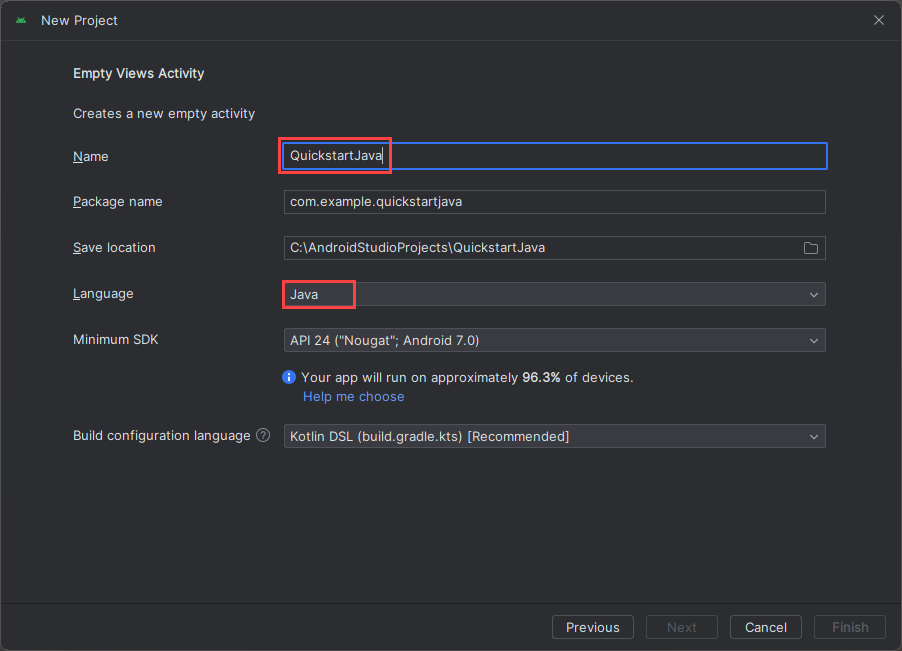
Asigne al proyecto el nombre QuickstartJava y seleccione una ubicación para guardarlo. Seleccione Java como lenguaje de programación y, a continuación, seleccione Finish (Finalizar).
Configuración de recursos y autenticación
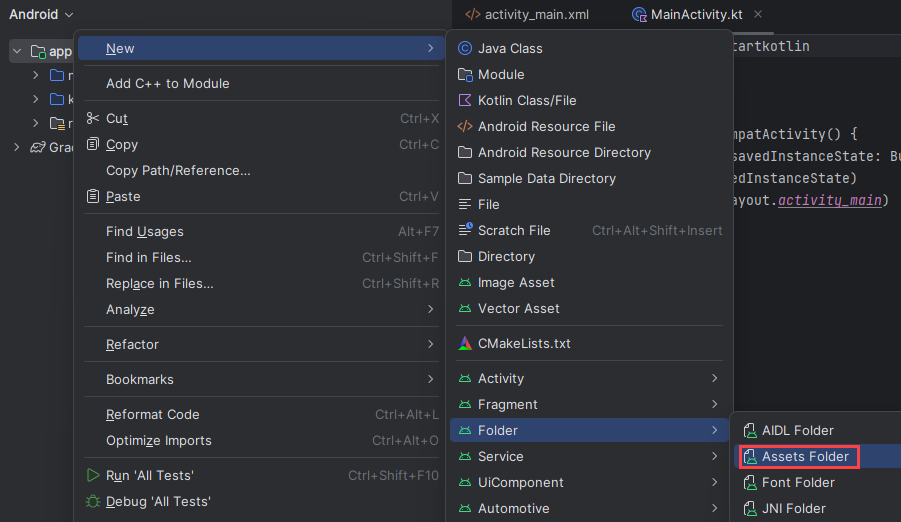
Para crear una carpeta de recursos, haga clic con el botón derecho en la aplicación y seleccione Carpeta ->Carpeta de recursos en la lista desplegable.
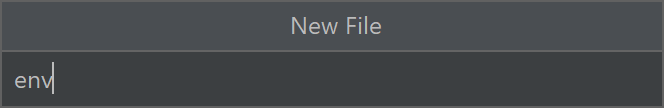
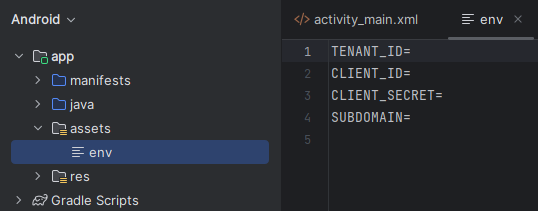
Haga clic con el botón derecho en recursos y seleccione Nuevo ->Archivo. Asigne al archivo el nombre env.
Agregue los siguientes nombres y valores y proporcione los valores según corresponda. No confirme este archivo env en el control de código fuente, ya que contiene secretos que no deben hacerse públicos.
TENANT_ID=<YOUR_TENANT_ID>
CLIENT_ID=<YOUR_CLIENT_ID>
CLIENT_SECRET=<YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET>
SUBDOMAIN=<YOUR_SUBDOMAIN>
Importante
Recuerde no publicar nunca secretos públicamente. En el caso de producción, use una forma segura de almacenar sus credenciales y acceder a ellas, como Azure Key Vault.
Adición de dependencias
Reemplace las dependencias existentes en el archivo build.gradle por las implementaciones siguientes para que gson (análisis y serialización de JSON) y dotenv puedan hacer referencia a las variables definidas en el archivo env. Es posible que tenga que volver a sincronizar el proyecto al implementar actividades más adelante en esta guía de inicio rápido.
dependencies {
implementation fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['*.jar'])
implementation 'androidx.appcompat:appcompat:1.0.2'
implementation 'androidx.constraintlayout:constraintlayout:1.1.3'
implementation 'com.google.code.gson:gson:2.8.6'
implementation 'io.github.cdimascio:java-dotenv:5.1.3'
testImplementation 'junit:junit:4.12'
androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test.ext:junit:1.1.0'
androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test.espresso:espresso-core:3.1.1'
}
Actualización de las cadenas y los recursos de diseño de la aplicación
Reemplace el contenido de res/values/strings.xml por las siguientes cadenas que se usarán en la aplicación.
<resources>
<!-- Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. -->
<!-- Licensed under the MIT License. -->
<string name="app_name">ImmersiveReaderSDK</string>
<string name="geographyTitle">Geography</string>
<string name="geographyTextEn">The study of Earth's landforms is called physical geography. Landforms can be mountains and valleys. They can also be glaciers, lakes or rivers. Landforms are sometimes called physical features. It is important for students to know about the physical geography of Earth. The seasons, the atmosphere and all the natural processes of Earth affect where people are able to live. Geography is one of a combination of factors that people use to decide where they want to live. The physical features of a region are often rich in resources. Within a nation, mountain ranges become natural borders for settlement areas. In the U.S., major mountain ranges are the Sierra Nevada, the Rocky Mountains, and the Appalachians. Fresh water sources also influence where people settle. People need water to drink. They also need it for washing. Throughout history, people have settled near fresh water. Living near a water source helps ensure that people have the water they need. There was an added bonus, too. Water could be used as a travel route for people and goods. Many Americans live near popular water sources, such as the Mississippi River, the Colorado River and the Great Lakes.Mountains and deserts have been settled by fewer people than the plains areas. However, they have valuable resources of their own.</string>
<string name="geographyTextFr">L\'étude des reliefs de la Terre est appelée géographie physique. Les reliefs peuvent être des montagnes et des vallées. Il peut aussi s\'agira de glaciers, delacs ou de rivières. Les reliefs sont parfois appelés caractéristiques physiques. Il est important que les élèves connaissent la géographie physique de laTerre. Les saisons, l\'atmosphère et tous les processus naturels de la Terre affectent l\'endroit où les gens sont capables de vivre. La géographie est l\'un desfacteurs que les gens utilisent pour décider où ils veulent vivre. Les caractéristiques physiques d\'une région sont souvent riches en ressources. Àl\'intérieur d\'une nation, les chaînes de montagnes deviennent des frontières naturelles pour les zones de peuplement. Aux États-Unis, les principaleschaînes de montagnes sont la Sierra Nevada, les montagnes Rocheuses et les Appalaches.Les sources d\'eau douce influencent également l\'endroit où lesgens s\'installent. Les gens ont besoin d\'eau pour boire. Ils en ont aussi besoin pour se laver. Tout au long de l\'histoire, les gens se sont installés près del\'eau douce. Vivre près d\'une source d\'eau permet de s\'assurer que les gens ont l\'eau dont ils ont besoin. Il y avait un bonus supplémentaire, aussi. L\'eaupourrait être utilisée comme voie de voyage pour les personnes et les marchandises. Beaucoup d\'Américains vivent près des sources d\'eau populaires,telles que le fleuve Mississippi, le fleuve Colorado et les Grands Lacs.Mountains et les déserts ont été installés par moins de gens que les zones desplaines. Cependant, ils disposent de ressources précieuses.Les gens ont une réponse.</string>
<string name="immersiveReaderButtonText">Immersive Reader</string>
</resources>
Reemplace el contenido de res/layout/activity_main.xml por el código XML siguiente que se usará en la aplicación. Este código XML es el diseño de la interfaz de usuario de la aplicación. Si no ve el código en el archivo activity_main.xml, haga clic con el botón derecho en el lienzo y seleccione Ir a XML.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!-- Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. -->
<!-- Licensed under the MIT License. -->
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#FFFFFF"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/linearLayout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:background="#FFFFFF"
android:orientation="vertical"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.0"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintVertical_bias="0.0">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/Title"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="48dp"
android:layout_marginTop="24dp"
android:layout_marginRight="48dp"
android:layout_marginBottom="24dp"
android:text="@string/geographyTitle"
android:textSize="24sp"
android:textStyle="bold" />
<ScrollView
android:id="@+id/ContentPane"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="480dp"
android:layout_marginBottom="48dp"
android:clipToPadding="false"
android:fillViewport="false"
android:paddingLeft="48dp"
android:paddingRight="48dp"
android:scrollbarStyle="outsideInset"
android:visibility="visible"
tools:visibility="visible">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/Content1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#00FFFFFF"
android:text="@string/geographyTextEn"
android:textSize="18sp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/Content2"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#00FFFFFF"
android:text="@string/geographyTextFr"
android:textSize="18sp" />
</LinearLayout>
</ScrollView>
<Button
android:id="@+id/LaunchImmersiveReaderButton"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="40dp"
android:layout_marginRight="40dp"
android:layout_marginBottom="80dp"
android:text="@string/immersiveReaderButtonText"
android:textAllCaps="false"
android:textSize="24sp"
android:visibility="visible"
tools:visibility="visible" />
</LinearLayout>
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
Incorporación del diseño de vista web
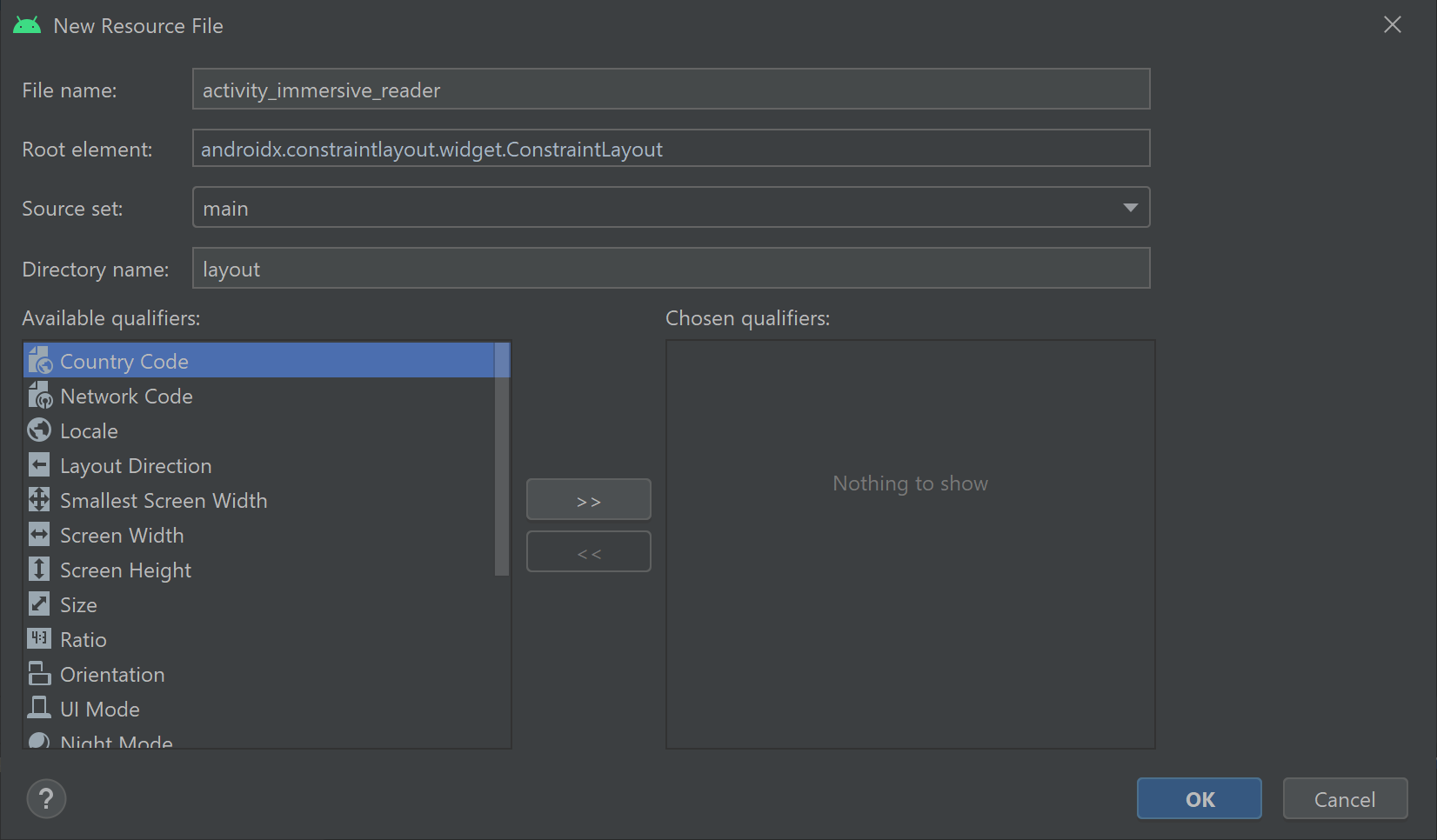
En la carpeta res/layout/, cree un nuevo archivo de recursos de diseño y asígnele el nombre activity_immersive_reader. A continuación, reemplace el contenido por el siguiente código XML. Este código XML agrega el componente WebView que se va a usar en el código de Java IRActivity en un paso posterior. Por ahora, no está definido y produce errores.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!-- Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. -->
<!-- Licensed under the MIT License. -->
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#FFFFFF"
tools:context=".IRActivity">
<WebView
android:id="@+id/webView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
Configuración del código Java de la aplicación
En la carpeta java/com.example.quickstartjava/, hay un archivo de clase java MainActivity.java. Esta carpeta es donde se crea la lógica de la aplicación.
Reemplace el contenido de MainActivity.java por el código siguiente. Hay algunas clases, a las que se hace referencia en el código, que todavía no existen y que se crearán más adelante.
/**
* Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
* Licensed under the MIT License.
*/
package com.example.quickstartjava;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Creates a new activity, finds its content and the Immersive Reader button.
* When clicked, the app sends the content to the Immersive Reader SDK and
* launches the Immersive Reader.
*/
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
final TextView irTitle = findViewById(R.id.Title);
final TextView irText1 = findViewById(R.id.Content1);
final TextView irText2 = findViewById(R.id.Content2);
final Button immersiveReaderButton = findViewById(R.id.LaunchImmersiveReaderButton);
immersiveReaderButton.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
List<ReadableTextChunk> readableTextChunks = new ArrayList<>();
readableTextChunks.add(new ReadableTextChunk(irText1.getText().toString(), "en"));
readableTextChunks.add(new ReadableTextChunk(irText2.getText().toString(), "fr"));
ReadableContent readableContent = new ReadableContent(irTitle.getText().toString(), readableTextChunks);
ImmersiveReader immersiveReader = new ImmersiveReader(MainActivity.this, new IRAuthenticator());
immersiveReader.read(readableContent);
}
});
}
}
Vamos a crear otros 16 archivos de clase Java en la carpeta java/com.example.quickstartjava/. La aplicación usa cada una de estas clases para integrar el SDK del Lector inmersivo. Con cada nuevo archivo se agregan algunas clases a las que se hace referencia en el código, que todavía no existen y que se crearán más adelante. Una vez creadas todas las clases, no debería haber ningún error de referencia nula.
Para crear un nuevo archivo de clase Java ImmersiveReader.java, haga clic con el botón derecho en la carpeta java/com.example.quickstartjava/, seleccione Nuevo y, a continuación, seleccione Clase Java. Escriba ImmersiveReader.
Use este mismo método para crear archivos de clase Java con cada nuevo archivo de clase Java que vaya a crear.
Reemplace el contenido de ImmersiveReader.java por el código siguiente:
/**
* Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
* Licensed under the MIT License.
*/
package com.example.quickstartjava;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import androidx.annotation.Keep;
import java.lang.ref.WeakReference;
/**
* This is the client facing class for invoking the new Immersive Reader functionality.
* Usage:
* ImmersiveReader immersiveReader = new ImmersiveReader(Activity, IRAuthenticator);
* immersiveReader.read(ReadableTextChunk);
*/
@Keep
public class ImmersiveReader {
WeakReference<Activity> mActivityWR;
/**
* Interface to accept access token from client app.
* Note that it is client's responsibility to give a valid Access Token whenever getAccessToken() is requested.
* In favor of latency perf, there would be no further validation by Immersive Reader module except to ensure that the provided access token is non-empty string
*/
@Keep
public interface IAuthenticator {
String getAccessToken();
}
public ImmersiveReader(Activity activity, IAuthenticator authenticator) {
mActivityWR = new WeakReference<>(activity);
IRDataHolder.getInstance().setAuthenticator(authenticator);
}
public ImmersiveReader(Activity activity) {
this(activity, null);
}
/**
* Launches a new activity to speak the content as described by ReadableContent object.
*
* @param dataToRead - Content to be read
* @return IRError - IRError, with following error codes:
* a) Error.NONE in case of successful launch of Immersive Reader
* b) Error.INVALID_ACCESS_TOKEN in case of empty access token
* c) Error.INVALID_STATE in case of empty activity
* d) Error.INVALID_CONTENT in case of empty list of text chunks
*/
public IRError read(ReadableContent dataToRead) {
Activity activity = mActivityWR.get();
if (activity == null) {
return new IRError(Error.INVALID_STATE, "Client activity is null");
}
if (dataToRead == null || dataToRead.getTextChunks().size() == 0) {
return new IRError(Error.INVALID_CONTENT, "Readable Text Chunks not passed to Immersive Reader");
}
IRDataHolder.getInstance().setContentToRead(dataToRead);
Intent intent = new Intent(mActivityWR.get(), IRActivity.class);
activity.startActivity(intent);
return new IRError(Error.NONE, "Immersive Reader launched");
}
}
Cree el nuevo archivo de clase Java IRActivity.java.
Reemplace el contenido de IRActivity.java por el código siguiente:
/**
* Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
* Licensed under the MIT License.
*/
package com.example.quickstartjava;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import androidx.annotation.Keep;
import java.lang.ref.WeakReference;
/**
* This is the client facing class for invoking the new Immersive Reader functionality.
* Usage:
* ImmersiveReader immersiveReader = new ImmersiveReader(Activity, IRAuthenticator);
* immersiveReader.read(ReadableTextChunk);
*/
@Keep
public class ImmersiveReader {
WeakReference<Activity> mActivityWR;
/**
* Interface to accept access token from client app.
* Note that it is the client's responsibility to give a valid Access Token whenever getAccessToken() is requested.
* In favor of latency perf, there would be no further validation by Immersive Reader module except to ensure that the provided access token is non-empty string.
*/
@Keep
public interface IAuthenticator {
String getAccessToken();
}
public ImmersiveReader(Activity activity, IAuthenticator authenticator) {
mActivityWR = new WeakReference<>(activity);
IRDataHolder.getInstance().setAuthenticator(authenticator);
}
public ImmersiveReader(Activity activity) {
this(activity, null);
}
/**
* Launches a new activity to speak the content as described by ReadableContent object.
*
* @param dataToRead - Content to be read
* @return IRError - IRError, with following error codes:
* a) Error.NONE in case of successful launch of Immersive Reader
* b) Error.INVALID_ACCESS_TOKEN in case of empty access token.
* c) Error.INVALID_STATE in case of empty activity
* d) Error.INVALID_CONTENT in case of empty list of text chunks
*/
public IRError read(ReadableContent dataToRead) {
Activity activity = mActivityWR.get();
if (activity == null) {
return new IRError(Error.INVALID_STATE, "Client activity is null");
}
if (dataToRead == null || dataToRead.getTextChunks().size() == 0) {
return new IRError(Error.INVALID_CONTENT, "Readable Text Chunks not passed to Immersive Reader");
}
IRDataHolder.getInstance().setContentToRead(dataToRead);
Intent intent = new Intent(mActivityWR.get(), IRActivity.class);
activity.startActivity(intent);
return new IRError(Error.NONE, "Immersive Reader launched");
}
}
Cree el nuevo archivo de clase Java IRError.java.
Reemplace el contenido de IRError.java por el código siguiente:
/**
* Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
* Licensed under the MIT License.
*/
package com.example.quickstartjava;
import android.os.Parcel;
import android.os.Parcelable;
import androidx.annotation.Keep;
/**
* Shared error handling of the app.
*/
@Keep
public class IRError implements Parcelable {
private int errorId;
private String errorMessage = "";
public String getErrorMessage() {
return errorMessage;
}
public void setErrorMessage(String errorMessage) {
this.errorMessage = errorMessage;
}
public int getErrorId() {
return errorId;
}
public void setErrorId(int errorId) {
this.errorId = errorId;
}
public IRError(int errorId, String errorMessage) {
this.errorId = errorId;
this.errorMessage = errorMessage;
}
// parcelable
@Override
public int describeContents() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public void writeToParcel(Parcel out, int flags) {
out.writeInt(this.errorId);
out.writeString(this.errorMessage);
}
public static final Creator<IRError> CREATOR
= new Creator<IRError>() {
public IRError createFromParcel(Parcel in) {
return new IRError(in);
}
public IRError[] newArray(int size) {
return new IRError[size];
}
};
private IRError(Parcel in) {
this.errorId = in.readInt();
this.errorMessage = in.readString();
}
}
Cree el nuevo archivo de clase Java Error.java.
Reemplace el contenido de Error.java por el código siguiente:
/**
* Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
* Licensed under the MIT License.
*/
package com.example.quickstartjava;
import androidx.annotation.Keep;
/**
* Adds some default error status codes.
*/
@Keep
public class Error {
public static final int NONE = 1000;
public static final int INVALID_ACCESS_TOKEN = 8001;
public static final int INVALID_STATE = 8002;
public static final int INVALID_CONTENT = 8003;
}
Cree el nuevo archivo de clase Java ReadableContent.java.
Reemplace el contenido de ReadableContent.java por el código siguiente:
/**
* Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
* Licensed under the MIT License.
*/
package com.example.quickstartjava;
import androidx.annotation.Keep;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Content data to be sent to the Immersive Reader SDK
*/
@Keep
public class ReadableContent {
private String mTitle;
private List<ReadableTextChunk> mTextChunks;
public ReadableContent(String title, List<ReadableTextChunk> textChunks) {
this.mTitle = title;
this.mTextChunks = textChunks;
}
public String getTitle() {
return mTitle;
}
public List<ReadableTextChunk> getTextChunks() {
return mTextChunks;
}
}
Cree el nuevo archivo de clase Java ReadableTextChunk.java.
Reemplace el contenido de ReadableTextChunk.java por el código siguiente:
/**
* Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
* Licensed under the MIT License.
*/
import androidx.annotation.Keep;
/**
* Content sent to the Immersive Reader SDK may be separated into chunks so that there may be
* different types of content sent in the same document. This includes content of different
* languages, math content, et cetera.
*/
@Keep
public class ReadableTextChunk {
public String mText;
public String mLocale;
public ReadableTextChunk(String text, String locale) {
this.mText = text;
this.mLocale = locale;
}
}
Cree el nuevo archivo de clase Java IRDataHolder.java.
Reemplace el contenido de IRDataHolder.java por el código siguiente:
/**
* Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
* Licensed under the MIT License.
*/
package com.example.quickstartjava;
import androidx.annotation.Keep;
/**
* A thin singleton class that is used to hold the Client's IAuthenticator's implementation and the Content to be read.
* This is required for two reasons:
* 1) As per Android guidelines, data being passed via intent should be limited to a few KBs. Alternative is to use Singleton holder classes like this one.
* 2) We need a way to make callbacks survive app configuration changes and killed in background scenarios.
*/
@Keep
public class IRDataHolder {
private static IRDataHolder mInstance = null;
private ReadableContent mActiveContent = null;
private ImmersiveReader.IAuthenticator mAuthenticator = null;
public static IRDataHolder getInstance() {
if (mInstance == null) {
synchronized (IRDataHolder.class) {
if (mInstance == null) {
mInstance = new IRDataHolder();
}
}
}
return mInstance;
}
public void setContentToRead(ReadableContent content) {
mActiveContent = content;
}
public ReadableContent getContentToRead() {
return mActiveContent;
}
public ImmersiveReader.IAuthenticator getAuthenticator() {
return mAuthenticator;
}
public void setAuthenticator(ImmersiveReader.IAuthenticator accessTokenProvider) {
this.mAuthenticator = accessTokenProvider;
}
public void clearContent() {
mActiveContent = null;
}
}
Cree el nuevo archivo de clase Java IRAuthenticator.java.
Reemplace el contenido de IRAuthenticator.java por el código siguiente:
/**
* Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
* Licensed under the MIT License.
*/
package com.example.quickstartjava;
import android.text.TextUtils;
import android.util.Log;
import org.json.JSONException;
import org.json.JSONObject;
import io.github.cdimascio.dotenv.Dotenv;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.HttpURLConnection;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
import static java.net.HttpURLConnection.HTTP_OK;
// This sample app uses the Dotenv. It's a module that loads environment variables from a .env file to better manage secrets.
// https://github.com/cdimascio/java-dotenv
// Be sure to add a "env" file to the /assets folder.
// Instead of '.env', use 'env'.
public class IRAuthenticator implements ImmersiveReader.IAuthenticator {
private static final String LOG_TAG = "IRAuthenticator";
Dotenv dotEnv = Dotenv.configure()
.directory("/assets")
.filename("env")
.ignoreIfMalformed()
.ignoreIfMissing()
.load();
@Override
public String getAccessToken() {
String clientId = dotEnv.get("CLIENT_ID");
String clientSecret = dotEnv.get("CLIENT_SECRET");
String tenantId = dotEnv.get("TENANT_ID");
String accessToken = null;
try {
StringBuilder urlStringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
urlStringBuilder.append("https://login.windows.net/");
urlStringBuilder.append(tenantId);
urlStringBuilder.append("/oauth2/token");
URL tokenUrl = new URL(urlStringBuilder.toString());
StringBuilder formStringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
formStringBuilder.append("grant_type=client_credentials&resource=https://cognitiveservices.azure.com/&client_id=");
formStringBuilder.append(clientId);
formStringBuilder.append("&client_secret=");
formStringBuilder.append(clientSecret);
String form = formStringBuilder.toString();
HttpURLConnection httpURLConnection = (HttpURLConnection) tokenUrl.openConnection();
httpURLConnection.setRequestMethod("POST");
httpURLConnection.setRequestProperty("content-type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded");
httpURLConnection.setDoOutput(true);
DataOutputStream dataOutputStream = new DataOutputStream(httpURLConnection.getOutputStream());
dataOutputStream.writeBytes(form);
dataOutputStream.flush();
dataOutputStream.close();
int responseCode = httpURLConnection.getResponseCode();
if (responseCode == HTTP_OK) {
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(httpURLConnection.getInputStream()));
StringBuffer response = new StringBuffer();
String line = bufferedReader.readLine();
while (!TextUtils.isEmpty(line)) {
response.append(line);
line = bufferedReader.readLine();
}
bufferedReader.close();
JSONObject accessTokenJson = new JSONObject(response.toString());
accessToken = accessTokenJson.getString("access_token");
}
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (JSONException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// accessToken = Constants.ACCESS_TOKEN;
Log.i(LOG_TAG, "Accesstoken: " + accessToken);
return accessToken;
}
}
Cree el nuevo archivo de clase Java IRLauncher.java.
Reemplace el contenido de IRLauncher.java por el código siguiente:
/**
* Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
* Licensed under the MIT License.
*/
package com.example.quickstartjava;
import android.content.Context;
import android.os.Build;
import android.text.TextUtils;
import android.view.View;
import android.webkit.CookieManager;
import android.webkit.WebView;
import android.webkit.WebViewClient;
import android.widget.Toast;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import com.google.gson.GsonBuilder;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import io.github.cdimascio.dotenv.Dotenv;
/**
* Responsible for setting up the web view with appropriate bridging between JavaScript and Java to launch the Immersive Reader url for reading the content.
*/
public class IRLauncher {
Dotenv dotEnv = Dotenv.configure()
.directory("/assets")
.filename("env")
.ignoreIfMalformed()
.ignoreIfMissing()
.load();
private WebView mWebView;
private Context mContext;
public final String SUBDOMAIN = dotEnv.get("SUBDOMAIN");
interface IRLaunchListener {
// Invoked in case of successful launch of Immersive Reader Activity. Note that content reading can still fail due to multiple reasons including expired access token.
void onSuccess();
// Invoked in case of empty access token or empty content request to be read
void onFailure(IRError error);
// Invoked when Immersive Reader is exiting (e.g.) user pressed back in the Immersive Reader experience
void onExit();
}
public IRLauncher(Context context, WebView webView) {
this.mContext = context;
this.mWebView = webView;
}
public void launch(final IRLaunchListener launchListener) {
AuthenticationTask authenticationTask = new AuthenticationTask();
AuthenticationTask.TaskParams params = authenticationTask.new TaskParams(IRDataHolder.getInstance().getAuthenticator(), new AuthenticationTask.ITaskListener() {
@Override
public void onAccessTokenObtained(String accessToken) {
// Basic validation for access token
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(accessToken)) {
launchListener.onFailure(new IRError(Error.INVALID_ACCESS_TOKEN, "Access token is empty"));
}
// Create list of chunks from data that was passed originally by the client and stored in the data holder
List<Chunk> chunkList = new ArrayList<>();
for (ReadableTextChunk textChunk : IRDataHolder.getInstance().getContentToRead().getTextChunks()) {
chunkList.add(new Chunk(textChunk.mText, textChunk.mLocale, "text/plain"));
}
Content content = new Content(IRDataHolder.getInstance().getContentToRead().getTitle(), chunkList);
Options options = new Options(new Callable<Void>() {
public Void call() {
launchListener.onExit();
return null;
}
}, "en", 0);
// Prepare the webview
prepareWebView(accessToken, content, options, launchListener);
mWebView.loadUrl("file:///android_asset/immersiveReader.html");
launchListener.onSuccess();
}
});
authenticationTask.setParams(params);
authenticationTask.execute();
}
private void prepareWebView(String accessToken, Content content, Options options, final IRLaunchListener launchListener) {
mWebView.getSettings().setAllowContentAccess(true);
mWebView.getSettings().setJavaScriptEnabled(true);
mWebView.getSettings().setLoadsImagesAutomatically(true);
mWebView.getSettings().setLoadWithOverviewMode(true);
mWebView.getSettings().setUseWideViewPort(true);
mWebView.getSettings().setUserAgentString("Android");
mWebView.getSettings().setDomStorageEnabled(true);
mWebView.getSettings().setAppCacheEnabled(false);
mWebView.getSettings().setSupportZoom(true);
mWebView.setInitialScale(1);
// Enable web view cookies
if (android.os.Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP) {
CookieManager.getInstance().setAcceptThirdPartyCookies(mWebView, true);
} else {
CookieManager.getInstance().setAcceptCookie(true);
}
final Date startPostMessageSentDurationInMs = new Date();
// Create the Message
final Message messageData = new Message(accessToken, SUBDOMAIN, content, 0, options);
// Set WebView Client
mWebView.setWebViewClient(new WebViewClient() {
@Override
public boolean shouldOverrideUrlLoading(WebView view, String url) {
mWebView.loadUrl(url);
return true;
}
@Override
public void onPageFinished(WebView view, String url) {
Date endPostMessageSentDurationInMs = new Date();
long postMessageSentDurationInMs = endPostMessageSentDurationInMs.getTime() - startPostMessageSentDurationInMs.getTime();
// Updates launchToPostMessageSentDurationInMs
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.N) {
messageData.launchToPostMessageSentDurationInMs = Math.toIntExact(postMessageSentDurationInMs);
} else {
messageData.launchToPostMessageSentDurationInMs = 0;
}
GsonBuilder gsonBuilder = new GsonBuilder();
Gson gson = gsonBuilder.create();
String messageJson = gson.toJson(messageData);
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.KITKAT) {
StringBuilder scriptStringBuilder = new StringBuilder().append("handleLaunchImmersiveReader(").append(messageJson).append(")");
view.evaluateJavascript(scriptStringBuilder.toString(), null);
} else {
StringBuilder urlStringBuilder = new StringBuilder().append("javascript:handleLaunchImmersiveReader(").append(messageJson).append(")");
view.loadUrl(urlStringBuilder.toString());
}
mWebView.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
}
});
// Prepare and set the WebAppInterface to hear back from the JavaScript
WebAppInterface jsInterface = new WebAppInterface(new WebAppInterface.WebAppListener() {
@Override
public void onShowToast(String toast) {
Toast.makeText(mContext, toast, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
@Override
public void onImmersiveReaderExit() {
IRDataHolder.getInstance().clearContent();
mWebView.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
mWebView.clearHistory();
mWebView.clearCache(true);
mWebView.loadUrl("about:blank");
mWebView.onPause();
mWebView.removeAllViews();
mWebView.pauseTimers();
mWebView.destroy();
}
});
launchListener.onExit();
}
});
mWebView.addJavascriptInterface(jsInterface, "Android");
}
}
Cree el nuevo archivo de clase Java IRStore.java.
Reemplace el contenido de IRStore.java por el código siguiente:
/**
* Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
* Licensed under the MIT License.
*/
package com.example.quickstartjava;
import androidx.annotation.Keep;
@Keep
public final class IRStore {
@Keep
public final static class Output {
public final static String ERROR = "Error";
}
}
Cree el nuevo archivo de clase Java AuthenticationTask.java.
Reemplace el contenido de AuthenticationTask.java por el código siguiente:
/**
* Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
* Licensed under the MIT License.
*/
package com.example.quickstartjava;
import android.os.AsyncTask;
/**
* Async task to request the client for the access token in background thread.
*/
public class AuthenticationTask extends AsyncTask<Void, Void, String> {
private TaskParams mParams;
public interface ITaskListener {
void onAccessTokenObtained(String accessToken);
}
public class TaskParams {
ImmersiveReader.IAuthenticator mAccessTokenProvider;
ITaskListener mTaskListener;
public TaskParams(ImmersiveReader.IAuthenticator accessTokenProvider, ITaskListener taskListener) {
this.mAccessTokenProvider = accessTokenProvider;
this.mTaskListener = taskListener;
}
}
public void setParams(TaskParams mParams) {
this.mParams = mParams;
}
@Override
protected String doInBackground(Void... voids) {
return mParams.mAccessTokenProvider.getAccessToken();
}
@Override
protected void onPostExecute(String accessToken) {
super.onPostExecute(accessToken);
if (mParams.mTaskListener != null) {
mParams.mTaskListener.onAccessTokenObtained(accessToken);
}
}
}
Cree el nuevo archivo de clase Java Chunk.java.
Reemplace el contenido de Chunk.java por el código siguiente:
/**
* Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
* Licensed under the MIT License.
*/
package com.example.quickstartjava;
import androidx.annotation.Keep;
/**
* The chunk object that will be sent to the Immersive Reader SDK.
* The content is a string of text, the lang is a string, e.g. 'll-cc',
* and the mimeType is also a string, e.g. 'text/plain'.
*/
@Keep
public class Chunk {
public String content;
public String lang;
public String mimeType;
public Chunk(String content, String lang, String mimeType) {
this.content = content;
this.lang = lang;
this.mimeType = mimeType;
}
}
Cree el nuevo archivo de clase Java Content.java.
Reemplace el contenido de Content.java por el código siguiente:
/**
* Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
* Licensed under the MIT License.
*/
package com.example.quickstartjava;
import androidx.annotation.Keep;
import java.util.List;
/**
* The content object that will be sent to the Immersive Reader SDK.
* This object contains the title and a list of Chunk objects.
*/
@Keep
public class Content {
public String title;
public List<Chunk> chunks;
public Content(String title, List<Chunk> chunks) {
this.title = title;
this.chunks = chunks;
}
}
Cree el nuevo archivo de clase Java Options.java.
Reemplace el contenido de Options.java por el código siguiente:
/**
* Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
* Licensed under the MIT License.
*/
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import androidx.annotation.Keep;
/**
* The options object that will be sent to the Immersive Reader SDK.
*/
@Keep
public class Options {
public Callable<Void> onExit;
public String uiLang;
public Integer timeout;
public Options(Callable<Void> exitCallback, String uiLang, Integer timeout) {
this.onExit = exitCallback;
this.uiLang = uiLang;
this.timeout = timeout;
}
}
Cree el nuevo archivo de clase Java Message.java.
Reemplace el contenido de Message.java por el código siguiente:
/**
* Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
* Licensed under the MIT License.
*/
import androidx.annotation.Keep;
/**
* The message object that will be sent to the Immersive Reader SDK.
* This object contains the access token, sub domain, Content, and Options.
*/
@Keep
public class Message {
public String cogSvcsAccessToken;
public String cogSvcsSubdomain;
public Content request;
public Integer launchToPostMessageSentDurationInMs;
public Options options;
public Message(String cogSvcsAccessToken, String cogSvcsSubdomain, Content request, Integer launchToPostMessageSentDurationInMs, Options options) {
this.cogSvcsAccessToken = cogSvcsAccessToken;
this.cogSvcsSubdomain = cogSvcsSubdomain;
this.request = request;
this.launchToPostMessageSentDurationInMs = launchToPostMessageSentDurationInMs;
this.options = options;
}
}
Cree el nuevo archivo de clase Java WebAppInterface.java.
Reemplace el contenido de WebAppInterface.java por el código siguiente:
/**
* Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
* Licensed under the MIT License.
*/
package com.example.quickstartjava;
import androidx.annotation.Keep;
import android.webkit.JavascriptInterface;
/**
* JavaScript interface implementation passed to the WebView to enable talking between JavaScript and Java.
*/
@Keep
public class WebAppInterface {
public static WebAppListener mListener;
interface WebAppListener {
void onShowToast(String toast);
void onImmersiveReaderExit();
}
public WebAppInterface(WebAppListener listener) {
this.mListener = listener;
}
@JavascriptInterface
public void showToast(String toast) {
mListener.onShowToast(toast);
}
@JavascriptInterface
public void immersiveReaderExit() {
mListener.onImmersiveReaderExit();
}
}
Incorporación del código HTML de la aplicación a la vista web
La implementación de la vista web necesita que el código HTML funcione. Haga clic con el botón derecho en la carpeta /assets, cree un nuevo archivo y asígnele el nombre immersiveReader.html.
Agregue el siguiente código HTML y JavaScript. Este código agrega el SDK de Immersive Reader a la aplicación y lo usa para abrir Immersive Reader mediante el código de la aplicación que hemos escrito.
<!-- Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the MIT License. -->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1, shrink-to-fit=no">
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://ircdname.azureedge.net/immersivereadersdk/immersive-reader-sdk.1.4.0.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
function handleLaunchImmersiveReader(message) {
if (!message) {
Android.showToast('Message is null or undefined!');
} else {
// Learn more about chunk usage and supported MIME types https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/ai-services/immersive-reader/reference#chunk
var data = {
title: message.request.title,
chunks: []
};
for (var chunkIndex = 0; chunkIndex < message.request.chunks.length; chunkIndex++) {
data.chunks.push({
content: message.request.chunks[chunkIndex].content,
lang: message.request.chunks[chunkIndex].lang,
mimeType: message.request.chunks[chunkIndex].mimeType
});
}
// Learn more about options https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/ai-services/immersive-reader/reference#options
var options = {
onExit: exitCallback,
uiZIndex: 2000
};
// Use the JavaScript SDK to launch the Immersive Reader.
ImmersiveReader.launchAsync(message.cogSvcsAccessToken, message.cogSvcsSubdomain, data, options);
// A simple declarative function used to close the Immersive Reader WebView via @JavaScriptInterface
function exitCallback() {
Android.immersiveReaderExit();
}
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Configuración de permisos de la aplicación
Dado que la aplicación necesita realizar llamadas de red al SDK del Lector inmersivo para funcionar, es necesario asegurarse de que los permisos de la aplicación están configurados para permitir el acceso a la red. Reemplace el contenido de /manifests/AndroidManifest.xml por el código XML siguiente:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.quickstartjava">
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<activity android:name=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<activity
android:name=".IRActivity"
android:multiprocess="true" />
</application>
</manifest>
Ejecución de la aplicación
Use Android Studio para ejecutar la aplicación en un emulador de dispositivos. Al seleccionar Lector inmersivo, se abre el Lector inmersivo con el contenido de la aplicación.

Paso siguiente
En este inicio rápido, creará una aplicación Android desde cero e integrará el Lector inmersivo. Hay disponible un ejemplo funcional completo de esta guía de inicio rápido en GitHub.
Requisitos previos
- Suscripción a Azure. Puede crear una de forma gratuita.
- Un recurso del Lector inmersivo configurado para la autenticación de Microsoft Entra. Siga estas instrucciones para realizar la configuración. Guarde la salida de la sesión en un archivo de texto para que pueda configurar las propiedades del entorno.
- Git.
- Android Studio.
Creación de un proyecto de Android
Inicie un nuevo proyecto en Android Studio.
En la ventana Plantillas, seleccione Actividad de vistas vacías y, a continuación, seleccione Siguiente.
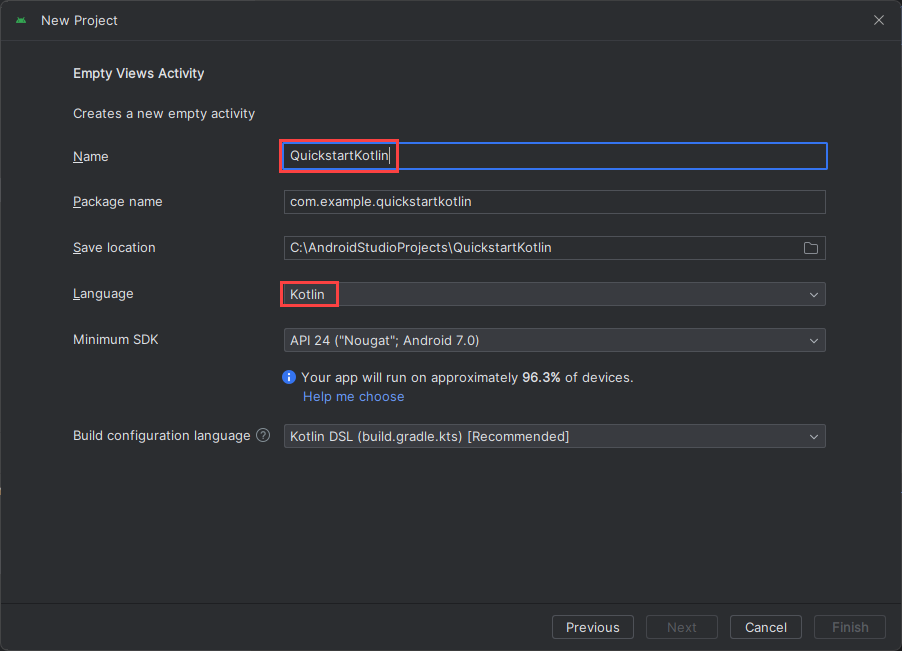
Configuración del proyecto
Asigne al proyecto el nombre QuickstartKotlin y seleccione una ubicación para guardarlo. Seleccione Kotlin como lenguaje de programación y, a continuación, seleccione Finish (Finalizar).
Configuración de recursos y autenticación
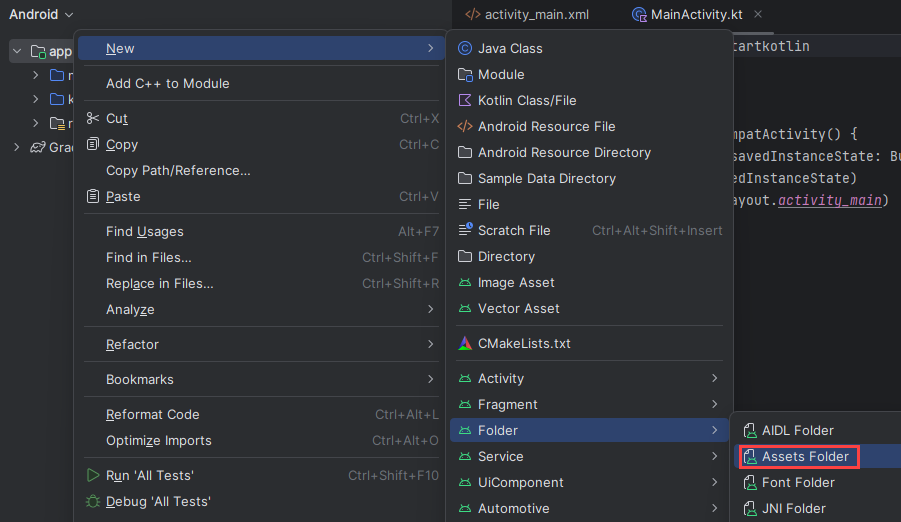
Para crear una carpeta de recursos, haga clic con el botón derecho en la aplicación y seleccione Carpeta ->Carpeta de recursos en la lista desplegable.
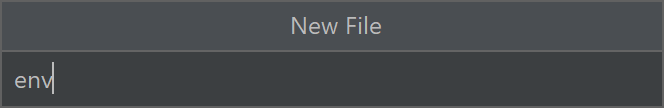
Haga clic con el botón derecho en recursos y seleccione Nuevo ->Archivo. Asigne al archivo el nombre env.
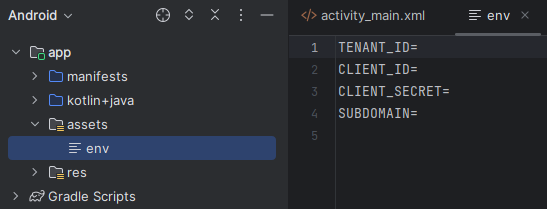
Agregue los siguientes nombres y valores y proporcione los valores según corresponda. No confirme este archivo env en el control de código fuente, ya que contiene secretos que no deben hacerse públicos.
TENANT_ID=<YOUR_TENANT_ID>
CLIENT_ID=<YOUR_CLIENT_ID>
CLIENT_SECRET=<YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET>
SUBDOMAIN=<YOUR_SUBDOMAIN>
Importante
Recuerde no publicar nunca secretos públicamente. En el caso de producción, use una forma segura de almacenar sus credenciales y acceder a ellas, como Azure Key Vault.
Adición de dependencias
Reemplace las dependencias existentes en el archivo build.gradle por las implementaciones siguientes para habilitar corutinas (programación asincrónica), gson (análisis y serialización de JSON) y dotenv para hacer referencia a las variables definidas en el archivo env. Es posible que tenga que volver a sincronizar el proyecto al implementar MainActivity.kt en un paso posterior de esta guía de inicio rápido.
dependencies {
implementation fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['*.jar'])
implementation"org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-stdlib-jdk7:$kotlin_version"
implementation 'androidx.appcompat:appcompat:1.0.2'
implementation 'androidx.core:core-ktx:1.0.2'
implementation 'androidx.constraintlayout:constraintlayout:1.1.3'
implementation "org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-core:1.1.1"
implementation "org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-android:1.1.1"
implementation 'com.google.code.gson:gson:2.8.6'
implementation 'io.github.cdimascio:java-dotenv:5.1.3'
testImplementation 'junit:junit:4.12'
androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test.ext:junit:1.1.0'
androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test.espresso:espresso-core:3.1.1'
}
Actualización de las cadenas y los recursos de diseño de la aplicación
Reemplace el contenido de res/values/strings.xml por las siguientes cadenas que se usarán en la aplicación.
<resources>
<!-- Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. -->
<!-- Licensed under the MIT License. -->
<string name="app_name">ImmersiveReaderSDK</string>
<string name="geographyTitle">Geography</string>
<string name="geographyTextEn">The study of Earth's landforms is called physical geography. Landforms can be mountains and valleys. They can also be glaciers, lakes or rivers. Landforms are sometimes called physical features. It is important for students to know about the physical geography of Earth. The seasons, the atmosphere and all the natural processes of Earth affect where people are able to live. Geography is one of a combination of factors that people use to decide where they want to live.The physical features of a region are often rich in resources. Within a nation, mountain ranges become natural borders for settlement areas. In the U.S., major mountain ranges are the Sierra Nevada, the Rocky Mountains, and the Appalachians. Fresh water sources also influence where people settle. People need water to drink. They also need it for washing. Throughout history, people have settled near fresh water. Living near a water source helps ensure that people have the water they need. There was an added bonus, too. Water could be used as a travel route for people and goods. Many Americans live near popular water sources, such as the Mississippi River, the Colorado River and the Great Lakes.Mountains and deserts have been settled by fewer people than the plains areas. However, they have valuable resources of their own.</string>
<string name="geographyTextFr">L\'étude des reliefs de la Terre est appelée géographie physique. Les reliefs peuvent être des montagnes et des vallées. Il peut aussi s\'agira de glaciers, delacs ou de rivières. Les reliefs sont parfois appelés caractéristiques physiques. Il est important que les élèves connaissent la géographie physique de laTerre. Les saisons, l\'atmosphère et tous les processus naturels de la Terre affectent l\'endroit où les gens sont capables de vivre. La géographie est l\'un desfacteurs que les gens utilisent pour décider où ils veulent vivre. Les caractéristiques physiques d\'une région sont souvent riches en ressources. Àl\'intérieur d\'une nation, les chaînes de montagnes deviennent des frontières naturelles pour les zones de peuplement. Aux États-Unis, les principaleschaînes de montagnes sont la Sierra Nevada, les montagnes Rocheuses et les Appalaches.Les sources d\'eau douce influencent également l\'endroit où lesgens s\'installent. Les gens ont besoin d\'eau pour boire. Ils en ont aussi besoin pour se laver. Tout au long de l\'histoire, les gens se sont installés près del\'eau douce. Vivre près d\'une source d\'eau permet de s\'assurer que les gens ont l\'eau dont ils ont besoin. Il y avait un bonus supplémentaire, aussi. L\'eaupourrait être utilisée comme voie de voyage pour les personnes et les marchandises. Beaucoup d\'Américains vivent près des sources d\'eau populaires,telles que le fleuve Mississippi, le fleuve Colorado et les Grands Lacs.Mountains et les déserts ont été installés par moins de gens que les zones desplaines. Cependant, ils disposent de ressources précieuses.Les gens ont une réponse.</string>
<string name="immersiveReaderButtonText">Immersive Reader</string>
</resources>
Reemplace el contenido de res/layout/activity_main.xml por el código XML siguiente que se usará en la aplicación. Este código XML es el diseño de la interfaz de usuario de la aplicación. Si no ve el código en el archivo activity_main.xml, haga clic con el botón derecho en el lienzo y seleccione Ir a XML.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!-- Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. -->
<!-- Licensed under the MIT License. -->
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#FFFFFF"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/linearLayout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:background="#FFFFFF"
android:orientation="vertical"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.0"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintVertical_bias="0.0">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/Title"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="48dp"
android:layout_marginTop="24dp"
android:layout_marginRight="48dp"
android:layout_marginBottom="24dp"
android:text="@string/geographyTitle"
android:textSize="24sp"
android:textStyle="bold" />
<ScrollView
android:id="@+id/ContentPane"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="480dp"
android:layout_marginBottom="48dp"
android:clipToPadding="false"
android:fillViewport="false"
android:paddingLeft="48dp"
android:paddingRight="48dp"
android:scrollbarStyle="outsideInset"
android:visibility="visible"
tools:visibility="visible">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/Content1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#00FFFFFF"
android:text="@string/geographyTextEn"
android:textSize="18sp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/Content2"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#00FFFFFF"
android:text="@string/geographyTextFr"
android:textSize="18sp" />
</LinearLayout>
</ScrollView>
<Button
android:id="@+id/LaunchImmersiveReaderButton"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="40dp"
android:layout_marginRight="40dp"
android:layout_marginBottom="80dp"
android:text="@string/immersiveReaderButtonText"
android:textAllCaps="false"
android:textSize="24sp"
android:visibility="visible"
tools:visibility="visible" />
</LinearLayout>
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
Configuración de la interfaz JavaScript del código Kotlin de la aplicación
En la carpeta kotlin+java/com.example.quickstartkotlin/, cree una nueva clase Kotlin y asígnela el nombre WebAppInterface. A continuación, agregue el código siguiente. Este código permite a la aplicación interactuar con las funciones JavaScript del HTML que se agregará en un paso posterior.
// Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
// Licensed under the MIT License.
package com.example.quickstartkotlin
import android.content.Context
import android.webkit.JavascriptInterface
import android.webkit.WebView
import android.widget.LinearLayout
import android.widget.Toast
class WebAppInterface(private val mContext: Context, var parentLayout: LinearLayout, var webView: WebView) {
// Show a toast from html.
@JavascriptInterface
fun showToast(toast: String) {
Toast.makeText(mContext, toast, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
// Exit the Immersive Reader.
@JavascriptInterface
fun immersiveReaderExit() {
webView.post(Runnable { destroyWebView(parentLayout, webView) })
// Any additional functionality may be added here.
Toast.makeText(mContext, "The Immersive Reader has been closed!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
// Disposes of the WebView when the back arrow is tapped.
private fun destroyWebView(parentLayout: LinearLayout, webView: WebView) {
// Removes the WebView from its parent view before doing anything.
parentLayout.removeView(webView)
// Cleans things up before destroying the WebView.
webView.clearHistory()
webView.clearCache(true)
webView.loadUrl("about:blank")
webView.onPause()
webView.removeAllViews()
webView.pauseTimers()
webView.destroy()
}
}
Configuración de la actividad principal del código Kotlin de la aplicación
En la carpeta kotlin+java/com.example.quickstartkotlin/, hay un archivo de clase Kotlin MainActivity.kt. En este archivo es donde se crea la lógica de la aplicación. Reemplace su contenido por el código siguiente.
// Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
// Licensed under the MIT License.
package com.example.quickstartkotlin
import android.app.Activity
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import android.os.Bundle
import android.webkit.CookieManager
import android.webkit.WebView
import android.widget.Button
import android.webkit.WebViewClient
import android.widget.LinearLayout
import android.widget.TextView
import com.google.gson.*
import io.github.cdimascio.dotenv.dotenv
import java.io.IOException
import java.io.*
import java.net.HttpURLConnection
import java.net.HttpURLConnection.HTTP_OK
import java.net.URL
import kotlinx.coroutines.*
import org.json.JSONObject
import java.util.*
// This sample app uses the Dotenv. It's a module that loads environment variables from a .env file to better manage secrets.
// https://github.com/cdimascio/java-dotenv
// Be sure to add a "env" file to the /assets folder.
// Instead of '.env', use 'env'.
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private val dotEnv = dotenv {
directory = "/assets"
filename = "env"
ignoreIfMalformed = true
ignoreIfMissing = true
}
private lateinit var contextualWebView: WebView
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
this.supportActionBar!!.hide()
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
val immersiveReaderButton = findViewById<Button>(R.id.LaunchImmersiveReaderButton)
immersiveReaderButton.setOnClickListener { GlobalScope.launch { handleLoadImmersiveReaderWebView() } }
}
// Assigns values to the objects sent to the Immersive Reader SDK,
// acquires the token and authorizes the app, then launches
// the Web View to get the response and load the Immersive Reader
// when the button is clicked in HTML.
private suspend fun handleLoadImmersiveReaderWebView() {
val exampleActivity = this
val subdomain = dotEnv["SUBDOMAIN"]
val irTitle = findViewById<TextView>(R.id.Title)
val irText1 = findViewById<TextView>(R.id.Content1)
val irText2 = findViewById<TextView>(R.id.Content2)
// The content of the request that's shown in the Immersive Reader.
// This basic example contains chunks of two different languages.
val chunk1 = Chunk()
chunk1.content = irText1.text.toString()
chunk1.lang = "en"
chunk1.mimeType = "text/plain"
val chunk2 = Chunk()
chunk2.content = irText2.text.toString()
chunk2.lang = "fr"
chunk2.mimeType = "text/plain"
val chunks = ArrayList<Chunk>()
chunks.add(chunk1)
chunks.add(chunk2)
val content = Content()
content.title = irTitle.text.toString()
content.chunks = chunks
// Options may be assigned values here (e.g. options.uiLang = "en").
val options = Options()
var token: String
runBlocking{
val resp = async { getImmersiveReaderTokenAsync() }
token = resp.await()
val jsonResp = JSONObject(token)
loadImmersiveReaderWebView(exampleActivity, jsonResp.getString("access_token"), subdomain, content, options)
}
}
// The next two functions get the token from the Immersive Reader SDK
// and authorize the app.
private suspend fun getImmersiveReaderTokenAsync(): String {
return getToken()
}
@Throws(IOException::class)
fun getToken(): String {
val clientId = dotEnv["CLIENT_ID"]
val clientSecret = dotEnv["CLIENT_SECRET"]
val tenantId = dotEnv["TENANT_ID"]
val tokenUrl = URL("https://login.windows.net/$tenantId/oauth2/token")
val form = "grant_type=client_credentials&resource=https://cognitiveservices.azure.com/&client_id=$clientId&client_secret=$clientSecret"
val connection = tokenUrl.openConnection() as HttpURLConnection
connection.requestMethod = "POST"
connection.setRequestProperty("content-type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded")
connection.doOutput = true
val writer = DataOutputStream(connection.outputStream)
writer.writeBytes(form)
writer.flush()
writer.close()
val responseCode = connection.responseCode
if (responseCode == HTTP_OK) {
val readerIn = BufferedReader(InputStreamReader(connection.inputStream))
var inputLine = readerIn.readLine()
val response = StringBuffer()
do {
response.append(inputLine)
} while (inputLine.length < 0)
readerIn.close()
// Return token
return response.toString()
} else {
val responseError = Error(code = "BadRequest", message = "There was an error getting the token.")
throw IOException(responseError.toString())
}
}
// To be assigned values and sent to the Immersive Reader SDK
class Chunk(var content: String? = null,
var lang: String? = null,
var mimeType: String? = null)
class Content(var title: String? = null,
var chunks: List<Chunk>? = null)
class Message(var cogSvcsAccessToken: String? = null,
var cogSvcsSubdomain: String? = null,
var content: Content? = null,
var launchToPostMessageSentDurationInMs: Int? = null,
var options: Options? = null)
// Only includes Immersive Reader options relevant to Android apps.
// For a complete list, visit https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/ai-services/immersive-reader/reference
class Options(var uiLang: String? = null, // Language of the UI, e.g. en, es-ES (optional). Defaults to browser language if not specified.
var timeout: Int? = null, // Duration (in milliseconds) before launchAsync fails with a timeout error (default is 15000 ms).
var uiZIndex: Int? = null, // Z-index of the iframe that will be created (default is 1000)
var onExit: (() -> Any)? = null, // Executes a callback function when the Immersive Reader exits
var customDomain: String? = null, // Reserved for internal use. Custom domain where the Immersive Reader webapp is hosted (default is null).
var allowFullscreen: Boolean? = null, // The ability to toggle fullscreen (default is true).
var hideExitButton: Boolean? = null // Whether or not to hide the Immersive Reader's exit button arrow (default is false). This should only be true if there is an alternative mechanism provided to exit the Immersive Reader (e.g a mobile toolbar's back arrow).
)
class Error(var code: String? = null,
var message: String? = null)
// A custom Web View component that launches inside the app
@Throws(IOException::class)
fun loadImmersiveReaderWebView(
exampleActivity: Activity,
token: String,
subdomain: String?,
content: Content,
options: Options
) {
val startPostMessageSentDurationInMs = Date()
// Populate the message
val messageData = Message()
messageData.cogSvcsAccessToken = token
messageData.cogSvcsSubdomain = subdomain
messageData.content = content
messageData.options = options
GlobalScope.launch {
withContext(Dispatchers.Main) {
contextualWebView = WebView(exampleActivity)
val parentLayout = findViewById<LinearLayout>(R.id.linearLayout)
val contextualWebViewSettings = contextualWebView.settings
contextualWebViewSettings.allowContentAccess = true
contextualWebViewSettings.builtInZoomControls = true
contextualWebViewSettings.javaScriptEnabled = true
contextualWebViewSettings.loadsImagesAutomatically = true
contextualWebViewSettings.loadWithOverviewMode = true
contextualWebViewSettings.useWideViewPort = true
contextualWebViewSettings.userAgentString = "Android"
contextualWebViewSettings.domStorageEnabled = true
contextualWebViewSettings.setAppCacheEnabled(false)
contextualWebViewSettings.setSupportZoom(true)
contextualWebView.setInitialScale(1)
// Enables WebView Cookies
if (android.os.Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP) {
CookieManager.getInstance().setAcceptThirdPartyCookies(contextualWebView, true)
} else {
CookieManager.getInstance().setAcceptCookie(true)
}
val contextualWebViewLayout = LinearLayout.LayoutParams(LinearLayout.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, LinearLayout.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT)
parentLayout.addView(contextualWebView, 0, contextualWebViewLayout)
// This is required to launch the WebView *inside* the host application.
contextualWebView.webViewClient = object : WebViewClient() {
override fun shouldOverrideUrlLoading(view: WebView, url: String): Boolean {
view.loadUrl(url)
return true
}
// Send message JSON object to Immersive Reader html
override fun onPageFinished(view: WebView, url: String) {
val endPostMessageSentDurationInMs = Date()
val postMessageSentDurationInMs = (endPostMessageSentDurationInMs.time - startPostMessageSentDurationInMs.time).toInt()
// Updates launchToPostMessageSentDurationInMs
messageData.launchToPostMessageSentDurationInMs = postMessageSentDurationInMs
// Serializes message data class to JSON
val gson = Gson()
val message = gson.toJson(messageData)
// Calls the handleLaunchImmersiveReader function in HTML
if (android.os.Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.KITKAT) {
view.evaluateJavascript("handleLaunchImmersiveReader($message)", null)
} else {
view.loadUrl("javascript:handleLaunchImmersiveReader($message)")
}
// Sets the visibility of the WebView after the function has been called.
view.visibility = WebView.VISIBLE
}
}
// This is where the WebAppInterface Class is used.
// Affords a way for JavaScript to work with the app directly from
// the Web View's HTML.
val jsInterface = WebAppInterface(exampleActivity, parentLayout, contextualWebView)
contextualWebView.addJavascriptInterface(jsInterface, "Android")
contextualWebView.loadUrl("file:///android_asset/immersiveReader.html")
}
}
}
}
Es posible que tenga que volver a sincronizar el proyecto.
Incorporación del código HTML de la aplicación a la vista web
La implementación de la vista web necesita que el código HTML funcione. Haga clic con el botón derecho en la carpeta /assets, cree un nuevo archivo y asígnele el nombre immersiveReader.html.
Agregue el siguiente código HTML y JavaScript. Este código agrega el SDK de Immersive Reader a la aplicación y lo usa para abrir Immersive Reader mediante el código de la aplicación que hemos escrito.
<!-- Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the MIT License. -->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1, shrink-to-fit=no">
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://ircdname.azureedge.net/immersivereadersdk/immersive-reader-sdk.1.4.0.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
function handleLaunchImmersiveReader(message) {
if (!message) {
Android.showToast('Message is null or undefined!');
} else {
// Learn more about chunk usage and supported MIME types https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/ai-services/immersive-reader/reference#chunk
var data = {
title: message.content.title,
chunks: message.content.chunks
};
// A simple declarative function used to close the Immersive Reader WebView via @JavaScriptInterface
var exitCallback = function() {
Android.immersiveReaderExit();
}
// Learn more about options https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/ai-services/immersive-reader/reference#options
var options = {
onExit: exitCallback,
uiZIndex: 2000
};
// Use the JavaScript SDK to launch the Immersive Reader.
ImmersiveReader.launchAsync(message.cogSvcsAccessToken, message.cogSvcsSubdomain, data, options);
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Configuración de permisos de la aplicación
Dado que la aplicación necesita realizar llamadas de red al SDK del Lector inmersivo para funcionar, es necesario asegurarse de que los permisos de la aplicación están configurados para permitir el acceso a la red. Reemplace el contenido de /manifests/AndroidManifest.xml por el código XML siguiente.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.quickstartkotlin">
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<activity android:name=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>
Ejecución de la aplicación
Use Android Studio para ejecutar la aplicación en un emulador de dispositivos. Al seleccionar Lector inmersivo, se abre el Lector inmersivo con el contenido de la aplicación.

Paso siguiente
En este inicio rápido, creará una aplicación iOS desde cero e integrará el Lector inmersivo. Hay disponible un ejemplo funcional completo de esta guía de inicio rápido en GitHub.
Requisitos previos
- Suscripción a Azure. Puede crear una de forma gratuita.
- Un recurso del Lector inmersivo configurado para la autenticación de Microsoft Entra. Siga estas instrucciones para realizar la configuración. Guarde la salida de la sesión en un archivo de texto para que pueda configurar las propiedades del entorno.
- macOS y Xcode.
Creación de un proyecto de Xcode
Cree un proyecto nuevo en Xcode.

Elija Single View App (Aplicación de vista única).
Configuración de la autenticación
En el menú superior, seleccione Producto > Esquema > Editar esquema...
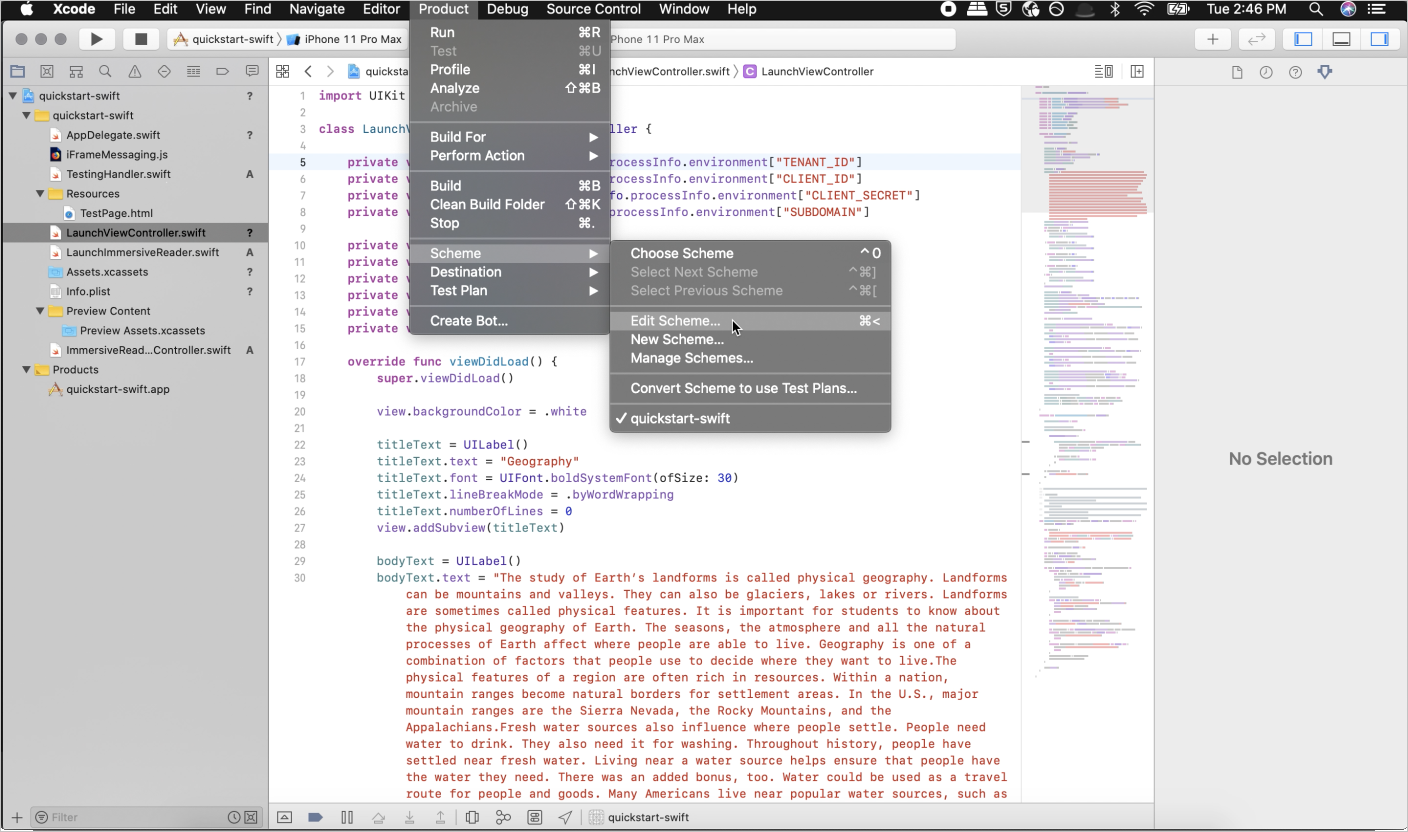
En la vista Ejecutar, seleccione la pestaña Argumentos.
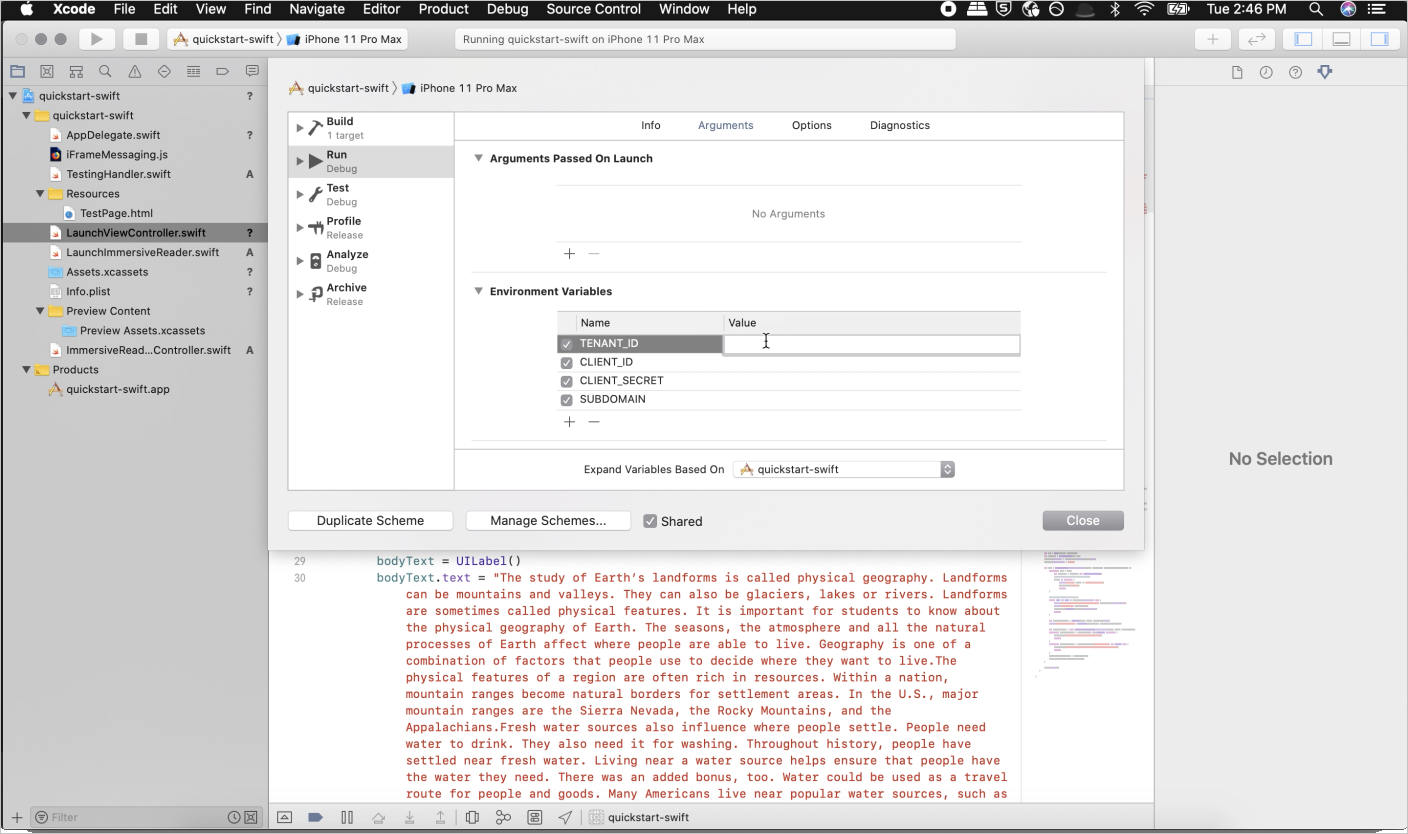
En la sección Environment Variables (Variables de entorno), agregue los siguientes nombres y valores, y proporcione los valores especificados al crear el recurso del Lector inmersivo.
Importante
Recuerde no publicar nunca secretos públicamente. En el caso de producción, use una forma segura de almacenar sus credenciales y acceder a ellas, como Azure Key Vault.
TENANT_ID=<YOUR_TENANT_ID>
CLIENT_ID=<YOUR_CLIENT_ID>
CLIENT_SECRET<YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET>
SUBDOMAIN=<YOUR_SUBDOMAIN>
Configuración de la aplicación para que se ejecute sin un guion gráfico
Abra AppDelegate.swift y reemplace el archivo por el siguiente código.
import UIKit
@UIApplicationMain
class AppDelegate: UIResponder, UIApplicationDelegate {
var window: UIWindow?
var navigationController: UINavigationController?
func application(_ application: UIApplication, didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions: [UIApplication.LaunchOptionsKey: Any]?) -> Bool {
// Override point for customization after application launch.
window = UIWindow(frame: UIScreen.main.bounds)
if let window = window {
let mainViewController = LaunchViewController()
navigationController = UINavigationController(rootViewController: mainViewController)
window.rootViewController = navigationController
window.makeKeyAndVisible()
}
return true
}
func applicationWillResignActive(_ application: UIApplication) {
// Sent when the application is about to move from active to inactive state. This can occur for certain types of temporary interruptions (such as an incoming phone call or SMS message) or when the user quits the application and it begins the transition to the background state.
// Use this method to pause ongoing tasks, disable timers, and invalidate graphics rendering callbacks. Games should use this method to pause the game.
}
func applicationDidEnterBackground(_ application: UIApplication) {
// Use this method to release shared resources, save user data, invalidate timers, and store enough application state information to restore your application to its current state in case it is terminated later.
// If your application supports background execution, this method is called instead of applicationWillTerminate: when the user quits.
}
func applicationWillEnterForeground(_ application: UIApplication) {
// Called as part of the transition from the background to the active state; here you can undo many of the changes made on entering the background.
}
func applicationDidBecomeActive(_ application: UIApplication) {
// Restart any tasks that were paused (or not yet started) while the application was inactive. If the application was previously in the background, optionally refresh the user interface.
}
func applicationWillTerminate(_ application: UIApplication) {
// Called when the application is about to terminate. Save data if appropriate. See also applicationDidEnterBackground:.
}
}
Creación de los controladores de vista e incorporación de contenido de ejemplo
Cambie el nombre de ViewController.swift a LaunchViewController.swift y reemplace el archivo por el código siguiente.
import UIKit
class LaunchViewController: UIViewController {
private var tenantId = ProcessInfo.processInfo.environment["TENANT_ID"]
private var clientId = ProcessInfo.processInfo.environment["CLIENT_ID"]
private var clientSecret = ProcessInfo.processInfo.environment["CLIENT_SECRET"]
private var subdomain = ProcessInfo.processInfo.environment["SUBDOMAIN"]
private var launchButton: UIButton!
private var titleText: UILabel!
private var bodyText: UILabel!
private var sampleContent: Content!
private var sampleChunk: Chunk!
private var sampleOptions: Options!
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
view.backgroundColor = .white
titleText = UILabel()
titleText.text = "Geography"
titleText.font = UIFont.boldSystemFont(ofSize: 30)
titleText.lineBreakMode = .byWordWrapping
titleText.numberOfLines = 0
view.addSubview(titleText)
bodyText = UILabel()
bodyText.text = "The study of Earth's landforms is called physical geography. Landforms can be mountains and valleys. They can also be glaciers, lakes or rivers. Landforms are sometimes called physical features. It is important for students to know about the physical geography of Earth. The seasons, the atmosphere and all the natural processes of Earth affect where people are able to live. Geography is one of a combination of factors that people use to decide where they want to live.The physical features of a region are often rich in resources. Within a nation, mountain ranges become natural borders for settlement areas. In the U.S., major mountain ranges are the Sierra Nevada, the Rocky Mountains, and the Appalachians.Fresh water sources also influence where people settle. People need water to drink. They also need it for washing. Throughout history, people have settled near fresh water. Living near a water source helps ensure that people have the water they need. There was an added bonus, too. Water could be used as a travel route for people and goods. Many Americans live near popular water sources, such as the Mississippi River, the Colorado River and the Great Lakes.Mountains and deserts have been settled by fewer people than the plains areas. However, they have valuable resources of their own."
bodyText.lineBreakMode = .byWordWrapping
bodyText.numberOfLines = 0
let screenSize = self.view.frame.height
if screenSize <= 667 {
// Font size for smaller iPhones.
bodyText.font = bodyText.font.withSize(14)
} else if screenSize <= 812 {
// Font size for medium iPhones.
bodyText.font = bodyText.font.withSize(15)
} else if screenSize <= 896 {
// Font size for larger iPhones.
bodyText.font = bodyText.font.withSize(17)
} else if screenSize <= 1024 {
// Font size for iPads.
bodyText.font = bodyText.font.withSize(25)
} else {
// Font size for large iPads.
bodyText.font = bodyText.font.withSize(28)
}
view.addSubview(bodyText)
launchButton = UIButton()
launchButton.backgroundColor = .darkGray
launchButton.contentEdgeInsets = UIEdgeInsets(top: 10, left: 10, bottom: 10, right: 10)
launchButton.setTitleColor(.white, for: .normal)
launchButton.setTitle("Immersive Reader", for: .normal)
launchButton.addTarget(self, action: #selector(launchImmersiveReaderButton(sender:)), for: .touchUpInside)
view.addSubview(launchButton)
let layoutGuide = view.safeAreaLayoutGuide
titleText.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
titleText.topAnchor.constraint(equalTo: layoutGuide.topAnchor, constant: 20).isActive = true
titleText.leadingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: layoutGuide.leadingAnchor, constant: 20).isActive = true
titleText.trailingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: layoutGuide.trailingAnchor, constant: -20).isActive = true
bodyText.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
bodyText.topAnchor.constraint(equalTo: titleText.bottomAnchor, constant: 15).isActive = true
bodyText.leadingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: layoutGuide.leadingAnchor, constant: 20).isActive = true
bodyText.trailingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: layoutGuide.trailingAnchor, constant: -20).isActive = true
launchButton.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
launchButton.widthAnchor.constraint(equalToConstant: 200).isActive = true
launchButton.heightAnchor.constraint(equalToConstant: 50).isActive = true
launchButton.centerXAnchor.constraint(equalTo: layoutGuide.centerXAnchor).isActive = true
launchButton.bottomAnchor.constraint(equalTo: layoutGuide.bottomAnchor, constant: -10).isActive = true
// Create content and options.
sampleChunk = Chunk(content: bodyText.text!, lang: nil, mimeType: nil)
sampleContent = Content(title: titleText.text!, chunks: [sampleChunk])
sampleOptions = Options(uiLang: nil, timeout: nil, uiZIndex: nil)
}
@IBAction func launchImmersiveReaderButton(sender: AnyObject) {
launchButton.isEnabled = false
// Callback to get token.
getToken(onSuccess: {cognitiveToken in
DispatchQueue.main.async {
launchImmersiveReader(navController: self.navigationController!, token: cognitiveToken, subdomain: self.subdomain!, content: self.sampleContent, options: self.sampleOptions, onSuccess: {
self.launchButton.isEnabled = true
}, onFailure: { error in
self.launchButton.isEnabled = true
})
}
}, onFailure: { error in
print("an error occurred: \(error)")
})
}
func getToken(onSuccess: @escaping (_ theToken: String) -> Void, onFailure: @escaping ( _ theError: String) -> Void) {
let tokenForm = "grant_type=client_credentials&resource=https://cognitiveservices.azure.com/&client_id=" + self.clientId! + "&client_secret=" + self.clientSecret!
let tokenUrl = "https://login.windows.net/" + self.tenantId! + "/oauth2/token"
var responseTokenString: String = "0"
let url = URL(string: tokenUrl)!
var request = URLRequest(url: url)
request.httpBody = tokenForm.data(using: .utf8)
request.httpMethod = "POST"
let task = URLSession.shared.dataTask(with: request) { data, response, error in
guard let data = data,
let response = response as? HTTPURLResponse,
error == nil else {
onFailure("Error")
return
}
guard (200 ... 299) ~= response.statusCode else {
onFailure(String(response.statusCode))
return
}
let responseString = String(data: data, encoding: .utf8)
let jsonResponse = try? JSONSerialization.jsonObject(with: data, options: [])
guard let jsonDictonary = jsonResponse as? [String: Any] else {
onFailure("Error parsing JSON response.")
return
}
guard let responseToken = jsonDictonary["access_token"] as? String else {
onFailure("Error retrieving token from JSON response.")
return
}
responseTokenString = responseToken
onSuccess(responseTokenString)
}
task.resume()
}
}
Agregue un nuevo archivo a la carpeta raíz del proyecto denominado ImmersiveReaderViewController.swift y agregue el código siguiente.
import UIKit
import Foundation
import WebKit
@available(iOS 11.0, *)
public class ImmersiveReaderWebView: WKWebView {
init(frame: CGRect, contentController: WKUserContentController) {
let conf = WKWebViewConfiguration()
conf.userContentController = contentController
super.init(frame: frame, configuration: conf)
}
required init?(coder: NSCoder) {
fatalError("init(coder:) has not been implemented")
}
}
public class ImmersiveReaderViewController: UIViewController, WKUIDelegate, WKNavigationDelegate {
let tokenToSend: String
let subdomainToSend: String
let contentToSend: Content
let optionsToSend: Options?
let onSuccessImmersiveReader: (() -> Void)?
let onFailureImmersiveReader: ((_ error: Error) -> Void)?
let onTimeout: ((_ timeoutValue: TimeInterval) -> Void)?
let onError: ((_ error: String) -> Void)?
let startTime = Date().timeIntervalSince1970*1000
var src: String
var webView: WKWebView!
var timer: Timer!
var timeoutValue: TimeInterval!
public init(tokenToPass: String, subdomainToPass: String, contentToPass: Content, optionsToPass: Options?, onSuccessImmersiveReader: @escaping () -> Void, onFailureImmersiveReader: @escaping (_ status: Error) -> Void, onTimeout: @escaping (_ timeoutValue: TimeInterval) -> Void, onError: @escaping (_ error: String) -> Void) {
self.tokenToSend = tokenToPass
self.subdomainToSend = subdomainToPass
self.contentToSend = contentToPass
self.optionsToSend = optionsToPass
self.onSuccessImmersiveReader = onSuccessImmersiveReader
self.onFailureImmersiveReader = onFailureImmersiveReader
self.onTimeout = onTimeout
self.onError = onError
self.src = "https://" + subdomainToPass + ".cognitiveservices.azure.com/immersivereader/webapp/v1.0/reader"
super.init(nibName: nil, bundle: nil)
}
required init?(coder aDecoder: NSCoder) {
fatalError("init(coder:) has not been implemented")
}
override public func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
// If uiLang options are set update src to reflect this.
switch optionsToSend?.uiLang {
case .none: break
case .some(let value):
src = src + "?omkt=" + value
}
// Set timeout to default or value user specifies.
switch optionsToSend?.timeout {
case .none:
timeoutValue = 15
case .some(let value):
timeoutValue = value
}
view.backgroundColor = .white
webView = WKWebView()
let contentController = WKUserContentController()
if #available(iOS 11.0, *) {
webView = ImmersiveReaderWebView(frame: .zero, contentController: contentController)
} else {
// Fallback on earlier versions
webView = WKWebView()
let config = WKWebViewConfiguration()
config.userContentController = contentController
webView = WKWebView(frame: .zero, configuration: config)
}
webView.navigationDelegate = self
webView.uiDelegate = self
contentController.add(self, name: "readyForContent")
contentController.add(self, name: "launchSuccessful")
contentController.add(self, name: "tokenExpired")
contentController.add(self, name: "throttled")
view.addSubview(webView)
webView.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
if #available(iOS 11.0, *) {
let layoutGuide = view.safeAreaLayoutGuide
webView.leadingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: layoutGuide.leadingAnchor).isActive = true
webView.trailingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: layoutGuide.trailingAnchor).isActive = true
webView.topAnchor.constraint(equalTo: layoutGuide.topAnchor).isActive = true
webView.bottomAnchor.constraint(equalTo: layoutGuide.bottomAnchor).isActive = true
} else {
webView.leadingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.leadingAnchor).isActive = true
webView.trailingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.trailingAnchor).isActive = true
webView.topAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.topAnchor).isActive = true
webView.bottomAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.bottomAnchor).isActive = true
}
// Get path to JavaScript file.
guard let scriptPath = Bundle.main.path(forResource: "iFrameMessaging", ofType: "js") else {
onError!("Could not create script path from resource.")
return
}
do {
let scriptSource = try String(contentsOfFile: scriptPath)
let userScript = WKUserScript(source: scriptSource, injectionTime: .atDocumentStart, forMainFrameOnly: true)
contentController.addUserScript(userScript)
} catch {
onError!("Could not parse JavaScript file.")
return
}
// Start the timer.
timer = Timer.scheduledTimer(timeInterval: timeoutValue, target: self, selector: #selector(self.timedOut), userInfo: nil, repeats: false)
// Load the iframe from HTML.
webView.loadHTMLString("<!DOCTYPE html><html style='width: 100%; height: 100%; margin: 0; padding: 0;'><head><meta name='viewport' content='width=device-width, initial-scale=1, shrink-to-fit=no'></head><body style='width: 100%; height: 100%; margin: 0; padding: 0;'><iframe id='immersiveReaderIframe' src = '\(src)' width='100%' height='100%' style='border: 0'></iframe></body></html>", baseURL: URL(string: "test://learningtools.onenote.com/learningtoolsapp/cognitive/reader"))
}
@objc func timedOut(_ timer: AnyObject) {
onTimeout!(timeoutValue)
}
public func webView(_ webView: WKWebView, decidePolicyFor navigationAction: WKNavigationAction, decisionHandler: @escaping (WKNavigationActionPolicy) -> Void) {
decisionHandler(.allow)
}
public func webView(_ webView: WKWebView, decidePolicyFor navigationResponse: WKNavigationResponse, decisionHandler: @escaping (WKNavigationResponsePolicy) -> Void ) {
decisionHandler(.allow)
}
}
extension ImmersiveReaderViewController: WKScriptMessageHandler {
public func userContentController(_ userContentController: WKUserContentController, didReceive message: WKScriptMessage) {
if message.name == "readyForContent" {
// Stop the timer.
timer.invalidate()
// Create the message variable
let message = Message(cogSvcsAccessToken: tokenToSend, cogSvcsSubdomain: subdomainToSend, resourceName: nil, request: contentToSend, launchToPostMessageSentDurationInMs: Int(Date().timeIntervalSince1970*1000 - startTime))
do {
let jsonData = try JSONEncoder().encode(message)
let jsonString = String(data: jsonData, encoding: .utf8)
self.webView.evaluateJavaScript("sendContentToReader(\(jsonString!))") { (result, error) in
if error != nil {
self.onError!("Error evaluating JavaScript \(String(describing: error))")
}
}
} catch { print(error)}
}
if message.name == "launchSuccessful" {
onSuccessImmersiveReader!()
}
if message.name == "tokenExpired" {
let tokenExpiredError = Error(code: "TokenExpired", message: "The access token supplied is expired.")
onFailureImmersiveReader!(tokenExpiredError)
}
if message.name == "throttled" {
let throttledError = Error(code: "Throttled", message: "You have exceeded the call rate limit.")
onFailureImmersiveReader!(throttledError)
}
}
}
Agregue un nuevo archivo a la carpeta raíz del proyecto denominado LaunchImmersiveReader.swift y agregue el código siguiente.
import UIKit
import Foundation
var navigationController: UINavigationController?
public struct Content: Encodable {
var title: String
var chunks: [Chunk]
public init(title: String, chunks: [Chunk]) {
self.title = title
self.chunks = chunks
}
}
public struct Chunk: Encodable {
var content: String
var lang: String?
var mimeType: String?
public init(content: String, lang: String?, mimeType: String?) {
self.content = content
self.lang = lang
self.mimeType = mimeType
}
}
public struct Options {
var uiLang: String?
var timeout: TimeInterval?
public init(uiLang: String?, timeout: TimeInterval?, uiZIndex: NSNumber?) {
self.uiLang = uiLang
self.timeout = timeout
}
}
public struct Error {
public var code: String
public var message: String
public init(code: String, message: String) {
self.code = code
self.message = message
}
}
struct Message: Encodable {
let cogSvcsAccessToken: String
let cogSvcsSubdomain: String
let resourceName: String?
let request: Content
let launchToPostMessageSentDurationInMs: Int
init(cogSvcsAccessToken: String, cogSvcsSubdomain: String, resourceName: String?, request: Content, launchToPostMessageSentDurationInMs: Int) {
self.cogSvcsAccessToken = cogSvcsAccessToken
self.cogSvcsSubdomain = cogSvcsSubdomain
self.resourceName = resourceName
self.request = request
self.launchToPostMessageSentDurationInMs = launchToPostMessageSentDurationInMs
}
}
public func launchImmersiveReader(navController: UINavigationController, token: String, subdomain: String, content: Content, options: Options?, onSuccess: @escaping () -> Void, onFailure: @escaping (_ error: Error) -> Void) {
if (content.chunks.count == 0) {
let badArgumentError = Error(code: "BadArgument", message: "Chunks must not be empty.")
onFailure(badArgumentError)
}
navigationController = navController
let immersiveReaderViewController = ImmersiveReaderViewController(tokenToPass: token, subdomainToPass: subdomain, contentToPass: content, optionsToPass: options, onSuccessImmersiveReader: {
onSuccess()
}, onFailureImmersiveReader: { error in
onFailure(error)
}, onTimeout: { timeout in
navigationController?.popViewController(animated: true)
let timeoutError = Error(code: "Timeout", message: "Page failed to load after timeout \(timeout) ms.")
onFailure(timeoutError)
}, onError: { error in
navigationController?.popViewController(animated: true)
let errorMessage = Error(code: "Internal Error", message: error)
onFailure(errorMessage)
})
navigationController!.pushViewController(immersiveReaderViewController, animated: true)
}
Agregue un archivo a la carpeta Resources (Recursos) denominado iFrameMessaging.js y agregue el código siguiente.
window.addEventListener("message", function(message) {
if(message.data == "ImmersiveReader-ReadyForContent") {
window.webkit.messageHandlers.readyForContent.postMessage(null);
}
if(message.data == "ImmersiveReader-LaunchSuccessful") {
window.webkit.messageHandlers.launchSuccessful.postMessage(null);
}
if(message.data == "ImmersiveReader-TokenExpired") {
window.webkit.messageHandlers.tokenExpired.postMessage(null);
}
if(message.data == "ImmersiveReader-Throttled") {
window.webkit.messageHandlers.throttled.postMessage(null);
}
});
function sendContentToReader(message) {
document.getElementById('immersiveReaderIframe').contentWindow.postMessage(JSON.stringify({messageType:'Content', messageValue: message}), '*');
}
Compilación y ejecución de la aplicación
Seleccione como destino un simulador o un dispositivo para establecer el esquema de archivo en Xcode.

En Xcode, presione Ctrl + R o seleccione el botón de reproducción para ejecutar el proyecto. La aplicación debe iniciarse en el simulador o el dispositivo especificados.
En la aplicación, debe ver lo siguiente:

Al seleccionar el botón Immersive Reader, verá que se inicia dicha herramienta con el contenido de la aplicación.
