Tutorial: Create a simple Visual Basic (VB) console app
Applies to: ![]() Visual Studio
Visual Studio ![]() Visual Studio for Mac
Visual Studio for Mac
Note
This article applies to Visual Studio 2017. If you're looking for the latest Visual Studio documentation, see Visual Studio documentation. We recommend upgrading to the latest version of Visual Studio. Download it here
This article shows how you'll use Visual Studio to create a simple Visual Basic application, a console app. In this app, you ask the user for their name, and then display it back with the current time. You'll also explore some features of the Visual Studio integrated development environment (IDE). Visual Basic is a type-safe programming language that's designed to be easy to learn. A console app takes input and displays output in a command-line window, also known as a console.
In this tutorial, you learn how to:
- Create a Visual Studio project
- Run the default application
- Add code to ask for user input
- Extra credit: Add two numbers
- Clean up resources
Prerequisites
If you haven't already installed Visual Studio, go to the Visual Studio downloads page to install it for free.
Create a project
First, you'll create a Visual Basic app project. The default project template includes all the files you'll need for a runnable app.
Open Visual Studio 2017.
From the top menu bar, choose File > New > Project.
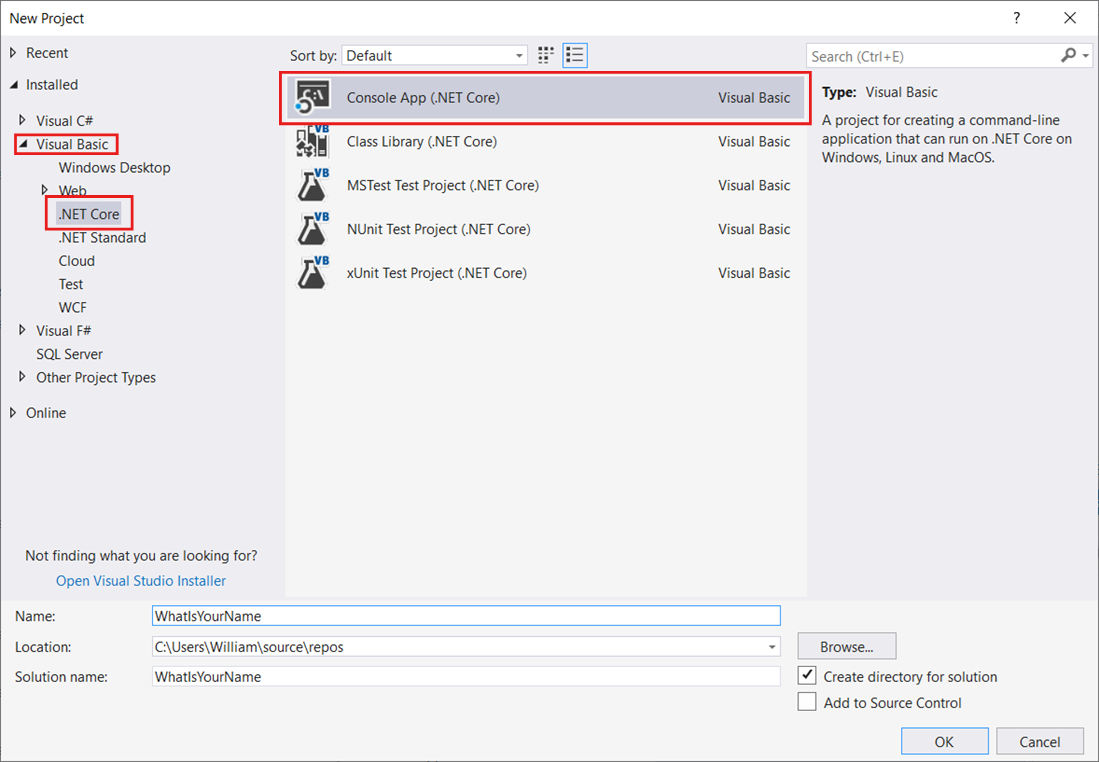
In the New Project dialog box in the left pane, expand Visual Basic, and then choose .NET Core. In the middle pane, choose Console App (.NET Core). Then name the project WhatIsYourName.
Add a workload (optional)
If you don't see the Console App (.NET Core) project template, you can get it by adding the .NET Core cross-platform development workload. You can add this workload in one of the two following ways, depending on which Visual Studio 2017 updates are installed on your machine.
Option 1: Use the New Project dialog box
Select the Open Visual Studio Installer link in the left pane of the New Project dialog box.
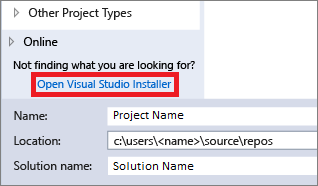
The Visual Studio Installer launches. Choose the .NET Core cross-platform development workload, and then choose Modify.

Option 2: Use the Tools menu bar
Cancel out of the New Project dialog box and from the top menu bar, choose Tools > Get Tools and Features.
The Visual Studio Installer launches. Choose the .NET Core cross-platform development workload, and then choose Modify.
Run the app
After you select your Visual Basic project template and name your project, Visual Studio creates a Program.vb file. The default code calls the WriteLine method to display the literal string "Hello World!" in the console window.
There are two ways to run this code, inside Visual Studio in debug mode, and from your computer as a regular standalone app.
Run the app in debug mode
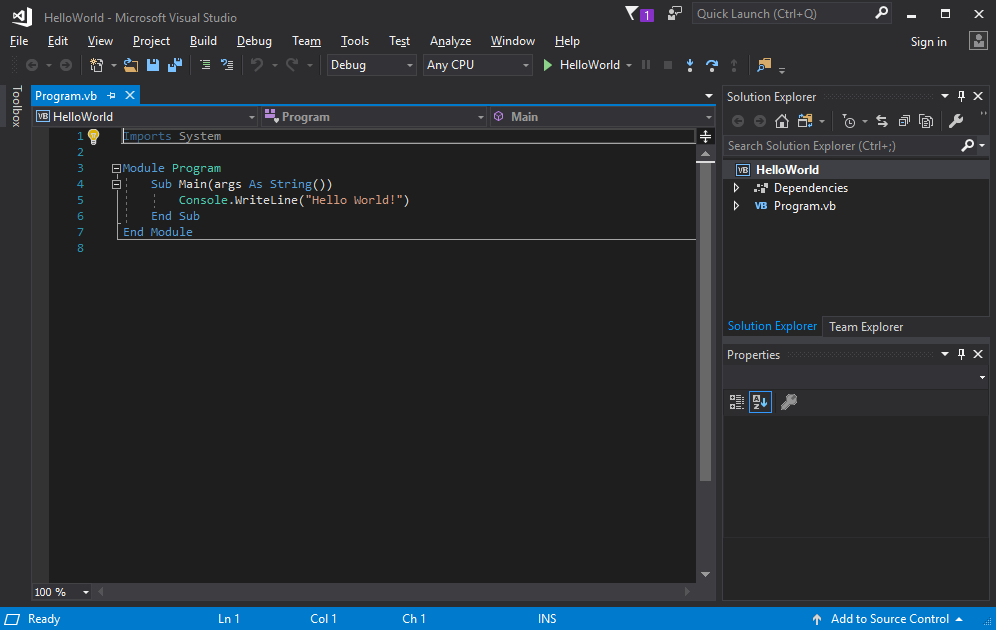
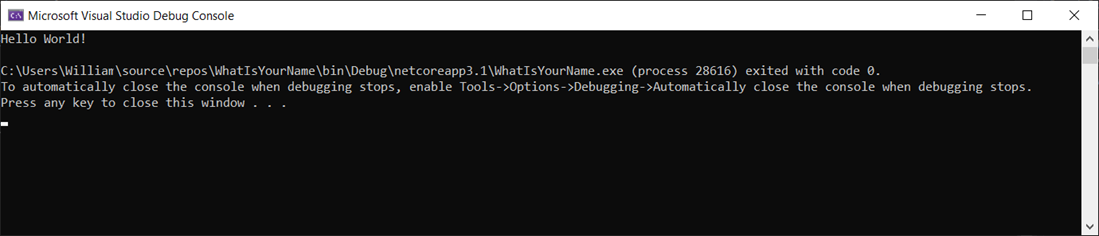
Select the WhatIsYourName button or press F5 to build and run the default "WhatIsYourName" code in Debug mode.
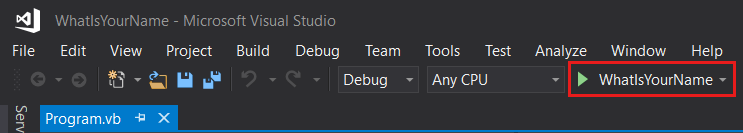
When the app runs in the Microsoft Visual Studio Debug Console, "Hello World!" displays. Press any key to close the debug console window and end the app:
Run the app as a standalone
To see the output outside of Visual Studio, in a system console window, build and run the executable (.exe file).
In the Build menu, choose Build Solution.
In Solution Explorer, right-click on WhatIsYourName and choose Open File in File Explorer.
In File Explorer, navigate to the bin\Debug\netcoreapp3.1 directory and run WhatIsYourName.exe.
The
Mainprocedure terminates after its single statement executes and the console window closes immediately. To keep the console visible until the user presses a key, see the next section.
Add code to ask for user input
Next, you'll add Visual Basic code that prompts you for your name and then displays it along with the current date and time. In addition, you'll add code that pauses the console window until the user presses a key.
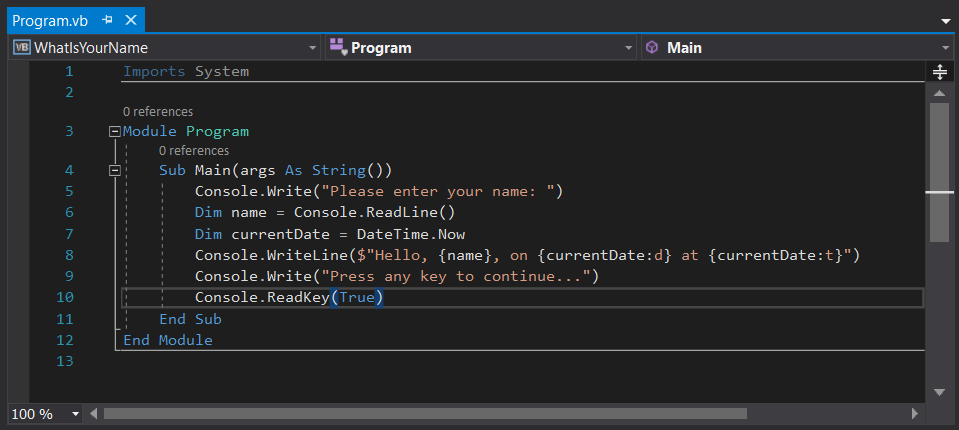
Enter the following Visual Basic code after the
Sub Main(args As String())line and before theEnd Subline, replacing the WriteLine line:Console.Write("Please enter your name: ") Dim name = Console.ReadLine() Dim currentDate = DateTime.Now Console.WriteLine($"Hello, {name}, on {currentDate:d} at {currentDate:t}") Console.Write("Press any key to continue...") Console.ReadKey(True)- Write and WriteLine write a string to the console.
- ReadLine reads input from the console, in this case a string.
- DateTime represents a datetime, and Now returns the current time.
- ReadKey() pauses the app and waits for a keypress.
Select the WhatIsYourName button or press F5 to build and run your first app in Debug mode.
When the debug console window opens, enter your name. Your console window should look similar to the following screenshot:
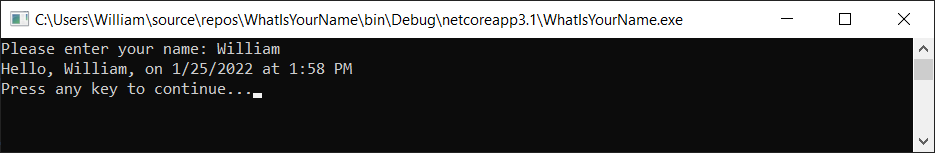
Press any key to end the app, and then press any key to close the debug console window.
Now that your new code is in the app, build and run the executable (.exe file) in a system console window, as described previously in Run the app as a standalone. Now when you press a key, the app exits, which closes the console window.
Extra credit: Add two numbers
This example shows how to read in numbers, rather than a string, and do some arithmetic. Try changing your code from:
Module Program
Sub Main(args As String())
Console.Write("Please enter your name: ")
Dim name = Console.ReadLine()
Dim currentDate = DateTime.Now
Console.WriteLine($"Hello, {name}, on {currentDate:d} at {currentDate:t}")
Console.Write("Press any key to continue...")
Console.ReadKey(True)
End Sub
End Module
to:
Module Program
Public num1 As Integer
Public num2 As Integer
Public answer As Integer
Sub Main(args As String())
Console.Write("Type a number and press Enter")
num1 = Console.ReadLine()
Console.Write("Type another number to add to it and press Enter")
num2 = Console.ReadLine()
answer = num1 + num2
Console.WriteLine("The answer is " & answer)
Console.Write("Press any key to continue...")
Console.ReadKey(True)
End Sub
End Module
And then run the updated app as described under "Run the app".
Clean up resources
If you're not going to continue to use this app, delete the project.
In Solution Explorer, right-click on WhatIsYourName to open the context menu for your project. Then, select Open Folder in File Explorer.
Close Visual Studio.
In the File Explorer dialog, go up two levels of folders.
Right-click on the WhatIsYourName folder and select Delete.
Next steps
Congratulations on completing this tutorial! To learn more, see the following tutorial.