File content data model
These parts of the content are to be stored on the host:
- Primary document content: Identified by StreamId = “MainContent”
- Multiple alternate streams within the document
- Set of content properties
All three of these content parts can be modified or fetched in a single request or response, and modifications must be processed within a transaction. In addition, if the document is updated using any mechanism other than the PutChunkedFile API, the host should clear the following parts of the content:
- Multiple alternate streams within the document (except MainContent stream)
- All Content Properties with
ContentPropertyRetention==DeleteOnContentChange
ContentProperty
A JSON-formatted object containing the following properties:
ContentPropertyRetention– A string value that indicates whether the content properties should (or shouldn't) be maintained after changes. Valid values areDeleteOnContentChangeandKeepOnContentChange.Name– A string value that indicates the name of the content property. The maximum length of this value is 256 characters.Value– A string value of the content property. The maximum length of this value is 1 KB.
{
"ContentPropertyRetention": "KeepOnContentChange",
"Name": "Property Name",
"Value": "Property Value"
}
The maximum number of unexpired content properties supported for a file is 256. A content property expires 30 days after it was last updated.
Chunk streams for efficient transfer
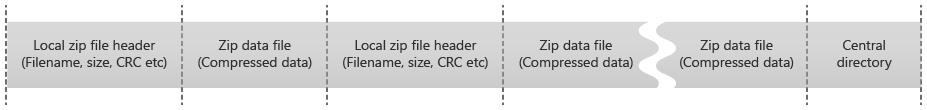
To achieve incremental file transfer, the file contents are broken into chunks. How a binary stream is broken into chunks depends on the chunkingScheme value.
Two chunking schemes are currently supported:
Zip– Zip files are the default format of Office files that support coauthoring.FullFile– Encrypted Office files. Full binary contents of a stream are represented as a single chunk.
For the Zip chunking scheme, ZipLocalFileHeader, ZipPayload, and the central directory are separate chunks. Delta chunks are transferred in the PutChunkedFile and GetChunkedFile methods.
Chunks are identified by ChunkId (128-bit Spooky hash). The order of chunks for each file stream is also specified by the protocol.
On processing a PutChunkedFile request, if the file on the host is a zip archive, the host should update the file based on the client's file signature and the delta chunks in the request body.
If the file is not a zip archive, the host needs to update the file with the single full file chunk in the request body.