Entities quickstart
This entities quickstart demonstrates how to work with entity objects and entity files.
For information on migrating from the legacy account and data systems to PlayFab entities, see Entities migration information
Requirements
- A PlayFab developer account.
- An installed copy of the Unity Editor. For information on installing the Unity Editor, see Installing Unity in the Unity documentation. You can also install a version of the Unity using the Visual Studio feature installer.
Note
The PlayFab Unity3D SDK supports Unity Editor version 5.3 and higher.
- A Unity Project. For information on creating a Unity Project, see the Quickstart guide.
Note
If you are unfamiliar with Unity, recent installation packages give you the option of installing game creation walkthroughs. You can use one of the walkthroughs to create a sample game to use in the following quickstart.
- The PlayFab Unity3D SDK.
The C# Samples in this article are written for the Unity SDK. The Unity SDK uses an event driven model to handle non-synchronous tasks. To run the sample code using the standard C# or Xamarin C# SDKs, you must modify the code to use an async Task model. Methods that must be modified have Async append to the method name in the signature. For example, SetObject in the Unity SDK becomes SetObjectAsync in the standard C# SDK. For more information, see Asynchronous programming with async and await.
Terminology
Entities are any PlayFab concept that can contain data. The built-in entity types are:
- title - A title contains global information available to all players. This is similar to TitleData. It's identified by the title ID (
TitleId) of the game/application. - master_player_account - This entity Type allows you to share information about a player across multiple games within a namespace. It's identified by the player ID (
PlayFabId) of the player, which is returned as part of any login or any call to retrieve account information for the player account (for example, the PlayFab Client API GetAccountInfo). - title_player_account - Identifies a player account that contains some information for the current title. This is identified by the entity ID (
EntityKey.Id) you get back in the EntityKey object on any login. - character - Identifies a character that the player owns which contains information that you can retrieve. It's identified by the character ID (
CharacterId) of the character.
For more information on the built-in entity types, see Available built-in Entity types.
Entity initialization
To call any of the Entity API, you must obtain the entity ID and entity Type. You use the ID and Type to make calls to other Entity API methods. These are members of an EntityKey object.
You do this by calling any of the login methods, such as LoginWithCustomID.
void Login()
{
var request = new PlayFab.ClientModels.LoginWithCustomIDRequest
{
CustomId = SystemInfo.deviceUniqueIdentifier,
CreateAccount = true,
};
PlayFabClientAPI.LoginWithCustomID(request, OnLogin, OnSharedFailure);
}
void OnLogin(PlayFab.ClientModels.LoginResult result)
{
entityId = result.EntityToken.Entity.Id;
// The expected entity type is title_player_account.
entityType = result.EntityToken.Entity.Type;
}
You can also obtain the entity ID and entity Type by calling the GetEntityToken method.
PlayFabAuthenticationAPI.GetEntityToken(new GetEntityTokenRequest(),
(entityResult) =>
{
var entityId = entityResult.Entity.Id;
var entityType = entityResult.Entity.Type;
}, OnPlayFabError); // Define your own OnPlayFabError function to report errors
When called from the client, this typically represents the logged-in player. When called from game servers, this represents your title.
Entity objects
Entity objects allow you to read and write small JSON-serializable objects attached to an entity. All entity types support the GetObjects and SetObjects methods.
The following code snippets show how to set and read an Object on a title_player_account entity.
Use the SetObjects method to set entity objects on a player or a title.
var data = new Dictionary<string, object>()
{
{"Health", 100},
{"Mana", 10000}
};
var dataList = new List<SetObject>()
{
new SetObject()
{
ObjectName = "PlayerData",
DataObject = data
},
// A free-tier customer may store up to 3 objects on each entity
};
PlayFabDataAPI.SetObjects(new SetObjectsRequest()
{
Entity = new EntityKey {Id = entityId, Type = entityType}, // Saved from GetEntityToken, or a specified key created from a titlePlayerId, CharacterId, etc
Objects = dataList,
}, (setResult) => {
Debug.Log(setResult.ProfileVersion);
}, OnPlayFabError);
Use the GetObjects method to retrieve entity objects on a player or a title.
var getRequest = new GetObjectsRequest {Entity = new EntityKey {Id = entityId, Type = entityType}};
PlayFabDataAPI.GetObjects(getRequest,
result => { var objs = result.Objects; },
OnPlayFabError
);
Entity files
Entity files allow you to read and write files attached to an entity, in any format.
Use the GetFiles method to retrieve entity files.
void LoadAllFiles()
{
if (GlobalFileLock != 0)
throw new Exception("This example overly restricts file operations for safety. Careful consideration must be made when doing multiple file operations in parallel to avoid conflict.");
GlobalFileLock += 1; // Start GetFiles
var request = new PlayFab.DataModels.GetFilesRequest { Entity = new PlayFab.DataModels.EntityKey { Id = entityId, Type = entityType } };
PlayFabDataAPI.GetFiles(request, OnGetFileMeta, OnSharedFailure);
}
Use the initiatefileuploads method to initiate a file upload to an entity's profile.
void UploadFile(string fileName)
{
if (GlobalFileLock != 0)
throw new Exception("This example overly restricts file operations for safety. Careful consideration must be made when doing multiple file operations in parallel to avoid conflict.");
ActiveUploadFileName = fileName;
GlobalFileLock += 1; // Start InitiateFileUploads
var request = new PlayFab.DataModels.InitiateFileUploadsRequest
{
Entity = new PlayFab.DataModels.EntityKey { Id = entityId, Type = entityType },
FileNames = new List<string> { ActiveUploadFileName },
};
PlayFabDataAPI.InitiateFileUploads(request, OnInitFileUpload, OnInitFailed);
}
Use the AbortFileUploads method to abort a pending file upload to an entity's profile.
void OnInitFailed(PlayFabError error)
{
if (error.Error == PlayFabErrorCode.EntityFileOperationPending)
{
// This is an error you should handle when calling InitiateFileUploads, but your resolution path may vary
GlobalFileLock += 1; // Start AbortFileUploads
var request = new PlayFab.DataModels.AbortFileUploadsRequest
{
Entity = new PlayFab.DataModels.EntityKey { Id = entityId, Type = entityType },
FileNames = new List<string> { ActiveUploadFileName },
};
PlayFabDataAPI.AbortFileUploads(request, (result) => { GlobalFileLock -= 1; UploadFile(ActiveUploadFileName); }, OnSharedFailure); GlobalFileLock -= 1; // Finish AbortFileUploads
GlobalFileLock -= 1; // Failed InitiateFileUploads
}
else
OnSharedFailure(error);
}
Use the FinalizeFileUploads method to finalize file uploads to an entity's profile. The entity system doesn't consider the file upload complete, nor reflect any changes to other callers until the atomic upload operation is successfully finalized.
void FinalizeUpload(byte[] data)
{
GlobalFileLock += 1; // Start FinalizeFileUploads
var request = new PlayFab.DataModels.FinalizeFileUploadsRequest
{
Entity = new PlayFab.DataModels.EntityKey { Id = entityId, Type = entityType },
FileNames = new List<string> { ActiveUploadFileName },
};
PlayFabDataAPI.FinalizeFileUploads(request, OnUploadSuccess, OnSharedFailure);
GlobalFileLock -= 1; // Finish SimplePutCall
}
The example shown below demonstrates a full entity-file loop, from logging in, to loading a file, and uploading a new file.
The steps for this are:
- login and retrieve the entity
IDand entityType. - Initialize the atomic upload operation.
- Upload all of the files.
- Finalize the atomic upload operation.
For simplicity, this example saves one file at a time, but files can be uploaded atomically in sets.
The example assumes that you're familiar with using the Unity 3D engine.
#if !DISABLE_PLAYFABENTITY_API && !DISABLE_PLAYFABCLIENT_API
using PlayFab;
using PlayFab.Internal;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
using UnityEngine;
public class EntityFileExample : MonoBehaviour
{
public string entityId; // Id representing the logged in player
public string entityType; // entityType representing the logged in player
private readonly Dictionary<string, string> _entityFileJson = new Dictionary<string, string>();
private readonly Dictionary<string, string> _tempUpdates = new Dictionary<string, string>();
public string ActiveUploadFileName;
public string NewFileName;
// GlobalFileLock provides is a simplistic way to avoid file collisions, specifically designed for this example.
public int GlobalFileLock = 0;
void OnSharedFailure(PlayFabError error)
{
Debug.LogError(error.GenerateErrorReport());
GlobalFileLock -= 1;
}
// OnGUI provides a way to build a Unity GUI entirely within script.
- // Your GUI will be game-specific.
void OnGUI()
{
if (!PlayFabClientAPI.IsClientLoggedIn() && GUI.Button(new Rect(0, 0, 100, 30), "Login"))
Login();
if (PlayFabClientAPI.IsClientLoggedIn() && GUI.Button(new Rect(0, 0, 100, 30), "LogOut"))
PlayFabClientAPI.ForgetAllCredentials();
if (PlayFabClientAPI.IsClientLoggedIn() && GUI.Button(new Rect(100, 0, 100, 30), "(re)Load Files"))
LoadAllFiles();
if (PlayFabClientAPI.IsClientLoggedIn())
{
// Display existing files
_tempUpdates.Clear();
var index = 0;
foreach (var each in _entityFileJson)
{
GUI.Label(new Rect(100 * index, 60, 100, 30), each.Key);
var tempInput = _entityFileJson[each.Key];
var tempOutput = GUI.TextField(new Rect(100 * index, 90, 100, 30), tempInput);
if (tempInput != tempOutput)
_tempUpdates[each.Key] = tempOutput;
if (GUI.Button(new Rect(100 * index, 120, 100, 30), "Save " + each.Key))
UploadFile(each.Key);
index++;
}
// Apply any changes
foreach (var each in _tempUpdates)
_entityFileJson[each.Key] = each.Value;
// Add a new file
NewFileName = GUI.TextField(new Rect(100 * index, 60, 100, 30), NewFileName);
if (GUI.Button(new Rect(100 * index, 90, 100, 60), "Create " + NewFileName))
UploadFile(NewFileName);
}
}
void Login()
{
var request = new PlayFab.ClientModels.LoginWithCustomIDRequest
{
CustomId = SystemInfo.deviceUniqueIdentifier,
CreateAccount = true,
};
PlayFabClientAPI.LoginWithCustomID(request, OnLogin, OnSharedFailure);
}
void OnLogin(PlayFab.ClientModels.LoginResult result)
{
entityId = result.EntityToken.Entity.Id;
entityType = result.EntityToken.Entity.Type;
}
void LoadAllFiles()
{
if (GlobalFileLock != 0)
throw new Exception("This example overly restricts file operations for safety. Careful consideration must be made when doing multiple file operations in parallel to avoid conflict.");
GlobalFileLock += 1; // Start GetFiles
var request = new PlayFab.DataModels.GetFilesRequest { Entity = new PlayFab.DataModels.EntityKey { Id = entityId, Type = entityType } };
PlayFabDataAPI.GetFiles(request, OnGetFileMeta, OnSharedFailure);
}
void OnGetFileMeta(PlayFab.DataModels.GetFilesResponse result)
{
Debug.Log("Loading " + result.Metadata.Count + " files");
_entityFileJson.Clear();
foreach (var eachFilePair in result.Metadata)
{
_entityFileJson.Add(eachFilePair.Key, null);
GetActualFile(eachFilePair.Value);
}
GlobalFileLock -= 1; // Finish GetFiles
}
void GetActualFile(PlayFab.DataModels.GetFileMetadata fileData)
{
GlobalFileLock += 1; // Start Each SimpleGetCall
PlayFabHttp.SimpleGetCall(fileData.DownloadUrl,
result => { _entityFileJson[fileData.FileName] = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(result); GlobalFileLock -= 1; }, // Finish Each SimpleGetCall
error => { Debug.Log(error); }
);
}
void UploadFile(string fileName)
{
if (GlobalFileLock != 0)
throw new Exception("This example overly restricts file operations for safety. Careful consideration must be made when doing multiple file operations in parallel to avoid conflict.");
ActiveUploadFileName = fileName;
GlobalFileLock += 1; // Start InitiateFileUploads
var request = new PlayFab.DataModels.InitiateFileUploadsRequest
{
Entity = new PlayFab.DataModels.EntityKey { Id = entityId, Type = entityType },
FileNames = new List<string> { ActiveUploadFileName },
};
PlayFabDataAPI.InitiateFileUploads(request, OnInitFileUpload, OnInitFailed);
}
void OnInitFailed(PlayFabError error)
{
if (error.Error == PlayFabErrorCode.EntityFileOperationPending)
{
// This is an error you should handle when calling InitiateFileUploads, but your resolution path may vary
GlobalFileLock += 1; // Start AbortFileUploads
var request = new PlayFab.DataModels.AbortFileUploadsRequest
{
Entity = new PlayFab.DataModels.EntityKey { Id = entityId, Type = entityType },
FileNames = new List<string> { ActiveUploadFileName },
};
PlayFabDataAPI.AbortFileUploads(request, (result) => { GlobalFileLock -= 1; UploadFile(ActiveUploadFileName); }, OnSharedFailure); GlobalFileLock -= 1; // Finish AbortFileUploads
GlobalFileLock -= 1; // Failed InitiateFileUploads
}
else
OnSharedFailure(error);
}
void OnInitFileUpload(PlayFab.DataModels.InitiateFileUploadsResponse response)
{
string payloadStr;
if (!_entityFileJson.TryGetValue(ActiveUploadFileName, out payloadStr))
payloadStr = "{}";
var payload = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(payloadStr);
GlobalFileLock += 1; // Start SimplePutCall
PlayFabHttp.SimplePutCall(response.UploadDetails[0].UploadUrl,
payload,
FinalizeUpload,
error => { Debug.Log(error); }
);
GlobalFileLock -= 1; // Finish InitiateFileUploads
}
void FinalizeUpload(byte[] data)
{
GlobalFileLock += 1; // Start FinalizeFileUploads
var request = new PlayFab.DataModels.FinalizeFileUploadsRequest
{
Entity = new PlayFab.DataModels.EntityKey { Id = entityId, Type = entityType },
FileNames = new List<string> { ActiveUploadFileName },
};
PlayFabDataAPI.FinalizeFileUploads(request, OnUploadSuccess, OnSharedFailure);
GlobalFileLock -= 1; // Finish SimplePutCall
}
void OnUploadSuccess(PlayFab.DataModels.FinalizeFileUploadsResponse result)
{
Debug.Log("File upload success: " + ActiveUploadFileName);
GlobalFileLock -= 1; // Finish FinalizeFileUploads
}
}
#endif
Note
Each file action requires many steps and multiple API calls, so don't try to access the same file in multiple ways at the same time. If you are very careful, you might not need a locking mechanism. If you want to do something complicated, your locking mechanism may be much more complex.
Game Manager and entities
The Game Manager allows you to manipulate objects and files for players. The player overview shows both the title player and master player account information.
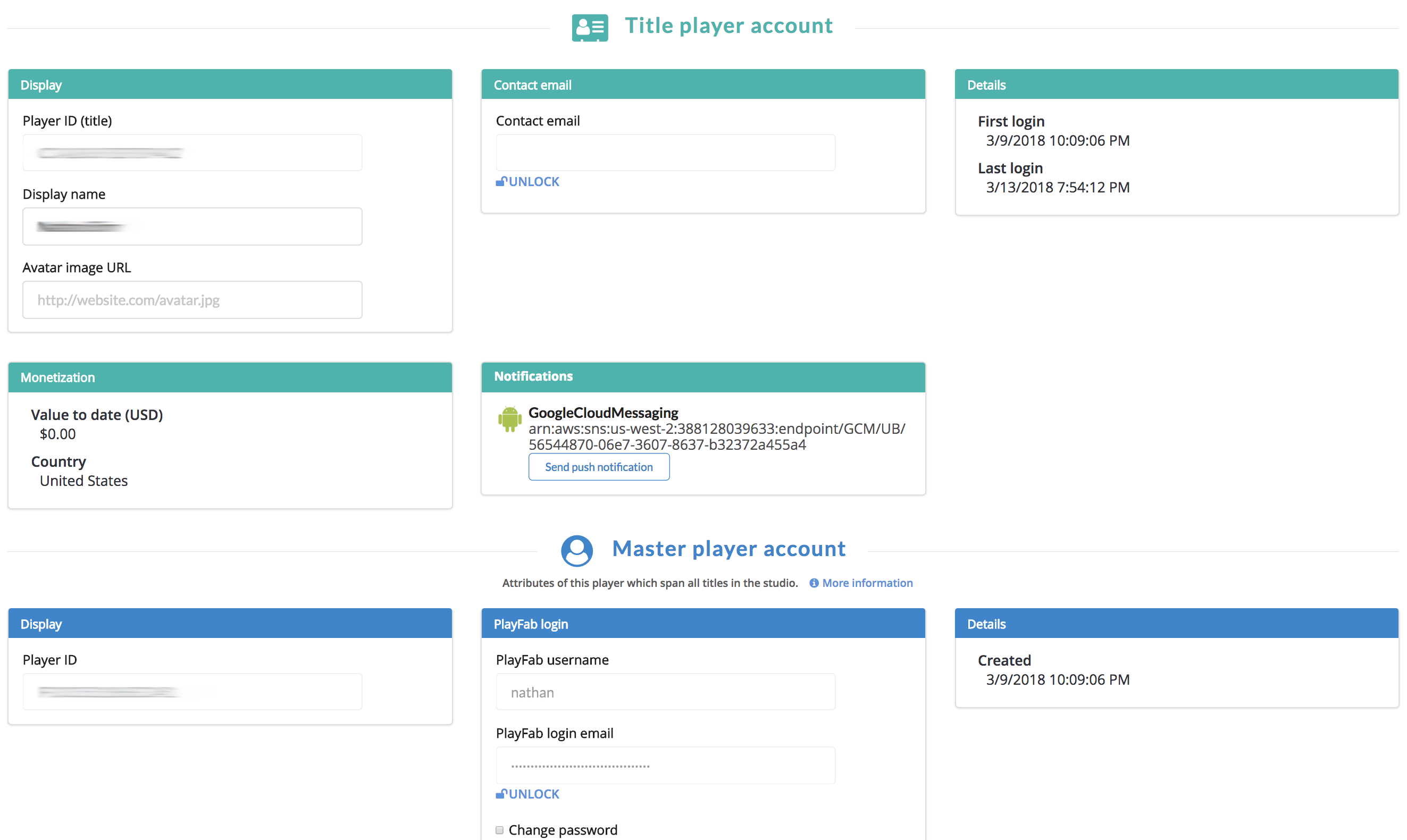
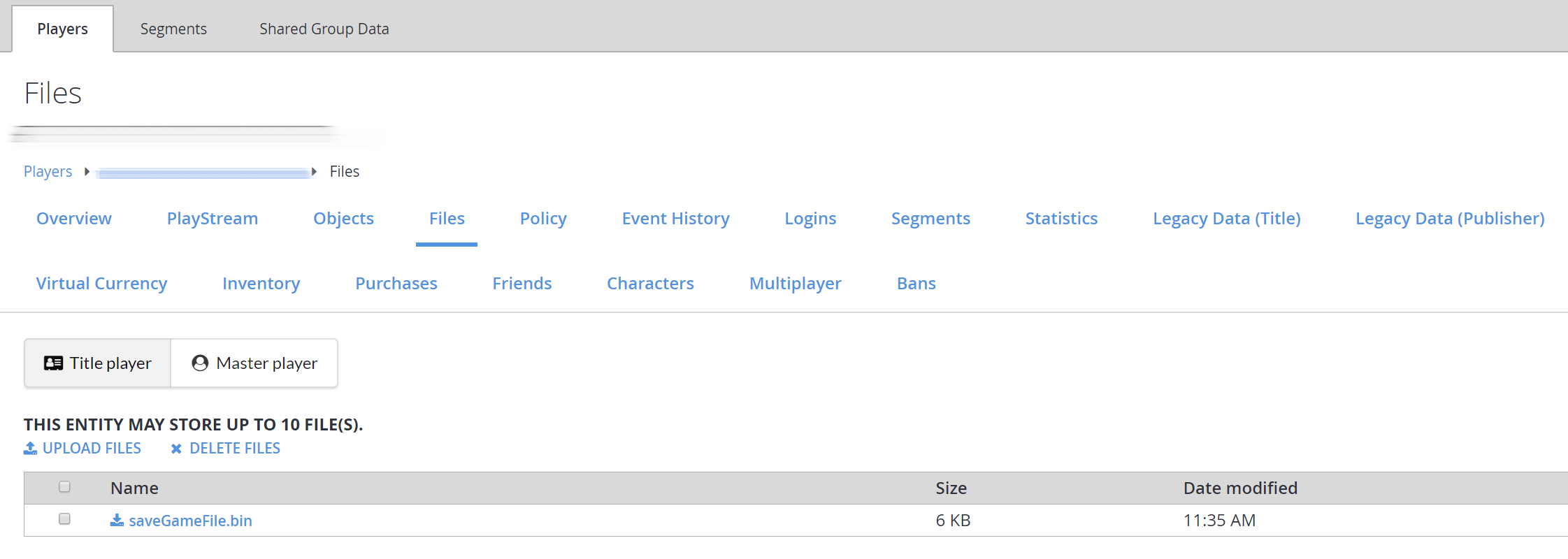
In addition, files and objects now have their own sections in the Players tab.
See also
Introducing Entities, Objects and Files on the PlayFab blog.