Target session initialization and QoS
This topic describes how a title confirms that enough players have joined and can connect when they're matched into a target session.
A group of players is matched into a target session by SmartMatch matchmaking. The title must take steps to confirm that enough players have joined so that they can successfully connect to one another if they need to. This process is known as target session initialization.
For games that use peer-to-peer network topologies, an important aspect of target session initialization is Quality of Service (QoS) measurement and evaluation. Associated operations are as follows.
- The measurement of latency and bandwidth between Xbox One (or later) consoles or between consoles and servers
- The evaluation of the resulting measurements to determine whether the network connection between nodes is good
The following flow chart illustrates how to implement the initialization of the target session and QoS operations.
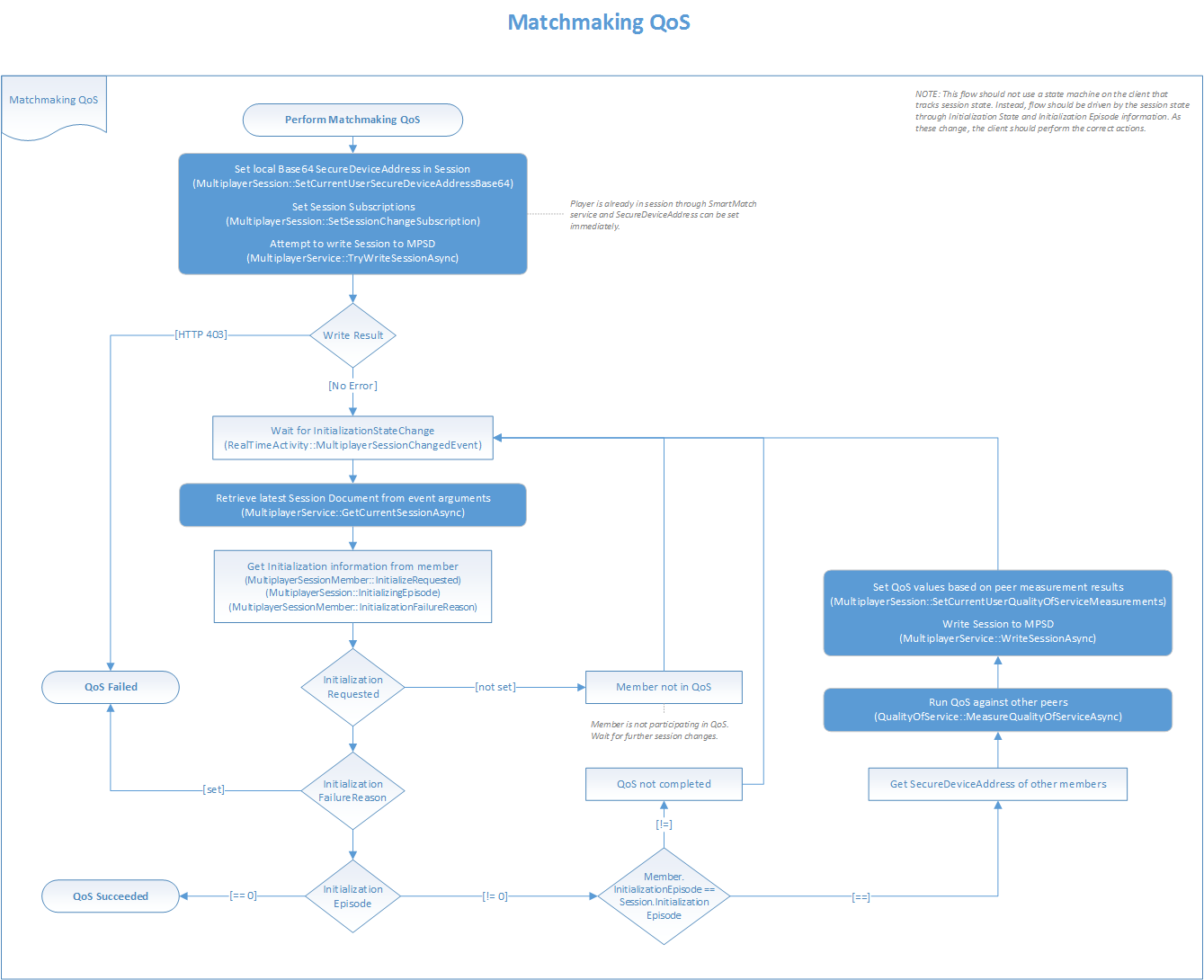
Managed initialization
Multiplayer Session Directory (MPSD) supports a feature called managed initialization, through which it coordinates the target session initialization process across the clients who are involved in a session. MPSD automatically tracks the initialization stages and the associated timeouts for the session. MPSD also evaluates the connectivity among clients, if needed. Managed initialization is represented by the XblMultiplayerInitializationStage enumeration.
Note
We highly recommend that your title use SmartMatch matchmaking to take advantage of the MPSD-managed initialization feature.
Managed initialization episodes and stages
A target session undergoes managed initialization whenever matchmaking adds new players to the session. SmartMatch adds session members as user state Reserved, meaning that each member takes up a slot but has not yet joined the session. Each group of new players triggers a new initialization episode.
When initialization is complete, each player either succeeds or fails the process. A player who succeeds in initializing can play by using the target session. A player who fails must be resubmitted to matchmaking to be matched into another session.
For cases where a session is submitted to matchmaking with the preserveSession parameter set to Always, the preexisting members of the session don't undergo initialization because MPSD assumes that they're properly set up.
Each managed initialization episode consists of the following stages.
- Joining: Session members write themselves to the session to move their user state from
ReservedtoActive. They can upload basic data, such as a secure device address. - Measurement: For peer-based topologies, session members measure QoS to one another, and then upload the results to the session.
- Evaluation: MPSD evaluates the results of the last two stages, and then determines whether the session or members have successfully initialized.
The title code operates on the session to advance each player (and therefore the session) through the joining and measurement phases. The title then can start play or go back to matchmaking after the evaluation stage has succeeded or failed.
Configuring the target session for initialization
The title can configure the managed initialization process by using constants in the target session that's being initialized. These constants are set under /constants/system in the session template with version 107. We recommend this template version.
You can make the following two types of configuration settings.
Settings that configure the managed initialization process as a whole
Settings that configure QoS requirements
For examples of session templates for common title scenarios, see Multiplayer session templates and Multiplayer Session Directory overview.
Note
If QoS requirements aren't defined in the target session initialization configuration, the measurement stage during initialization is skipped.
Configuring managed initialization as a whole
To control managed initialization overall, set the following fields.
The fields to set to control managed initialization are part of the /constants/system/memberInitialization object.
joinTimeout: Specifies how long MPSD waits for each member to join, after the initialization episode has begun. The default is 10 seconds.measurementTimeout: Specifies how long MPSD waits for each member to upload QoS measurement results, after the measurement stage has begun. The default is 30,000 seconds.membersNeededToStart: Specifies the number of members who must succeed at initialization for the first initialization episode to succeed. The default is 1.
Note
If this threshold isn't met, all members fail initialization.
Configuring QoS requirements
QoS is only needed during initialization if the title uses a peer-to-peer or peer-to-host topology. Each topology maps to a topology-specific constant under /constants/system/.
Configuring QoS requirements for peer-to-peer topology
Note
It's rare for titles to make QoS requirement settings for peer-to-peer topology. These settings are very restrictive and cause problems for players who have strict network address translations (NATs).
You can set peer-to-peer topology QoS requirements in the peerToPeerRequirements object.
Every client must be able to connect to every other client.
The peerToPeerRequirements object has the following pertinent fields.
latencyMaximum: Specifies the maximum latency between any two clientsbandwidthMinimum: Specifies the minimum bandwidth between any two clients
Configuring QoS requirements for peer-to-host topology
You can set peer-to-host topology QoS requirements in the peerToHostRequirements object.
Every client must be able to connect to a single common host.
If this object is configured and initialization succeeds, MPSD creates an initial list of clients that are potential hosts, known as the host candidates.
Set the following fields.
latencyMaximum: Specifies the maximum latency between each peer and the hostbandwidthDownMinimum: Specifies the minimum downstream bandwidth between each peer and the hostbandwidthUpMinimum: Specifies the minimum upstream bandwidth between each peer and the hosthostSelectionMetric: Specifies the metric that was used to select the host