View and manage the work exceptions log
Work exceptions are work-related errors that can occur during warehouse operations (such as discrepancies in inventory or missing goods at a given location). The system registers these exceptions in the work exceptions log, which lets managers track and diagnose issues related to warehouse workflows such as pick or pack procedures.
Example of how a worker can create a work exception
The Warehouse Management mobile app automatically creates exceptions during some types some workflows in response to certain events. For example, one possible way that a worker can trigger a work exception is by completing the following procedure to perform a short pick (assuming the required work record already exists):
- Open the Warehouse Management mobile app.
- Go to Outbound > Sales Picking.
- Enter the Work ID and select OK.
- Enter the Location and select OK.
- Select Short Pick.
- Specify the following values:
- The target license plate
- The quantity picked
- The reason for the short pick (for example, the item wasn't available at the expected location)
- Select OK and complete the work.
The short pick event generates a work exception for the specified Location.
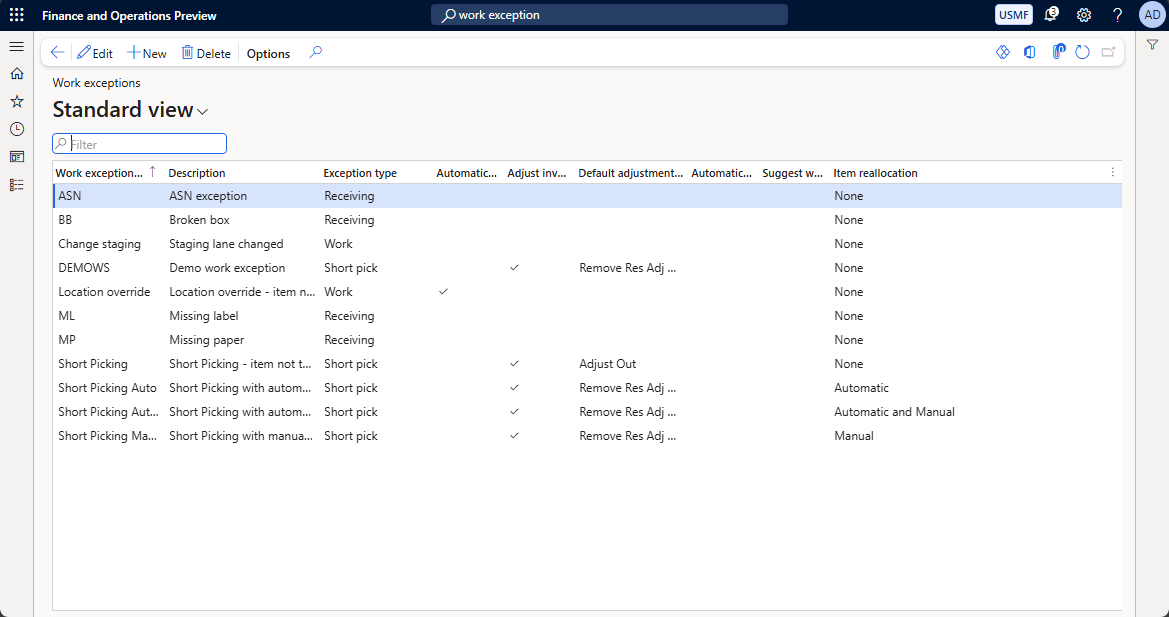
Configure behaviors for handling each type of work exception
You can configure the way the system should handle each relevant type of work exception. For example, you could set the system to adjust inventory at an affected license plate or allow automatic item reallocation.
To configure these system behaviors, follow these steps.
Go to Warehouse management > Setup > Work > Work exceptions.
Use the buttons on the Action Pane to add, edit, and delete rows as needed. To learn how to use the settings in each column, hover your mouse pointer over the column header to see a tooltip.
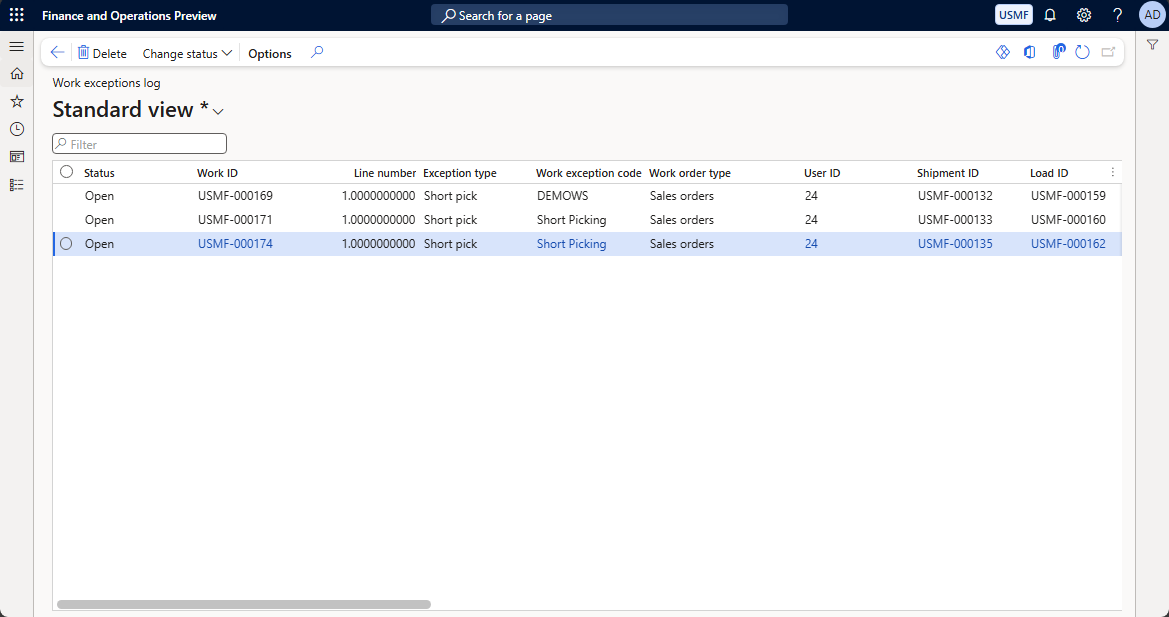
View the work exceptions log
To view the work exceptions log, go to Warehouse management > Work > Work exceptions log. You can sort and filter the list using the column headers or by entering a value in the Filter field and selecting where to search for it (for example by Status).
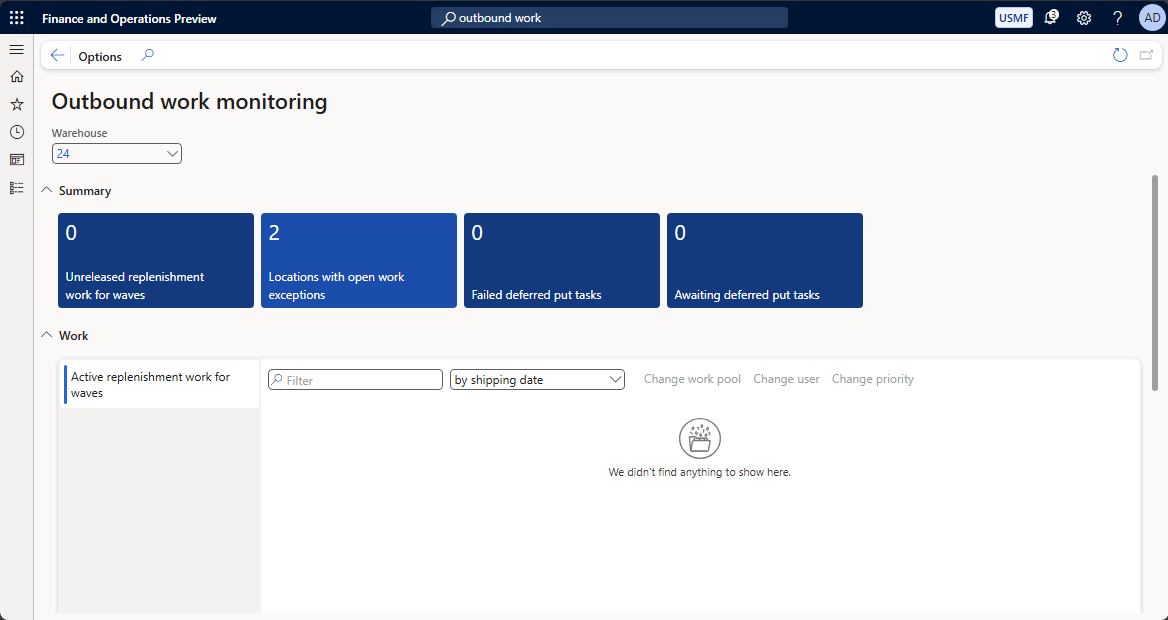
Work exceptions can also be shown on other pages, such as the Outbound work monitoring workspace (available at Warehouse management > Workspaces > Outbound work monitoring), which provides a tile that shows the number of Locations with open work exceptions. Select that tile to view and explore full details about the exceptions at each location.
Clean up the work exceptions log (preview)
[This section is prerelease documentation and is subject to change.]
Even after they're resolved, the system keeps all log entries until they are explicitly removed. Cleaning out old work exceptions helps make it easier for users to search for locations with open work exceptions and improves the performance of pages that show work exceptions.
The system provides a clean-up batch job to help you delete multiple entries in the work exceptions log once they're resolved or no longer necessary. When you set up the job, you'll set the criteria for selecting which entries should be deleted (for example, according to the status and/or age of each entry). When the job runs, it removes all work exceptions that match the criteria.
This feature requires Supply Chain Management version 10.0.43 or later.
Important
- This is a preview feature.
- Preview features aren’t meant for production use and might have restricted functionality. These features are subject to supplemental terms of use, and are available before an official release so that customers can get early access and provide feedback.
To clean up the work exceptions log, follow these steps.
- Go to Warehouse management > Periodic tasks > Clean up > Clean up work exceptions logs.
- In the dialog, expand the Parameters FastTab and make the following settings:
- The number of days to keep – Specify the age (in days) of the oldest entries to keep. Entries older than this will be deleted.
- Status – Select the status of the exception logs to delete (Open or Closed).
- Maximum cleanup records count – Specify the maximum number of records to delete. Setting a limit here can improve system performance by preventing too many records from being deleted in a single operation. (Default is 100,000.)
- On the Run in the background FastTab, set up batch, batch group, scheduling, and alert options as you require, just as you might do for other batch jobs in Supply Chain Management.
When the job finishes execution, the system shows a notification of how many records were removed.