Creación y ejecución de un flujo de trabajo de larga duración
Una de las características principales de Windows Workflow Foundation (WF) es la capacidad del entorno de ejecución de conservar y descargar flujos de trabajo inactivos en una base de datos. Los pasos que se describen en Procedimiento para ejecutar un flujo de trabajo demostraron los fundamentos del hospedaje de flujos de trabajo mediante una aplicación de consola. Se mostraron ejemplos de cómo iniciar flujos de trabajo, de los controladores de ciclo de vida de los flujos de trabajo y de los marcadores de reanudación. Para demostrar la persistencia del flujo de trabajo con efectividad, es necesario un host de flujo de trabajo más complejo que admita el inicio y la reanudación de varias instancias de flujo de trabajo. En este paso del tutorial se muestra cómo crear una aplicación host de Windows Forms que admita iniciar y reanudar varias instancias de flujo de trabajo o la persistencia del flujo de trabajo, y que proporcione una base para características avanzadas como el seguimiento y el control de versiones mostrado en los siguientes pasos del tutorial.
Nota
Este paso y los pasos siguientes del tutorial usan los tres tipos de flujo de trabajo de Procedimiento para crear un flujo de trabajo.
Para crear la base de datos de persistencia
Abra SQL Server Management Studio y conéctese al servidor local, por ejemplo, .\SQLEXPRESS. Haga clic con el botón derecho en el nodo Bases de datos en el servidor local y seleccione Nueva base de datos. Asigne a la nueva base de datos el nombre WF45GettingStartedTutorial, acepte el resto de valores y seleccione Aceptar.
Nota
Asegúrese de que tiene el permiso Crear base de datos en el servidor local antes de crear la base de datos.
Elija Abrir, Archivo en el menú Archivo. Vaya a la carpeta siguiente: C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v4.0.30319\sql\en
Seleccione los dos archivos siguientes y haga clic en Abrir.
SqlWorkflowInstanceStoreLogic.sql
SqlWorkflowInstanceStoreSchema.sql
Elija SqlWorkflowInstanceStoreSchema.sql en el menú Ventana. Asegúrese de que esté seleccionado WF45GettingStartedTutorial en la lista desplegable Bases de datos disponibles y elija Ejecutar en el menú Consulta.
Elija SqlWorkflowInstanceStoreLogic.sql en el menú Ventana. Asegúrese de que esté seleccionado WF45GettingStartedTutorial en la lista desplegable Bases de datos disponibles y elija Ejecutar en el menú Consulta.
Advertencia
Es importante realizar los dos pasos anteriores en el orden correcto. Si las consultas se ejecutan de manera desordenada, aparecerán errores y la base de datos de persistencia no se configurará correctamente.
Para agregar la referencia a los ensamblados de DurableInstancing
Haga clic con el botón derecho en NumberGuessWorkflowHost en el Explorador de soluciones y seleccione Agregar referencia.
Seleccione Ensamblados en la lista Agregar referencia y escriba
DurableInstancingen el cuadro Buscar ensamblados. Esto filtrará los ensamblados y simplificará la selección de las referencias deseadas.Active la casilla situada junto a System.Activities.DurableInstancing y System.Runtime.DurableInstancing de la lista Resultados de la búsqueda y haga clic en Aceptar.
Para crear el formulario de host de flujo de trabajo
Haga clic con el botón derecho en NumberGuessWorkflowHost en el Explorador de soluciones y elija Agregar, Nuevo elemento.
En la lista de plantillas Instalado, elija Windows Forms, escriba
WorkflowHostFormen el cuadro Nombre y haga clic en Agregar.Configure las siguientes propiedades en el formulario.
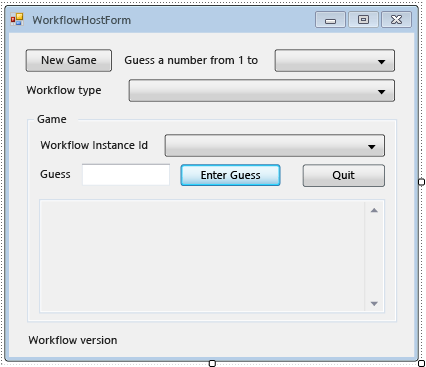
Propiedad Valor FormBorderStyle FixedSingle MaximizeBox False Size 400, 420 Agregue los siguientes controles al formulario en el orden especificado y configure las propiedades como dirigidas.
Control Propiedad: Valor Botón Name: NewGame
Location: 13, 13
Size: 75, 23
Text: New GameLabel Location: 94, 18
Text: Guess a number from 1 toComboBox Name: NumberRange
DropDownStyle: DropDownList
Items: 10, 100, 1000
Location: 228, 12
Size: 143, 21Label Location: 13, 43
Text: Workflow typeComboBox Name: WorkflowType
DropDownStyle: DropDownList
Items: StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow, FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow, SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow
Location: 94, 40
Size: 277, 21Label Name: WorkflowVersion
Location: 13, 362
Text: Workflow versionGroupBox Location: 13, 67
Size: 358, 287
Text: GameNota
Al agregar los siguientes controles, colóquelos en el elemento GroupBox.
Control Propiedad: Valor Label Location: 7, 20
Text: Workflow Instance IdComboBox Name: InstanceId
DropDownStyle: DropDownList
Location: 121, 17
Size: 227, 21Label Location: 7, 47
Text: GuessTextBox Name: Guess
Location: 50, 44
Size: 65, 20Botón Name: EnterGuess
Location: 121, 42
Size: 75, 23
Text: Enter GuessBotón Name: QuitGame
Location: 274, 42
Size: 75, 23
Text: QuitTextBox Name: WorkflowStatus
Location: 10, 73
Multiline: True
ReadOnly: True
ScrollBars: Vertical
Size: 338, 208Establezca la propiedad AcceptButton del formulario en EnterGuess.
En el siguiente ejemplo se muestra el formulario completado.
Para agregar las propiedades y métodos del asistente del formulario
Los pasos de esta sección agregan propiedades y métodos del asistente a la clase de formulario que configuran la interfaz de usuario del formulario para que se admita la ejecución y la reanudación de flujos de trabajo de acierto de números.
Haga clic con el botón derecho en WorkflowHostForm en Explorador de soluciones y elija Ver código.
Agregue las siguientes instrucciones
using(oImports) al principio del archivo con las demás instruccionesusing(oImports).Imports System.Activities Imports System.Activities.DurableInstancing Imports System.Data.SqlClient Imports System.IO Imports System.Windows.Formsusing System.Activities; using System.Activities.DurableInstancing; using System.Data.SqlClient; using System.IO; using System.Windows.Forms;Agregue las siguientes declaraciones del miembro a la clase WorkflowHostForm.
Importante
Microsoft recomienda usar el flujo de autenticación más seguro disponible. Si se conecta a Azure SQL, el método de autenticación recomendado es Identidades administradas para recursos de Azure.
Const connectionString = "Server=.\SQLEXPRESS;Initial Catalog=WF45GettingStartedTutorial;Integrated Security=SSPI" Dim store As SqlWorkflowInstanceStore Dim workflowStarting As Booleanconst string connectionString = "Server=.\\SQLEXPRESS;Initial Catalog=WF45GettingStartedTutorial;Integrated Security=SSPI"; SqlWorkflowInstanceStore store; bool workflowStarting;Nota:
Si la cadena de conexión es diferente, actualice
connectionStringpara consultar la base de datos.Agregue una propiedad
WorkflowInstanceIda la claseWorkflowFormHost.Public ReadOnly Property WorkflowInstanceId() As Guid Get If InstanceId.SelectedIndex = -1 Then Return Guid.Empty Else Return New Guid(InstanceId.SelectedItem.ToString()) End If End Get End Propertypublic Guid WorkflowInstanceId { get { return InstanceId.SelectedIndex == -1 ? Guid.Empty : (Guid)InstanceId.SelectedItem; } }El cuadro combinado
InstanceIdmuestra una lista de identificadores de instancia de flujo de trabajo persistentes y la propiedadWorkflowInstanceIddevuelve el flujo de trabajo seleccionado actualmente.Agregue un controlador para el evento del formulario
Load. Para agregar el controlador, cambie a Vista de diseño para el formulario, haga clic en el icono Eventos en la parte superior de la ventana Propiedades y haga doble clic en Cargar.Private Sub WorkflowHostForm_Load(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Me.Load End Subprivate void WorkflowHostForm_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) { }Agregue el siguiente código a
WorkflowHostForm_Load.' Initialize the store and configure it so that it can be used for ' multiple WorkflowApplication instances. store = New SqlWorkflowInstanceStore(connectionString) WorkflowApplication.CreateDefaultInstanceOwner(store, Nothing, WorkflowIdentityFilter.Any) ' Set default ComboBox selections. NumberRange.SelectedIndex = 0 WorkflowType.SelectedIndex = 0 ListPersistedWorkflows()// Initialize the store and configure it so that it can be used for // multiple WorkflowApplication instances. store = new SqlWorkflowInstanceStore(connectionString); WorkflowApplication.CreateDefaultInstanceOwner(store, null, WorkflowIdentityFilter.Any); // Set default ComboBox selections. NumberRange.SelectedIndex = 0; WorkflowType.SelectedIndex = 0; ListPersistedWorkflows();Cuando el formulario se carga, se configura
SqlWorkflowInstanceStore, los intervalos y los cuadros combinados de tipo de flujo de trabajo se establecen en valores predeterminados y las instancias de flujo de trabajo persistentes se agregan al cuadro combinadoInstanceId.Agregue un controlador
SelectedIndexChangedparaInstanceId. Para agregar el controlador, cambie a Vista de diseño para el formulario, seleccione el cuadro combinadoInstanceId, haga clic en el icono Eventos en la parte superior de la ventana Propiedades y haga doble clic en SelectedIndexChanged.Private Sub InstanceId_SelectedIndexChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles InstanceId.SelectedIndexChanged End Subprivate void InstanceId_SelectedIndexChanged(object sender, EventArgs e) { }Agregue el siguiente código a
InstanceId_SelectedIndexChanged. Siempre que el usuario selecciona un flujo de trabajo mediante el cuadro combinado, este controlador actualiza la ventana de estado.If InstanceId.SelectedIndex = -1 Then Return End If ' Clear the status window. WorkflowStatus.Clear() ' Get the workflow version and display it. ' If the workflow is just starting then this info will not ' be available in the persistence store so do not try and retrieve it. If Not workflowStarting Then Dim instance As WorkflowApplicationInstance = _ WorkflowApplication.GetInstance(WorkflowInstanceId, store) WorkflowVersion.Text = _ WorkflowVersionMap.GetIdentityDescription(instance.DefinitionIdentity) ' Unload the instance. instance.Abandon() End Ifif (InstanceId.SelectedIndex == -1) { return; } // Clear the status window. WorkflowStatus.Clear(); // Get the workflow version and display it. // If the workflow is just starting then this info will not // be available in the persistence store so do not try and retrieve it. if (!workflowStarting) { WorkflowApplicationInstance instance = WorkflowApplication.GetInstance(this.WorkflowInstanceId, store); WorkflowVersion.Text = WorkflowVersionMap.GetIdentityDescription(instance.DefinitionIdentity); // Unload the instance. instance.Abandon(); }Agregue el siguiente método
ListPersistedWorkflowsa la clase de formulario.Private Sub ListPersistedWorkflows() Using localCon As New SqlConnection(connectionString) Dim localCmd As String = _ "SELECT [InstanceId] FROM [System.Activities.DurableInstancing].[Instances] ORDER BY [CreationTime]" Dim cmd As SqlCommand = localCon.CreateCommand() cmd.CommandText = localCmd localCon.Open() Using reader As SqlDataReader = cmd.ExecuteReader(CommandBehavior.CloseConnection) While (reader.Read()) ' Get the InstanceId of the persisted Workflow. Dim id As Guid = Guid.Parse(reader(0).ToString()) InstanceId.Items.Add(id) End While End Using End Using End Subusing (var localCon = new SqlConnection(connectionString)) { string localCmd = "SELECT [InstanceId] FROM [System.Activities.DurableInstancing].[Instances] ORDER BY [CreationTime]"; SqlCommand cmd = localCon.CreateCommand(); cmd.CommandText = localCmd; localCon.Open(); using (SqlDataReader reader = cmd.ExecuteReader(CommandBehavior.CloseConnection)) { while (reader.Read()) { // Get the InstanceId of the persisted Workflow. Guid id = Guid.Parse(reader[0].ToString()); InstanceId.Items.Add(id); } } }ListPersistedWorkflowsconsulta el almacén de instancias con respecto a las instancias de flujo de trabajo persistentes y agrega los identificadores de instancia al cuadro combinadocboInstanceId.Agregue el siguiente método
UpdateStatusy el delegado correspondiente a la clase de formulario. Este método actualiza la ventana de estado en el formulario con el estado del flujo de trabajo en funcionamiento.Private Delegate Sub UpdateStatusDelegate(msg As String) Public Sub UpdateStatus(msg As String) ' We may be on a different thread so we need to ' make this call using BeginInvoke. If InvokeRequired Then BeginInvoke(New UpdateStatusDelegate(AddressOf UpdateStatus), msg) Else If Not msg.EndsWith(vbCrLf) Then msg = msg & vbCrLf End If WorkflowStatus.AppendText(msg) ' Ensure that the newly added status is visible. WorkflowStatus.SelectionStart = WorkflowStatus.Text.Length WorkflowStatus.ScrollToCaret() End If End Subprivate delegate void UpdateStatusDelegate(string msg); public void UpdateStatus(string msg) { // We may be on a different thread so we need to // make this call using BeginInvoke. if (InvokeRequired) { BeginInvoke(new UpdateStatusDelegate(UpdateStatus), msg); } else { if (!msg.EndsWith("\r\n")) { msg += "\r\n"; } WorkflowStatus.AppendText(msg); WorkflowStatus.SelectionStart = WorkflowStatus.Text.Length; WorkflowStatus.ScrollToCaret(); } }Agregue el siguiente método
GameOvery el delegado correspondiente a la clase de formulario. Cuando se completa un flujo de trabajo, este método actualiza la interfaz de usuario del formulario mediante la eliminación del identificador de instancia del flujo de trabajo completado en el cuadro combinado InstanceId.Private Delegate Sub GameOverDelegate() Private Sub GameOver() If InvokeRequired Then BeginInvoke(New GameOverDelegate(AddressOf GameOver)) Else ' Remove this instance from the InstanceId combo box. InstanceId.Items.Remove(InstanceId.SelectedItem) InstanceId.SelectedIndex = -1 End If End Subprivate delegate void GameOverDelegate(); private void GameOver() { if (InvokeRequired) { BeginInvoke(new GameOverDelegate(GameOver)); } else { // Remove this instance from the combo box. InstanceId.Items.Remove(InstanceId.SelectedItem); InstanceId.SelectedIndex = -1; } }
Para configurar el almacén de instancias, los controladores de ciclo de vida del flujo de trabajo y las extensiones
Agregue un método
ConfigureWorkflowApplicationa la clase de formulario.Private Sub ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp As WorkflowApplication) End Subprivate void ConfigureWorkflowApplication(WorkflowApplication wfApp) { }Este método configura
WorkflowApplication, agrega las extensiones deseadas y agrega los controladores para los eventos de ciclo de vida de flujo de trabajo.En
ConfigureWorkflowApplication, especifiqueSqlWorkflowInstanceStorepara laWorkflowApplication.' Configure the persistence store. wfApp.InstanceStore = store// Configure the persistence store. wfApp.InstanceStore = store;A continuación, cree una instancia
StringWritery agréguela a la colecciónExtensionsdeWorkflowApplication. Cuando se agregaStringWritera las extensiones, captura toda la salida de actividadWriteLine. Cuando el flujo de trabajo se vuelve inactivo, el resultado deWriteLinepuede extraerse desdeStringWritery mostrarse en el formulario.' Add a StringWriter to the extensions. This captures the output ' from the WriteLine activities so we can display it in the form. Dim sw As New StringWriter() wfApp.Extensions.Add(sw)// Add a StringWriter to the extensions. This captures the output // from the WriteLine activities so we can display it in the form. var sw = new StringWriter(); wfApp.Extensions.Add(sw);Agregue el controlador siguiente para el evento
Completed. Cuando un flujo de trabajo se ha completado con éxito, el número de intentos que han sido necesarios para acertar el número se muestra en la ventana de estado. Si el flujo de trabajo finaliza, se muestra la información de excepción que ha provocado la finalización. Al final del controlador se llama al métodoGameOver, que quita el flujo de trabajo completado de la lista de flujos de trabajo.wfApp.Completed = _ Sub(e As WorkflowApplicationCompletedEventArgs) If e.CompletionState = ActivityInstanceState.Faulted Then UpdateStatus($"Workflow Terminated. Exception: {e.TerminationException.GetType().FullName}{vbCrLf}{e.TerminationException.Message}") ElseIf e.CompletionState = ActivityInstanceState.Canceled Then UpdateStatus("Workflow Canceled.") Else Dim turns As Integer = Convert.ToInt32(e.Outputs("Turns")) UpdateStatus($"Congratulations, you guessed the number in {turns} turns.") End If GameOver() End SubwfApp.Completed = delegate(WorkflowApplicationCompletedEventArgs e) { if (e.CompletionState == ActivityInstanceState.Faulted) { UpdateStatus($"Workflow Terminated. Exception: {e.TerminationException.GetType().FullName}\r\n{e.TerminationException.Message}"); } else if (e.CompletionState == ActivityInstanceState.Canceled) { UpdateStatus("Workflow Canceled."); } else { int turns = Convert.ToInt32(e.Outputs["Turns"]); UpdateStatus($"Congratulations, you guessed the number in {turns} turns."); } GameOver(); };Agregue los siguientes controladores
AbortedyOnUnhandledException. No se llama al método deGameOverdesde el controladorAbortedporque cuando una instancia de flujo de trabajo se anula, no se finaliza y es posible reanudar la instancia posteriormente.wfApp.Aborted = _ Sub(e As WorkflowApplicationAbortedEventArgs) UpdateStatus($"Workflow Aborted. Exception: {e.Reason.GetType().FullName}{vbCrLf}{e.Reason.Message}") End Sub wfApp.OnUnhandledException = _ Function(e As WorkflowApplicationUnhandledExceptionEventArgs) UpdateStatus($"Unhandled Exception: {e.UnhandledException.GetType().FullName}{vbCrLf}{e.UnhandledException.Message}") GameOver() Return UnhandledExceptionAction.Terminate End FunctionwfApp.Aborted = delegate(WorkflowApplicationAbortedEventArgs e) { UpdateStatus($"Workflow Aborted. Exception: {e.Reason.GetType().FullName}\r\n{e.Reason.Message}"); }; wfApp.OnUnhandledException = delegate(WorkflowApplicationUnhandledExceptionEventArgs e) { UpdateStatus($"Unhandled Exception: {e.UnhandledException.GetType().FullName}\r\n{e.UnhandledException.Message}"); GameOver(); return UnhandledExceptionAction.Terminate; };Agregue el siguiente controlador
PersistableIdle. Este controlador recupera la extensiónStringWriterque se había agregado, extrae la salida de las actividades deWriteLiney la muestra en la ventana de estado.wfApp.PersistableIdle = _ Function(e As WorkflowApplicationIdleEventArgs) ' Send the current WriteLine outputs to the status window. Dim writers = e.GetInstanceExtensions(Of StringWriter)() For Each writer In writers UpdateStatus(writer.ToString()) Next Return PersistableIdleAction.Unload End FunctionwfApp.PersistableIdle = delegate(WorkflowApplicationIdleEventArgs e) { // Send the current WriteLine outputs to the status window. var writers = e.GetInstanceExtensions<StringWriter>(); foreach (var writer in writers) { UpdateStatus(writer.ToString()); } return PersistableIdleAction.Unload; };La enumeración PersistableIdleAction tiene tres valores: None, Persist y Unload. Persist hace que el flujo de trabajo sea persistente pero no hace que se descargue. Unload hace que el flujo de trabajo sea persistente y se descargue.
El siguiente ejemplo es el método
ConfigureWorkflowApplicationcompletado.Private Sub ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp As WorkflowApplication) ' Configure the persistence store. wfApp.InstanceStore = store ' Add a StringWriter to the extensions. This captures the output ' from the WriteLine activities so we can display it in the form. Dim sw As New StringWriter() wfApp.Extensions.Add(sw) wfApp.Completed = _ Sub(e As WorkflowApplicationCompletedEventArgs) If e.CompletionState = ActivityInstanceState.Faulted Then UpdateStatus($"Workflow Terminated. Exception: {e.TerminationException.GetType().FullName}{vbCrLf}{e.TerminationException.Message}") ElseIf e.CompletionState = ActivityInstanceState.Canceled Then UpdateStatus("Workflow Canceled.") Else Dim turns As Integer = Convert.ToInt32(e.Outputs("Turns")) UpdateStatus($"Congratulations, you guessed the number in {turns} turns.") End If GameOver() End Sub wfApp.Aborted = _ Sub(e As WorkflowApplicationAbortedEventArgs) UpdateStatus($"Workflow Aborted. Exception: {e.Reason.GetType().FullName}{vbCrLf}{e.Reason.Message}") End Sub wfApp.OnUnhandledException = _ Function(e As WorkflowApplicationUnhandledExceptionEventArgs) UpdateStatus($"Unhandled Exception: {e.UnhandledException.GetType().FullName}{vbCrLf}{e.UnhandledException.Message}") GameOver() Return UnhandledExceptionAction.Terminate End Function wfApp.PersistableIdle = _ Function(e As WorkflowApplicationIdleEventArgs) ' Send the current WriteLine outputs to the status window. Dim writers = e.GetInstanceExtensions(Of StringWriter)() For Each writer In writers UpdateStatus(writer.ToString()) Next Return PersistableIdleAction.Unload End Function End Subprivate void ConfigureWorkflowApplication(WorkflowApplication wfApp) { // Configure the persistence store. wfApp.InstanceStore = store; // Add a StringWriter to the extensions. This captures the output // from the WriteLine activities so we can display it in the form. var sw = new StringWriter(); wfApp.Extensions.Add(sw); wfApp.Completed = delegate(WorkflowApplicationCompletedEventArgs e) { if (e.CompletionState == ActivityInstanceState.Faulted) { UpdateStatus($"Workflow Terminated. Exception: {e.TerminationException.GetType().FullName}\r\n{e.TerminationException.Message}"); } else if (e.CompletionState == ActivityInstanceState.Canceled) { UpdateStatus("Workflow Canceled."); } else { int turns = Convert.ToInt32(e.Outputs["Turns"]); UpdateStatus($"Congratulations, you guessed the number in {turns} turns."); } GameOver(); }; wfApp.Aborted = delegate(WorkflowApplicationAbortedEventArgs e) { UpdateStatus($"Workflow Aborted. Exception: {e.Reason.GetType().FullName}\r\n{e.Reason.Message}"); }; wfApp.OnUnhandledException = delegate(WorkflowApplicationUnhandledExceptionEventArgs e) { UpdateStatus($"Unhandled Exception: {e.UnhandledException.GetType().FullName}\r\n{e.UnhandledException.Message}"); GameOver(); return UnhandledExceptionAction.Terminate; }; wfApp.PersistableIdle = delegate(WorkflowApplicationIdleEventArgs e) { // Send the current WriteLine outputs to the status window. var writers = e.GetInstanceExtensions<StringWriter>(); foreach (var writer in writers) { UpdateStatus(writer.ToString()); } return PersistableIdleAction.Unload; }; }
Para habilitar el inicio y la reanudación de varios tipos de flujo de trabajo
Para reanudar una instancia de flujo de trabajo, el host tiene que proporcionar la definición de flujo de trabajo. En este tutorial hay tres tipos de flujo de trabajo, y los pasos siguientes del tutorial presentan varias versiones de estos tipos. WorkflowIdentity proporciona una manera para que una aplicación de host asocie información de identificación con una instancia de flujo de trabajo persistente. Los pasos de esta sección muestran cómo crear una clase de utilidad para contribuir a la asignación de la identidad de flujo de trabajo desde una instancia de flujo de trabajo persistente a la definición de flujo de trabajo correspondiente. Para obtener más información sobre WorkflowIdentity y el control de versiones, consulte Usar WorkflowIdentity y el control de versiones.
Haga clic con el botón derecho en NumberGuessWorkflowHost en el Explorador de soluciones y elija Agregar, Clase. Escriba
WorkflowVersionMapen el cuadro Nombre y haga clic en Agregar.Agregue las siguientes instrucciones
using(oImports) al principio del archivo con las demás instruccionesusingoImports.Imports System.Activities Imports NumberGuessWorkflowActivitiesusing System.Activities; using NumberGuessWorkflowActivities;Reemplace la declaración de clase
WorkflowVersionMappor la declaración siguiente.Public Module WorkflowVersionMap Dim map As Dictionary(Of WorkflowIdentity, Activity) ' Current version identities. Public StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity As WorkflowIdentity Public FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity As WorkflowIdentity Public SequentialNumberGuessIdentity As WorkflowIdentity Sub New() map = New Dictionary(Of WorkflowIdentity, Activity) ' Add the current workflow version identities. StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity = New WorkflowIdentity With { .Name = "StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow", .Version = New Version(1, 0, 0, 0) } FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity = New WorkflowIdentity With { .Name = "FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow", .Version = New Version(1, 0, 0, 0) } SequentialNumberGuessIdentity = New WorkflowIdentity With { .Name = "SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow", .Version = New Version(1, 0, 0, 0) } map.Add(StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity, New StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow()) map.Add(FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity, New FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow()) map.Add(SequentialNumberGuessIdentity, New SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow()) End Sub Public Function GetWorkflowDefinition(identity As WorkflowIdentity) As Activity Return map(identity) End Function Public Function GetIdentityDescription(identity As WorkflowIdentity) As String Return identity.ToString() End Function End Modulepublic static class WorkflowVersionMap { static Dictionary<WorkflowIdentity, Activity> map; // Current version identities. static public WorkflowIdentity StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity; static public WorkflowIdentity FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity; static public WorkflowIdentity SequentialNumberGuessIdentity; static WorkflowVersionMap() { map = new Dictionary<WorkflowIdentity, Activity>(); // Add the current workflow version identities. StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity = new WorkflowIdentity { Name = "StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow", Version = new Version(1, 0, 0, 0) }; FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity = new WorkflowIdentity { Name = "FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow", Version = new Version(1, 0, 0, 0) }; SequentialNumberGuessIdentity = new WorkflowIdentity { Name = "SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow", Version = new Version(1, 0, 0, 0) }; map.Add(StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity, new StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow()); map.Add(FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity, new FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow()); map.Add(SequentialNumberGuessIdentity, new SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow()); } public static Activity GetWorkflowDefinition(WorkflowIdentity identity) { return map[identity]; } public static string GetIdentityDescription(WorkflowIdentity identity) { return identity.ToString(); } }WorkflowVersionMapcontiene tres identidades de flujo de trabajo que se asignan a las tres definiciones de flujo de trabajo de este tutorial y se usan en las secciones siguientes al iniciar o al reanudar los flujos de trabajo.
Para iniciar un nuevo flujo de trabajo
Agregue un controlador
ClickparaNewGame. Para agregar el controlador, cambie a Vista de diseño para el formulario y haga doble clic enNewGame. Se agrega un controladorNewGame_Clicky la vista cambia a vista de código para el formulario. Siempre que el usuario haga clic en este botón se inicia un nuevo flujo de trabajo.Private Sub NewGame_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles NewGame.Click End Subprivate void NewGame_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { }Agregue el código siguiente al controlador de clic. Este código crea un diccionario de argumentos de entrada para el flujo de trabajo, por clave de nombre de argumento. Este diccionario tiene una entrada que contiene el intervalo del número generado aleatoriamente recuperado en el cuadro combinado del intervalo.
Dim inputs As New Dictionary(Of String, Object)() inputs.Add("MaxNumber", Convert.ToInt32(NumberRange.SelectedItem))var inputs = new Dictionary<string, object>(); inputs.Add("MaxNumber", Convert.ToInt32(NumberRange.SelectedItem));A continuación, agregue el siguiente código que inicia el flujo de trabajo. ph x="1" /> y la definición de flujo de trabajo correspondiente al tipo de flujo de trabajo seleccionado se recuperan mediante la clase del asistente
WorkflowVersionMap. A continuación, se crea una nueva instancia deWorkflowApplicationmediante la definición de flujo de trabajo,WorkflowIdentity, y el diccionario de argumentos de entrada.Dim identity As WorkflowIdentity = Nothing Select Case WorkflowType.SelectedItem.ToString() Case "SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow" identity = WorkflowVersionMap.SequentialNumberGuessIdentity Case "StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow" identity = WorkflowVersionMap.StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity Case "FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow" identity = WorkflowVersionMap.FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity End Select Dim wf As Activity = WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(identity) Dim wfApp = New WorkflowApplication(wf, inputs, identity)WorkflowIdentity identity = null; switch (WorkflowType.SelectedItem.ToString()) { case "SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow": identity = WorkflowVersionMap.SequentialNumberGuessIdentity; break; case "StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow": identity = WorkflowVersionMap.StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity; break; case "FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow": identity = WorkflowVersionMap.FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity; break; }; Activity wf = WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(identity); WorkflowApplication wfApp = new WorkflowApplication(wf, inputs, identity);A continuación, agregue el siguiente código que agrega el flujo de trabajo a la lista de flujos de trabajo y muestra la información de la versión del flujo de trabajo en el formulario.
' Add the workflow to the list and display the version information. workflowStarting = True InstanceId.SelectedIndex = InstanceId.Items.Add(wfApp.Id) WorkflowVersion.Text = identity.ToString() workflowStarting = False// Add the workflow to the list and display the version information. workflowStarting = true; InstanceId.SelectedIndex = InstanceId.Items.Add(wfApp.Id); WorkflowVersion.Text = identity.ToString(); workflowStarting = false;Llame a
ConfigureWorkflowApplicationpara configurar el almacén de instancias, las extensiones y los controladores de ciclo de vida del flujo de trabajo para esta instanciaWorkflowApplication.' Configure the instance store, extensions, and ' workflow lifecycle handlers. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp)// Configure the instance store, extensions, and // workflow lifecycle handlers. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp);Por último, llame a
Run.' Start the workflow. wfApp.Run()// Start the workflow. wfApp.Run();El siguiente ejemplo es el controlador
NewGame_Clickcompletado.Private Sub NewGame_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles NewGame.Click ' Start a new workflow. Dim inputs As New Dictionary(Of String, Object)() inputs.Add("MaxNumber", Convert.ToInt32(NumberRange.SelectedItem)) Dim identity As WorkflowIdentity = Nothing Select Case WorkflowType.SelectedItem.ToString() Case "SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow" identity = WorkflowVersionMap.SequentialNumberGuessIdentity Case "StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow" identity = WorkflowVersionMap.StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity Case "FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow" identity = WorkflowVersionMap.FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity End Select Dim wf As Activity = WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(identity) Dim wfApp = New WorkflowApplication(wf, inputs, identity) ' Add the workflow to the list and display the version information. workflowStarting = True InstanceId.SelectedIndex = InstanceId.Items.Add(wfApp.Id) WorkflowVersion.Text = identity.ToString() workflowStarting = False ' Configure the instance store, extensions, and ' workflow lifecycle handlers. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp) ' Start the workflow. wfApp.Run() End Subprivate void NewGame_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { var inputs = new Dictionary<string, object>(); inputs.Add("MaxNumber", Convert.ToInt32(NumberRange.SelectedItem)); WorkflowIdentity identity = null; switch (WorkflowType.SelectedItem.ToString()) { case "SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow": identity = WorkflowVersionMap.SequentialNumberGuessIdentity; break; case "StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow": identity = WorkflowVersionMap.StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity; break; case "FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow": identity = WorkflowVersionMap.FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity; break; }; Activity wf = WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(identity); var wfApp = new WorkflowApplication(wf, inputs, identity); // Add the workflow to the list and display the version information. workflowStarting = true; InstanceId.SelectedIndex = InstanceId.Items.Add(wfApp.Id); WorkflowVersion.Text = identity.ToString(); workflowStarting = false; // Configure the instance store, extensions, and // workflow lifecycle handlers. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp); // Start the workflow. wfApp.Run(); }
Para reanudar un flujo de trabajo
Agregue un controlador
ClickparaEnterGuess. Para agregar el controlador, cambie a Vista de diseño para el formulario y haga doble clic enEnterGuess. Siempre que el usuario haga clic en este botón se reanudará un flujo de trabajo.Private Sub EnterGuess_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles EnterGuess.Click End Subprivate void EnterGuess_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { }Agregue el código siguiente para asegurarse de que un flujo de trabajo está seleccionado en la lista de flujos de trabajo y de que el acierto del usuario es válido.
If WorkflowInstanceId = Guid.Empty Then MessageBox.Show("Please select a workflow.") Return End If Dim userGuess As Integer If Not Int32.TryParse(Guess.Text, userGuess) Then MessageBox.Show("Please enter an integer.") Guess.SelectAll() Guess.Focus() Return End Ifif (WorkflowInstanceId == Guid.Empty) { MessageBox.Show("Please select a workflow."); return; } int guess; if (!Int32.TryParse(Guess.Text, out guess)) { MessageBox.Show("Please enter an integer."); Guess.SelectAll(); Guess.Focus(); return; }A continuación, recupere
WorkflowApplicationInstancede la instancia de flujo de trabajo persistente.WorkflowApplicationInstancerepresenta una instancia de flujo de trabajo persistente que aún no se ha asociado a una definición de flujo de trabajo.DefinitionIdentitydeWorkflowApplicationInstancecontieneWorkflowIdentityde la instancia de flujo de trabajo persistente. En este tutorial, la clase de utilidad deWorkflowVersionMapse usa para asignarWorkflowIdentitya la definición de flujo de trabajo correcta. Una vez que se recupera la definición de flujo de trabajo, se creaWorkflowApplication, mediante la definición de flujo de trabajo correcta.Dim instance As WorkflowApplicationInstance = _ WorkflowApplication.GetInstance(WorkflowInstanceId, store) ' Use the persisted WorkflowIdentity to retrieve the correct workflow ' definition from the dictionary. Dim wf As Activity = _ WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(instance.DefinitionIdentity) ' Associate the WorkflowApplication with the correct definition Dim wfApp As New WorkflowApplication(wf, instance.DefinitionIdentity)WorkflowApplicationInstance instance = WorkflowApplication.GetInstance(WorkflowInstanceId, store); // Use the persisted WorkflowIdentity to retrieve the correct workflow // definition from the dictionary. Activity wf = WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(instance.DefinitionIdentity); // Associate the WorkflowApplication with the correct definition var wfApp = new WorkflowApplication(wf, instance.DefinitionIdentity);Una vez que se ha creado
WorkflowApplication, configure el almacén de instancias, los controladores de ciclo de vida del flujo de trabajo y las extensiones mediante una llamada aConfigureWorkflowApplication. Deben llevarse a cabo estos pasos cada vez que se crea un nuevo objetoWorkflowApplicationy antes de que se cargue la instancia de flujo de trabajo enWorkflowApplication. Cuando el flujo de trabajo ya está cargado, se reanuda con el intento del usuario.' Configure the extensions and lifecycle handlers. ' Do this before the instance is loaded. Once the instance is ' loaded it is too late to add extensions. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp) ' Load the workflow. wfApp.Load(instance) ' Resume the workflow. wfApp.ResumeBookmark("EnterGuess", userGuess)// Configure the extensions and lifecycle handlers. // Do this before the instance is loaded. Once the instance is // loaded it is too late to add extensions. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp); // Load the workflow. wfApp.Load(instance); // Resume the workflow. wfApp.ResumeBookmark("EnterGuess", guess);Finalmente, desactive el cuadro donde se indica el número y prepare el formulario para aceptar otro intento.
' Clear the Guess textbox. Guess.Clear() Guess.Focus()// Clear the Guess textbox. Guess.Clear(); Guess.Focus();El siguiente ejemplo es el controlador
EnterGuess_Clickcompletado.Private Sub EnterGuess_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles EnterGuess.Click If WorkflowInstanceId = Guid.Empty Then MessageBox.Show("Please select a workflow.") Return End If Dim userGuess As Integer If Not Int32.TryParse(Guess.Text, userGuess) Then MessageBox.Show("Please enter an integer.") Guess.SelectAll() Guess.Focus() Return End If Dim instance As WorkflowApplicationInstance = _ WorkflowApplication.GetInstance(WorkflowInstanceId, store) ' Use the persisted WorkflowIdentity to retrieve the correct workflow ' definition from the dictionary. Dim wf As Activity = _ WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(instance.DefinitionIdentity) ' Associate the WorkflowApplication with the correct definition Dim wfApp As New WorkflowApplication(wf, instance.DefinitionIdentity) ' Configure the extensions and lifecycle handlers. ' Do this before the instance is loaded. Once the instance is ' loaded it is too late to add extensions. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp) ' Load the workflow. wfApp.Load(instance) ' Resume the workflow. wfApp.ResumeBookmark("EnterGuess", userGuess) ' Clear the Guess textbox. Guess.Clear() Guess.Focus() End Subprivate void EnterGuess_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { if (WorkflowInstanceId == Guid.Empty) { MessageBox.Show("Please select a workflow."); return; } int guess; if (!Int32.TryParse(Guess.Text, out guess)) { MessageBox.Show("Please enter an integer."); Guess.SelectAll(); Guess.Focus(); return; } WorkflowApplicationInstance instance = WorkflowApplication.GetInstance(WorkflowInstanceId, store); // Use the persisted WorkflowIdentity to retrieve the correct workflow // definition from the dictionary. Activity wf = WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(instance.DefinitionIdentity); // Associate the WorkflowApplication with the correct definition var wfApp = new WorkflowApplication(wf, instance.DefinitionIdentity); // Configure the extensions and lifecycle handlers. // Do this before the instance is loaded. Once the instance is // loaded it is too late to add extensions. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp); // Load the workflow. wfApp.Load(instance); // Resume the workflow. wfApp.ResumeBookmark("EnterGuess", guess); // Clear the Guess textbox. Guess.Clear(); Guess.Focus(); }
Para finalizar un flujo de trabajo
Agregue un controlador
ClickparaQuitGame. Para agregar el controlador, cambie a Vista de diseño para el formulario y haga doble clic enQuitGame. Siempre que el usuario haga clic en este botón se finalizará el flujo de trabajo seleccionado actualmente.Private Sub QuitGame_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles QuitGame.Click End Subprivate void QuitGame_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { }Agregue el código siguiente al controlador
QuitGame_Click. Este código primero comprueba que un flujo de trabajo está seleccionado en la lista de flujos de trabajo. Después, carga la instancia persistente enWorkflowApplicationInstance, usaDefinitionIdentitypara determinar la definición correcta de flujo de trabajo e inicializaWorkflowApplication. A continuación, las extensiones y los controladores de ciclo de vida de flujo de trabajo se configuran mediante una llamada aConfigureWorkflowApplication. Una vez se ha configuradoWorkflowApplication, se carga y, a continuación,Terminaterecibe una llamada.If WorkflowInstanceId = Guid.Empty Then MessageBox.Show("Please select a workflow.") Return End If Dim instance As WorkflowApplicationInstance = _ WorkflowApplication.GetInstance(WorkflowInstanceId, store) ' Use the persisted WorkflowIdentity to retrieve the correct workflow ' definition from the dictionary. Dim wf As Activity = WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(instance.DefinitionIdentity) ' Associate the WorkflowApplication with the correct definition. Dim wfApp As New WorkflowApplication(wf, instance.DefinitionIdentity) ' Configure the extensions and lifecycle handlers. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp) ' Load the workflow. wfApp.Load(instance) ' Terminate the workflow. wfApp.Terminate("User resigns.")if (WorkflowInstanceId == Guid.Empty) { MessageBox.Show("Please select a workflow."); return; } WorkflowApplicationInstance instance = WorkflowApplication.GetInstance(WorkflowInstanceId, store); // Use the persisted WorkflowIdentity to retrieve the correct workflow // definition from the dictionary. Activity wf = WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(instance.DefinitionIdentity); // Associate the WorkflowApplication with the correct definition var wfApp = new WorkflowApplication(wf, instance.DefinitionIdentity); // Configure the extensions and lifecycle handlers ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp); // Load the workflow. wfApp.Load(instance); // Terminate the workflow. wfApp.Terminate("User resigns.");
Para generar y ejecutar la aplicación
Haga doble clic en Program.cs (o en Module1.vb) en el Explorador de soluciones para mostrar el código.
Agregue las siguientes instrucciones
using(oImports) al principio del archivo con las demás instruccionesusing(oImports).Imports System.Windows.Formsusing System.Windows.Forms;Quite o comente el código de hospedaje de flujo de trabajo existente de Procedimiento para ejecutar un flujo de trabajo y reemplácelo por el código siguiente.
Sub Main() Application.EnableVisualStyles() Application.Run(New WorkflowHostForm()) End Substatic void Main(string[] args) { Application.EnableVisualStyles(); Application.Run(new WorkflowHostForm()); }Haga clic con el botón derecho en NumberGuessWorkflowHost en el Explorador de soluciones y elija Propiedades. En la pestaña Aplicación, especifique Aplicación para Windows para Tipo de resultado. Este paso es opcional, pero si no se realiza la ventana de la consola se muestra además del formulario.
Presione Ctrl+Mayús+B para compilar la aplicación.
Asegúrese de que se haya establecido NumberGuessWorkflowHost como la aplicación de inicio y pulse Ctrl+F5 para iniciar la aplicación.
Seleccione un intervalo para el juego de adivinar un numero y el tipo de flujo de trabajo que se va a iniciar, y haga clic en New Game (Nuevo juego). Escriba un intento en el cuadro de Guess (Adivinar) y haga clic en Go (Ir) para enviarlo. Observe que el resultado de las actividades
WriteLinese muestra en el formulario.Inicie varios flujos de trabajo mediante diferentes tipos de flujo de trabajo e intervalos de números, escriba algunos números y cambie de un flujo de trabajo a otro seleccionándolos en la lista Identificador de instancia de flujo de trabajo.
Observe que al cambiar a un nuevo flujo de trabajo, los intentos anteriores y el progreso del flujo de trabajo no aparecen en la ventana de estado. El estado no está disponible porque no se captura ni guarda en ningún lugar. En el siguiente paso del tutorial, Procedimiento para crear un participante de seguimiento personalizado, se crea un participante de seguimiento personalizado que guarda esta información.
