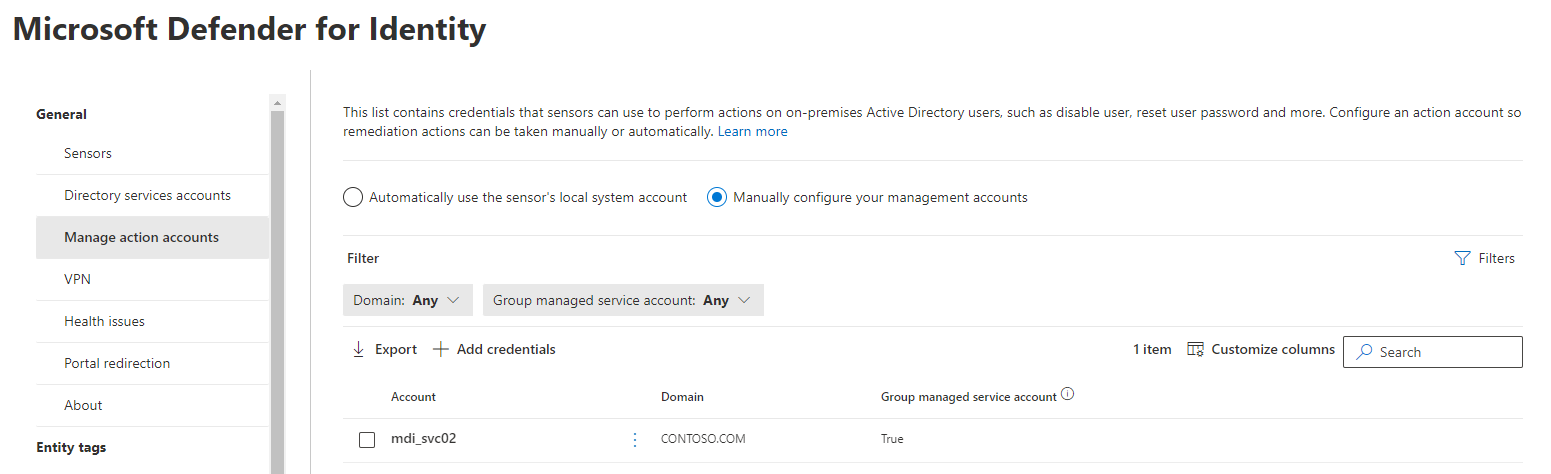
Configuración de cuentas de acción de Microsoft Defender for Identity
Defender for Identity le permite realizar acciones de corrección destinadas a cuentas Active Directory local en caso de que una identidad esté en peligro. Para realizar estas acciones, Microsoft Defender for Identity debe tener los permisos necesarios para hacerlo.
De forma predeterminada, el sensor de Microsoft Defender for Identity suplanta la LocalSystem cuenta del controlador de dominio y realiza las acciones, incluidos los escenarios de interrupción de ataques de Microsoft Defender XDR.
Si necesita cambiar este comportamiento, configure una gMSA dedicada y establezca el ámbito de los permisos que necesita. Por ejemplo:
Nota:
El uso de una gMSA dedicada como cuenta de acción es opcional. Se recomienda usar la configuración predeterminada de la LocalSystem cuenta.
Procedimientos recomendados para cuentas de acción
Se recomienda evitar el uso de la misma cuenta de gMSA que configuró para las acciones administradas de Defender for Identity en servidores distintos de los controladores de dominio. Si usa la misma cuenta y el servidor está en peligro, un atacante podría recuperar la contraseña de la cuenta y obtener la capacidad de cambiar contraseñas y deshabilitar cuentas.
También se recomienda evitar el uso de la misma cuenta que la cuenta de servicio de directorio y la cuenta administrar acción. Esto se debe a que la cuenta de servicio de directorio solo requiere permisos de solo lectura para Active Directory y las cuentas de acción de administración necesitan permisos de escritura en las cuentas de usuario.
Si tiene varios bosques, la cuenta de acción administrada de gMSA debe ser de confianza en todos los bosques o crear una independiente para cada bosque. Para obtener más información, consulte Microsoft Defender for Identity compatibilidad con varios bosques.
Creación y configuración de una cuenta de acción específica
Cree una nueva cuenta de gMSA. Para obtener más información, consulte Introducción a las cuentas de servicio administradas de grupo.
Asigne el derecho Iniciar sesión como servicio a la cuenta de gMSA en cada controlador de dominio que ejecute el sensor de Defender for Identity.
Conceda los permisos necesarios a la cuenta de gMSA de la siguiente manera:
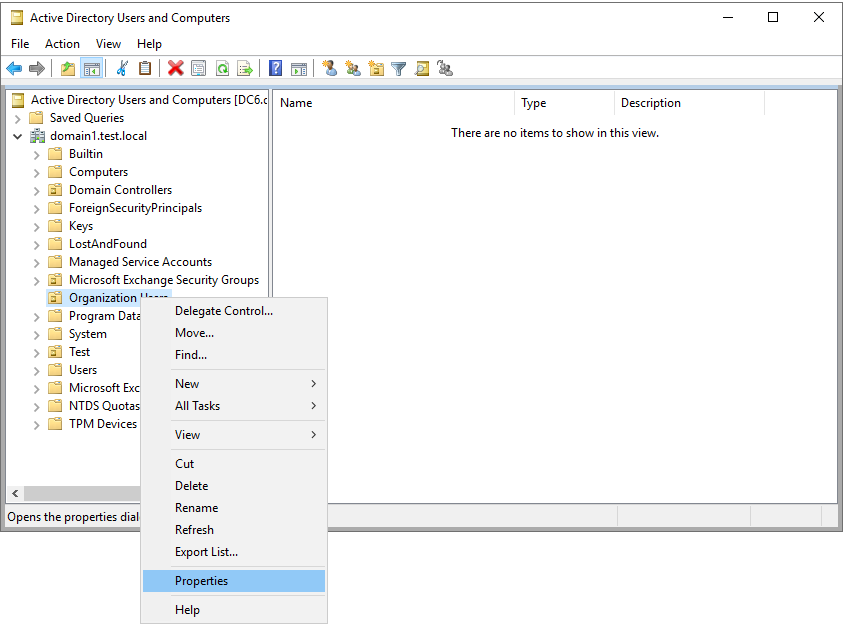
Abra Usuarios y equipos de Active Directory.
Haga clic con el botón derecho en el dominio o unidad organizativa pertinente y seleccione Propiedades. Por ejemplo:
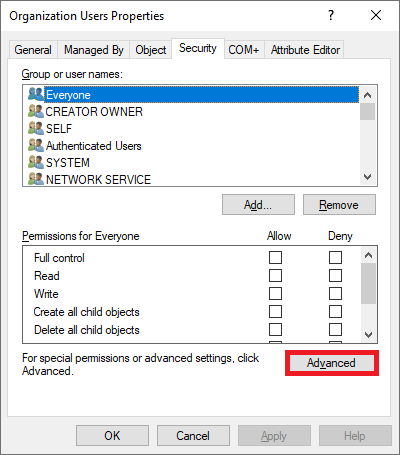
Vaya a la pestaña Seguridad y seleccione Avanzadas. Por ejemplo:
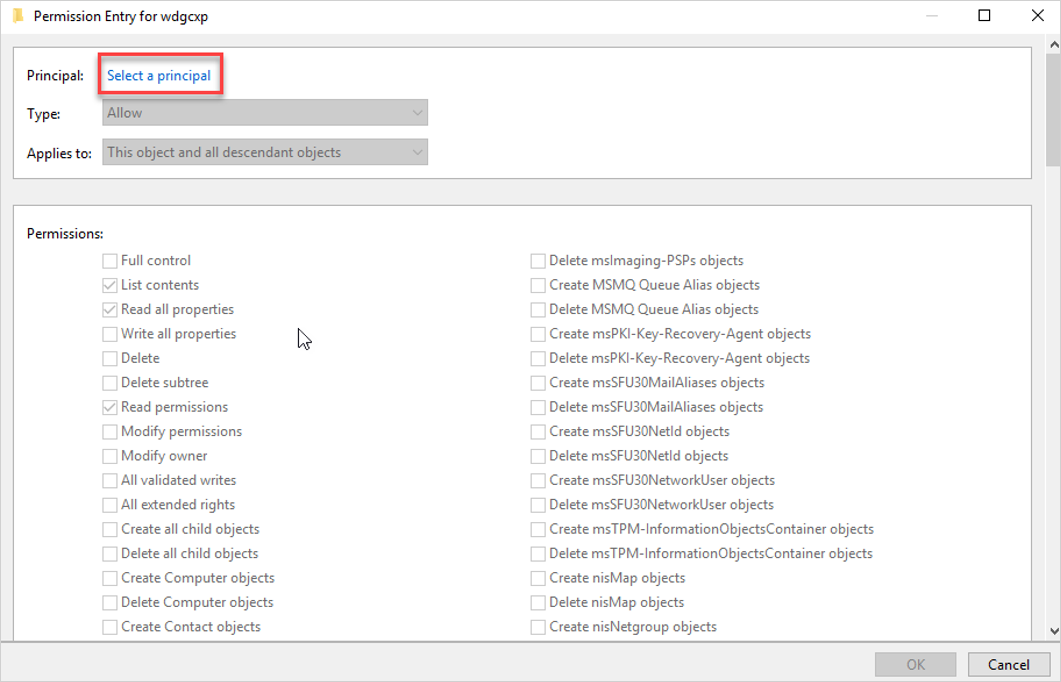
Seleccione Agregar Seleccione>una entidad de seguridad. Por ejemplo:
Asegúrese de que las cuentas de servicio están marcadas en Tipos de objeto. Por ejemplo:
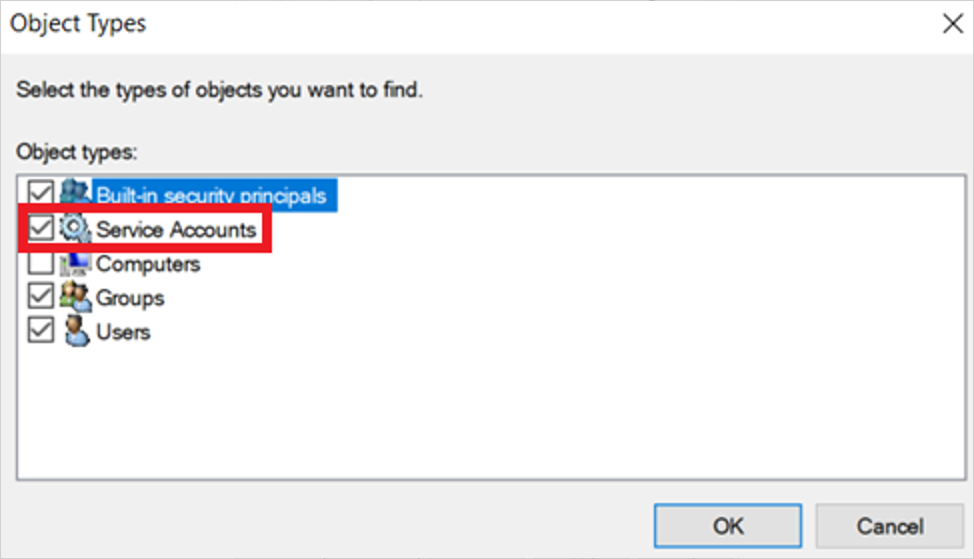
En el cuadro Escribir el nombre del objeto que se va a seleccionar , escriba el nombre de la cuenta de gMSA y seleccione Aceptar.
En el campo Se aplica a , seleccione Objetos de usuario descendiente, deje la configuración existente y agregue los permisos y propiedades que se muestran en el ejemplo siguiente:
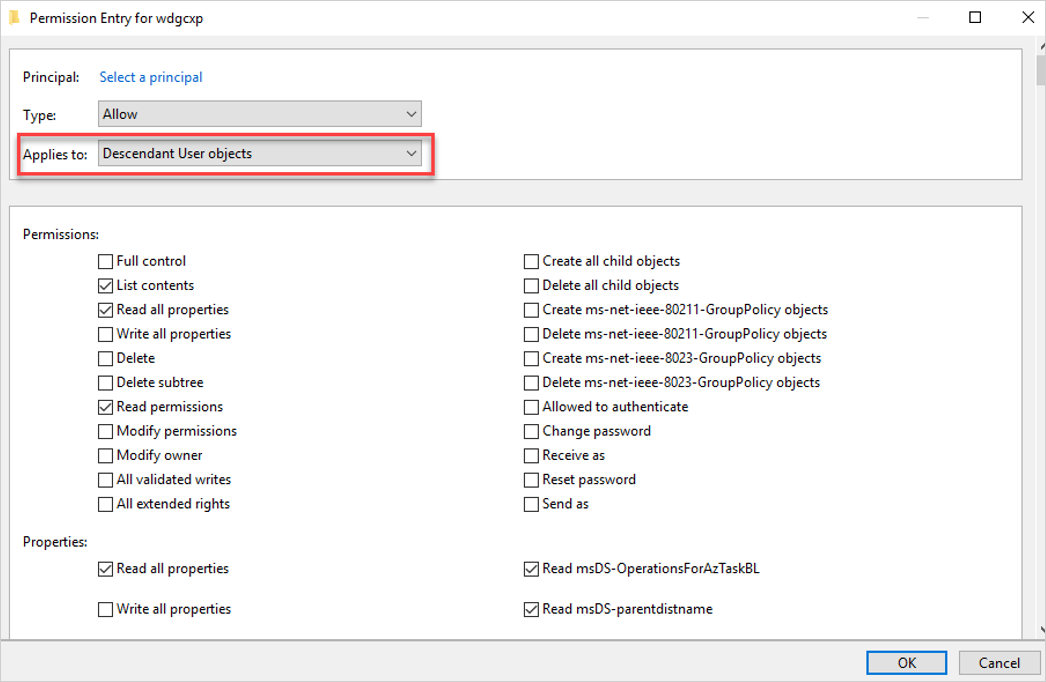
Los permisos necesarios incluyen:
Acción Permissions Propiedades Habilitar forzar el restablecimiento de contraseña Restablecer contraseña - Read pwdLastSet
-Write pwdLastSetPara deshabilitar el usuario - - Read userAccountControl
-Write userAccountControl(Opcional) En el campo Se aplica a , seleccione Objetos de grupo descendiente y establezca las siguientes propiedades:
Read membersWrite members
Seleccione Aceptar.
Agregar la cuenta de gMSA en el portal de Microsoft Defender
Vaya al portal de Microsoft Defender y seleccione Configuración ->Identidades>Microsoft Defender for Identity>Administrar cuentas> de acción+Crear nueva cuenta.
Por ejemplo:
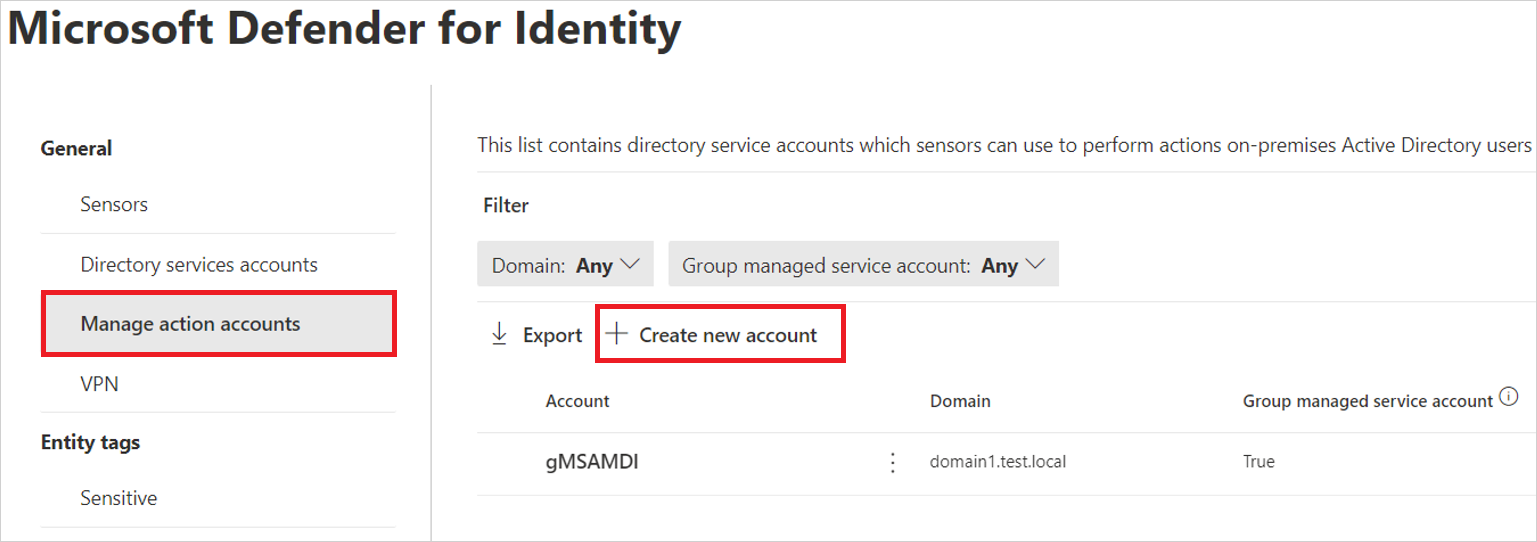
Escriba el nombre de cuenta y el dominio y seleccione Guardar.
La cuenta de acción aparece en la página Administrar cuentas de acción .
Contenido relacionado
Para obtener más información, vea Acciones de corrección en Microsoft Defender for Identity.