Diagram of the sequence of the deployment guide including these locations, in order: Overview, Plan, Prepare, Publish, Monitor, and Optimization. The 'Publish' location is currently highlighted.
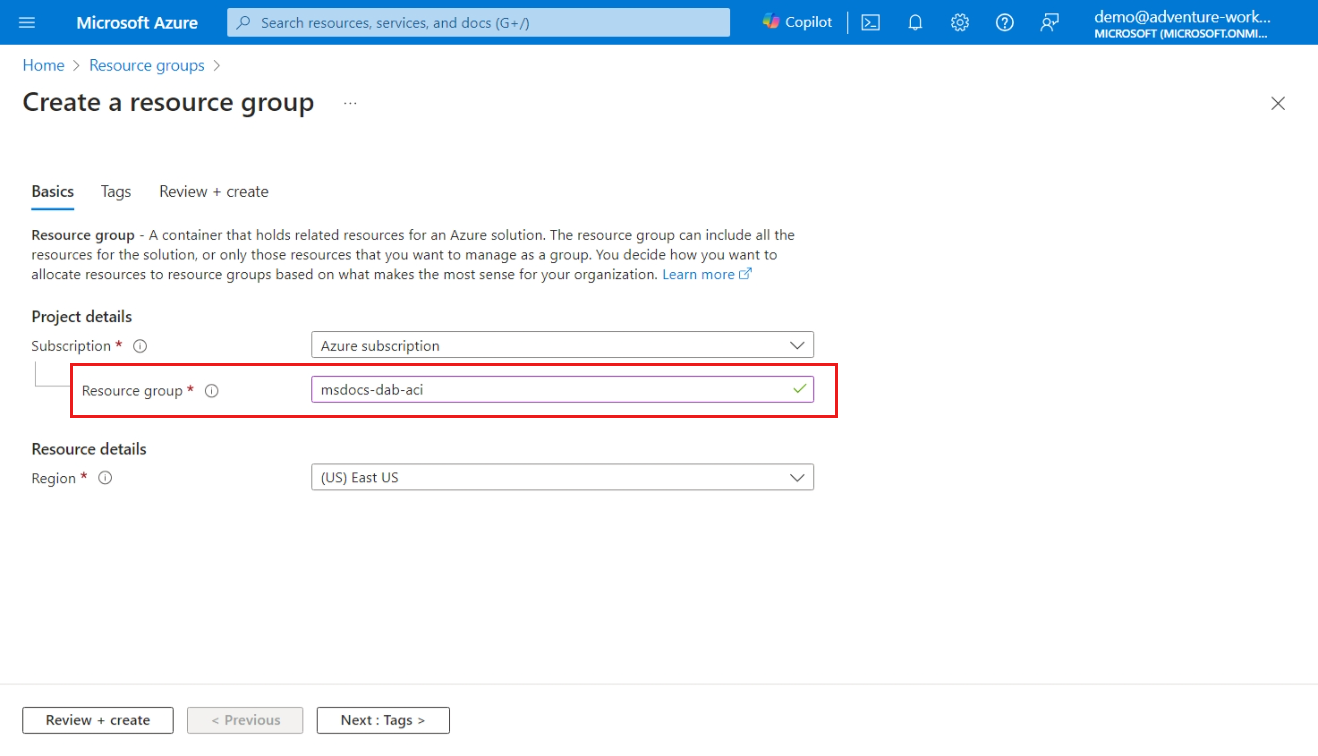
Deploy the Data API builder quickly to Azure using just a configuration file and no custom code. This guide includes steps to host the Data API builder container image from Docker as a container in Azure Container Instances.
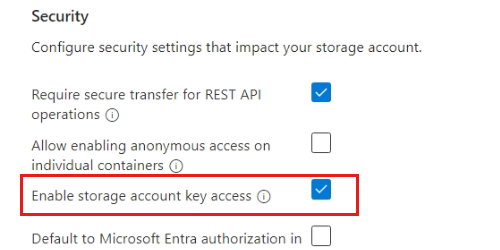
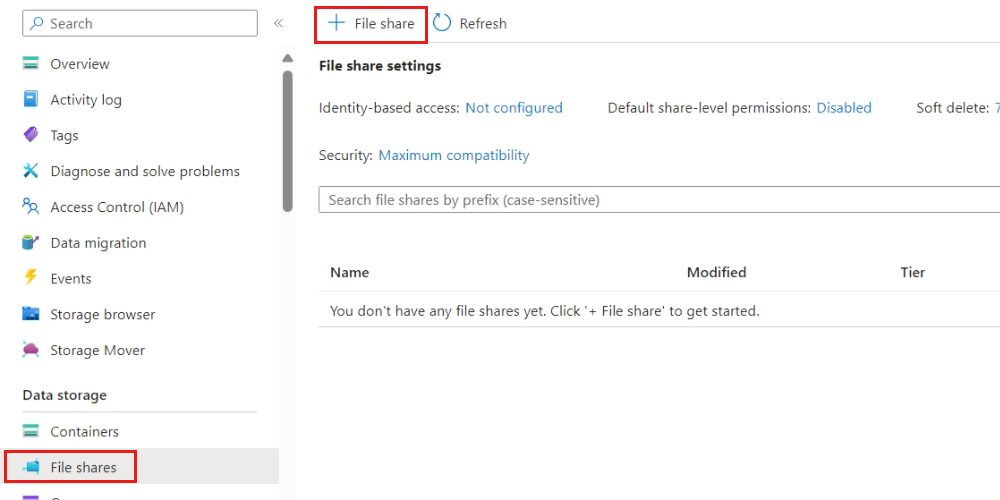
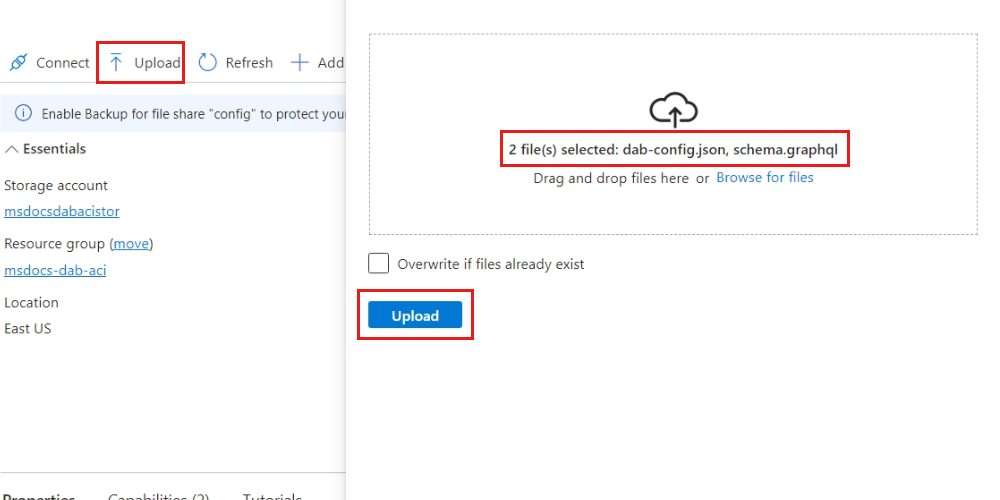
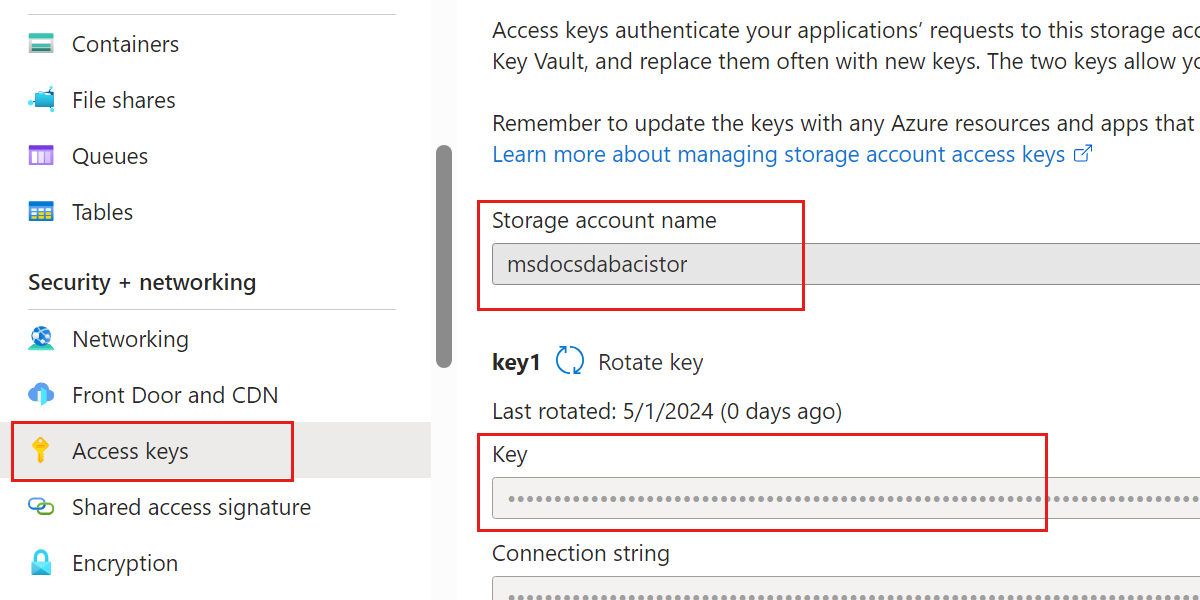
In this guide, walk through the steps to build a Data API builder configuration file, host the file in Azure Files, and then mount the file to a container in Azure Container Instances.