Búsqueda y validación de conectores de Microsoft Graph de contenido indexado
Puede usar el explorador de índices para probar la indexación cuando no pueda encontrar un elemento determinado durante las pruebas de conexión. Si necesita comprobar las propiedades y el acceso de usuario, ayuda a revisar los metadatos y las listas de control de acceso (ACL) de los elementos indexados. Además, es beneficioso para solucionar problemas de búsqueda; si los usuarios notifican problemas al acceder a los elementos, esta característica confirma si el elemento se indexó correctamente e incluye los datos correctos.
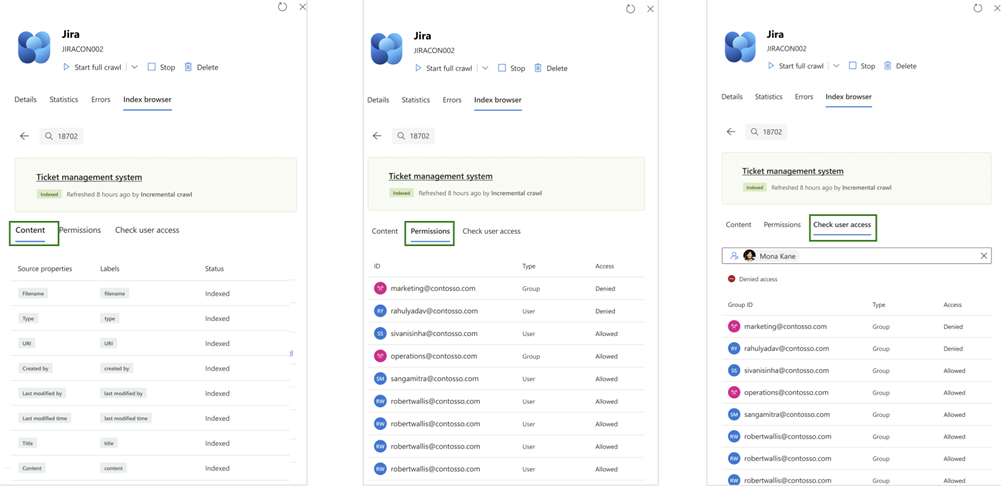
Acerca del explorador de índices
Al escribir un identificador de elemento para comprobar su estado de índice, puede ver los detalles siguientes si el elemento está indexado.
- Nombre del contenido: el nombre del elemento indexado.
- Estado: estado actual del elemento y su última hora de actualización.
- Propiedades: indica el estado de todas las propiedades definidas durante la configuración del elemento.
- Permisos: Listas todos los grupos y usuarios individuales asociados al elemento. Si el estado es allow, todos los usuarios de esos grupos pueden ver el elemento. Si el estado es denegado, los usuarios de esos grupos no podrán acceder al elemento. Si los permisos de acceso están configurados como Permitir a todos en lugar de Solo personas con acceso para la conexión, todos los elementos del índice son visibles para todos y no se aplican permisos específicos.
- Comprobar el acceso del usuario: permite buscar un usuario específico para comprobar su acceso al elemento. Escriba el nombre de usuario o la dirección de correo electrónico para mostrar una lista de grupos a los que pertenece el usuario. Si al usuario se le deniega el acceso a cualquiera de estos grupos, se revoca su permiso general para ver el elemento.
Nota:
- En los permisos, puede ver los usuarios que se muestran individualmente (fuera de un grupo) en el origen de datos y los grupos dentro del origen de datos. Para comprobar si hay un usuario presente en un grupo, use Comprobar el acceso de usuario.
- Si un usuario no aparece en Comprobar el acceso de usuario, puede deberse a un error en la asignación de usuarios o a que el usuario no se detecte (por ejemplo, no se encontró el id. de usuario de AAD). Para resolver esto, compruebe si el usuario tiene acceso en el origen de datos, revise la fórmula de asignación de usuarios y los informes de errores.
Para buscar contenido indexado, escriba el identificador único del elemento en el explorador de índices.
| Nombre del conector | Entrada por identificador de elemento | Dónde encontrar el identificador de elemento |
|---|---|---|
| ADO WI | Id. | El identificador es el identificador del elemento de trabajo. |
| ADO Wiki | Nombre de la organización, id. de página | Se puede encontrar en la dirección URL. |
| ServiceNow KB | Sys_Id.DisplayValue | Vaya al registro donde busca un sys_id, haga clic con el botón derecho en la barra de encabezado y seleccione Copiar sys_id.También puede hacer clic en la sys_id Copiar hamburguesa > . Para obtener más información, consulte la documentación de ServiceNow. |
| Catálogo de ServiceNow | Sys_Id.value | Vaya al registro donde busca un sys_id, haga clic con el botón derecho en la barra de encabezado y seleccione Copiar sys_id.También puede hacer clic en la sys_id Copiar hamburguesa > . Para obtener más información, consulte la documentación de ServiceNow. |
| Vales de servicio de ServiceNow | Sys_Id.value | Vaya al registro donde busca un sys_id, haga clic con el botón derecho en la barra de encabezado y seleccione Copiar sys_id.También puede hacer clic en la sys_id Copiar hamburguesa > . Para obtener más información, consulte la documentación de ServiceNow. |
| Salesforce | Id. | Se puede encontrar en la dirección URL. |
| Intranet (Cloud/OnPrem) | URL | Dirección URL final en minúsculas. Identificador de problema de Jira. Siga el vínculo (https://confluence.atlassian.com/jirakb/how-to-get-issue-id-from-the-jira-user-interface-1115156394.html#:~:text=User%20needs%20to%20get%20the%20issue%20id%20in%20an%20easier). |
| Confluence (Cloud/OnPrem) | id. de entrada de blog de página | Se puede encontrar en el identificador de elemento de la dirección URL. Puede encontrar ejemplos en la dirección URL de Confluence Cloud desde el origen de datos. |
| CSV | Lista de identificadores únicos, clave de elemento | Administración detalles configurados. |
| Azure SQL, Oracle DB, MS SQL | Valores para todas las columnas de columnas de clave única | Administración detalles configurados. |
| Mediawiki | id. de página, espacio de nombres, sourceUrl | Administración detalles configurados. |
| ADLS gen 2 | URI de archivo | Administración detalles configurados. |
| Sharepoint | GUID | Administración detalles configurados. |
| FileShare | ruta de acceso al archivo | Administración detalles configurados. |
| Conector personalizado | id. de elemento | Administración detalles configurados. |
| SAP | Identificador de usuario | Administración detalles configurados. |
Ejemplos
Ejemplo 1: El estado del elemento se indexa parcialmente
Indica que al elemento le falta cierta información, como propiedades, detalles del usuario o contenido, pero que se puede buscar en Microsoft Search y Microsoft 365 Copilot. Para asegurarse de que el elemento está completo, revise la pestaña Errores para obtener más información.
Ejemplo 2: El estado del elemento es denegar todo
Indica que el elemento está indexado, pero sigue siendo inaccesible para todos los usuarios, como se muestra en una respuesta vacía en la pestaña permisos. Aunque el elemento está presente en el índice, los usuarios no pueden verlo.
En el caso de un conector de ServiceNow, el estado Denegar todo puede deberse a diferentes causas.
Criterios avanzados en un elemento: si se aplican criterios avanzados a un elemento de la lista de denegación, se puede marcar como Denegar todo. Para resolverlo, intente quitar los criterios avanzados y desencadenar un rastreo completo. Para obtener más información, consulte la sección de solución de problemas de cada conector.
Criterios avanzados en un knowledge base: si los criterios avanzados de una lista de denegación de knowledge base afectan a todos los artículos de esa knowledge base. Puede dar lugar a un estado Denegar todo para esos artículos. Identifique el knowledge base al que pertenece el elemento y quite los criterios avanzados. Para obtener más información, consulte la sección de solución de problemas de cada conector.
Además, los problemas temporales pueden provocar un estado Denegar todo , que se podría resolver durante el siguiente rastreo completo.
Ejemplo 3: El estado del elemento está permitido para todos los usuarios
Cuando un elemento está configurado para ser visible para todos, todos los usuarios de la organización pueden acceder a él, independientemente de los permisos establecidos en el origen de datos.
Si se detecta un elemento pero no se indexa, compruebe en la pestaña Errores cualquier problema que impidiera el proceso de indexación.
Nota:
- Los cambios en los permisos de usuario o grupo (ACL) pueden tardar hasta 24 horas en reflejarse en Microsoft Search y Microsoft 365 Copilot.
- Las actualizaciones de permisos se producen durante un rastreo completo, no durante un rastreo incremental.
- Si los permisos del origen de datos cambian después del último rastreo completo, se debe desencadenar un nuevo rastreo completo a petición o programado para actualizar el índice.
- Al realizar pruebas en Microsoft Search o Microsoft 365 Copilot, asegúrese de que está buscando con una propiedad que permite búsquedas o que se puede consultar. Para obtener más información, vea Administrar esquema.