Crear una máquina virtual de Azure con las redes aceleradas
En este artículo se describe cómo crear una máquina virtual (VM) Linux o Windows con redes aceleradas (AccelNet) habilitada mediante la interfaz de la línea de comandos de la CLI de Azure.
Requisitos previos
- Una cuenta de Azure con una suscripción activa. También puede crear una cuenta de forma gratuita.
Creación de una red virtual
Crear una red virtual y un host de Azure Bastion
El procedimiento siguiente crea una red virtual con una subred de recursos, una subred de Azure Bastion y un host de Bastion:
En el portal, busque y seleccione Redes virtuales.
En la página Redes virtuales, seleccione y Crear.
En la pestaña Datos básicos de Crear red virtual, escriba o seleccione la siguiente información:
Configuración Valor Detalles del proyecto Suscripción Selecciona tu suscripción. Resource group Seleccione Crear nuevo.
Escriba test-rg para el nombre.
Seleccione Aceptar.Detalles de instancia Nombre Escriba vnet-1. Region Seleccione Este de EE. UU. 2. 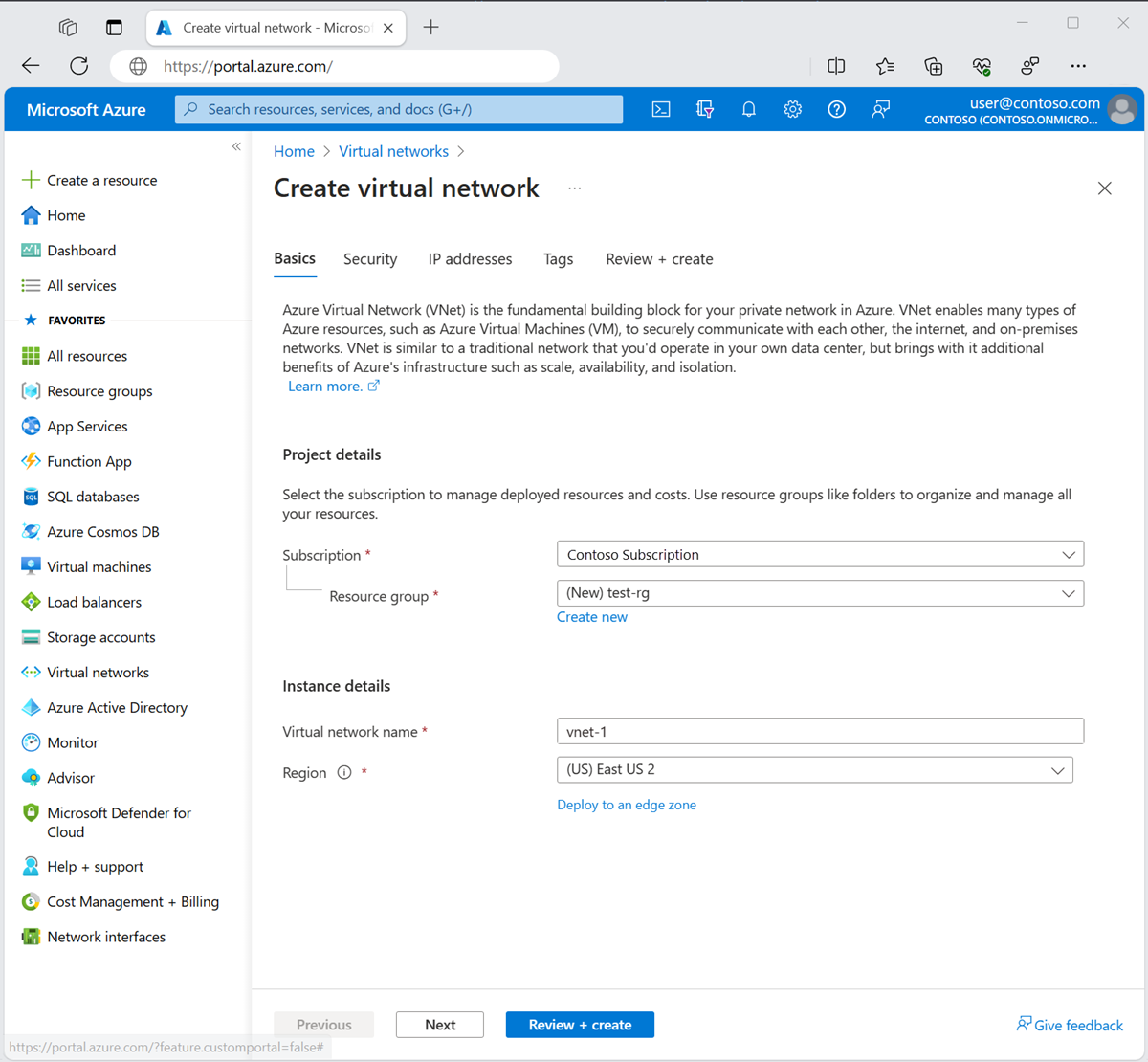
Seleccione Siguiente para ir a la pestaña Seguridad.
En la sección Azure Bastion, seleccione Habilitar Azure Bastion.
Bastion usa el explorador para conectarse a las máquinas virtuales de la red virtual a través del shell seguro (SSH) o el protocolo de escritorio remoto (RDP) mediante sus direcciones IP privadas. Las máquinas virtuales no necesitan direcciones IP públicas, software cliente ni configuración especial. Para más información, consulte ¿Qué es Azure Bastion?.
Nota:
Los precios por hora comienzan desde el momento en que se implementa Bastion, independientemente del uso de datos salientes. Para más información, consulte Precios y SKU. Si va a implementar Bastion como parte de un tutorial o prueba, se recomienda eliminar este recurso una vez que haya terminado de usarlo.
En Azure Bastion, escriba o seleccione la información siguiente:
Configuración Valor Nombre de host de Azure Bastion Escriba bastión. Dirección IP pública de Azure Bastion Seleccione Crear una dirección IP pública.
Escriba public-ip-bastion en Nombre.
Seleccione Aceptar.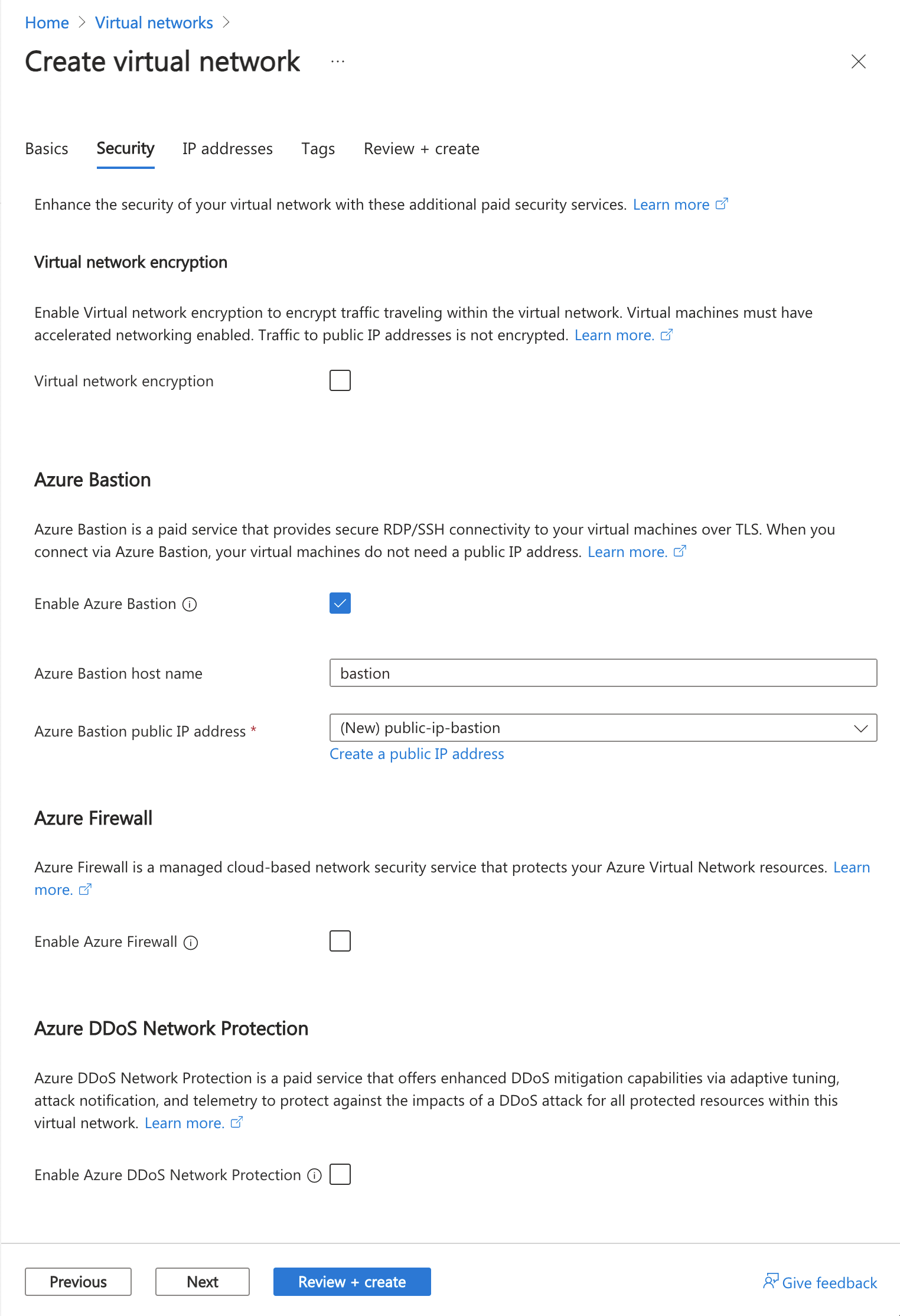
Seleccione Siguiente para continuar a la pestaña Direcciones IP.
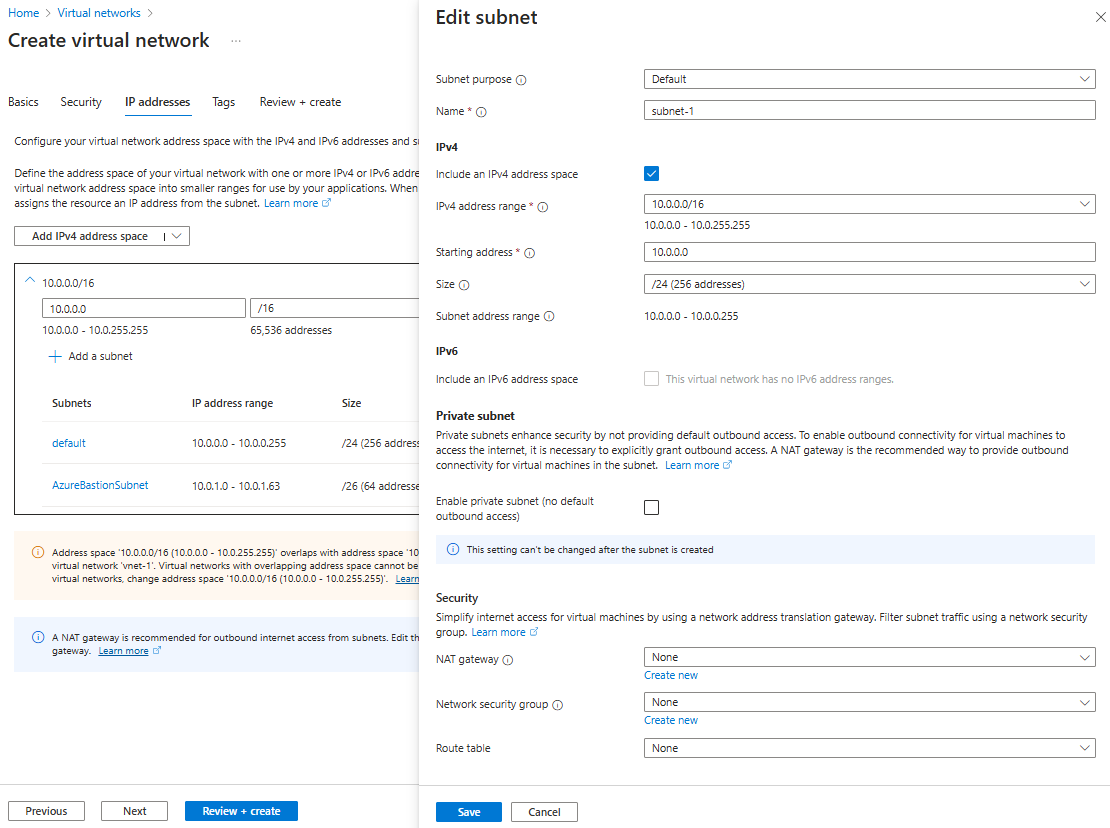
En el cuadro espacio de direcciones de Subredes, seleccione la subred predeterminada.
En Agregar subred, escriba o seleccione la información siguiente:
Configuración Valor Propósito de la subred Deje el valor predeterminado Predeterminado. Nombre Escriba subnet-1. IPv4 Intervalo de direcciones IPv4 Deje el valor predeterminado de 10.0.0.0/16. Dirección inicial Deje el valor predeterminado de 10.0.0.0. Size Deje el valor predeterminado de /24 (256 direcciones). Seleccione Guardar.
En la parte inferior de la ventana, seleccione Revisar y crear. Cuando se supera la validación, seleccione Crear.
Creación de una interfaz de red con redes aceleradas
Las redes aceleradas se habilitan en el portal durante la creación de máquinas virtuales. Cree una máquina virtual en la sección siguiente.
Creación de una máquina virtual y conexión de NIC
Creación de una máquina virtual de prueba
El procedimiento siguiente crea una máquina virtual (VM) de prueba denominada vm-1 en la red virtual.
En el portal, busque y seleccione Máquinas virtuales.
En Máquinas virtuales, seleccione + Crear y, después, Máquina virtual de Azure.
En la pestaña Datos básicos de Crear una máquina virtual, escriba o seleccione la siguiente información:
Configuración Valor Detalles del proyecto Suscripción Selecciona tu suscripción. Resource group Seleccione test-rg. Detalles de instancia Nombre de la máquina virtual Escriba vm-1. Region Seleccione Este de EE. UU. 2. Opciones de disponibilidad Seleccione No se requiere redundancia de la infraestructura. Tipo de seguridad Deje el valor predeterminado Estándar. Imagen Seleccione Ubuntu Server 22.04 LTS: x64 Gen2. Arquitectura VM Deje el valor predeterminado, x64. Size Seleccione un tamaño. Cuenta de administrador Tipo de autenticación Seleccione Contraseña. Nombre de usuario escriba usuarioazure. Contraseña Escriba una contraseña. Confirmar contraseña Reescriba la contraseña. Reglas de puerto de entrada Puertos de entrada públicos Seleccione Ninguno. Seleccione la pestaña Redes en la parte superior de la página.
En la pestaña Redes, escriba o seleccione la siguiente información:
Parámetro Valor Interfaz de red Virtual network Seleccione vnet-1. Subnet Seleccione subnet-1 (10.0.0.0/24). Dirección IP pública Selecciona Ninguno. Grupo de seguridad de red de NIC Seleccione Advanced (Avanzadas). Configuración del grupo de seguridad de red Seleccione Crear nuevo.
Escriba nsg-1 como nombre.
Deje el resto de los valores predeterminados y seleccione Aceptar.Deje el resto de las opciones en sus valores predeterminados y luego seleccione Revisar + crear.
Revise la configuración y seleccione Crear.
Nota
Las máquinas virtuales de una red virtual con un host bastión no necesitarán direcciones IP públicas. Bastion proporcionará la dirección IP pública y las máquinas virtuales usarán direcciones IP privadas para comunicarse dentro de la red. Es posible quitar las direcciones IP públicas de cualquier máquina virtual en redes virtuales hospedadas por Bastion. Para obtener más información, consulte Desasociación de una dirección IP pública de una máquina virtual de Azure.
Nota:
Azure proporciona una dirección IP de acceso de salida predeterminada para las máquinas virtuales que no tienen asignada una dirección IP pública o están en el grupo back-end de un equilibrador de carga de Azure básico interno. El mecanismo de dirección IP de acceso de salida predeterminado proporciona una dirección IP de salida que no se puede configurar.
La dirección IP de acceso de salida predeterminada está deshabilitada cuando se produce uno de los siguientes eventos:
- Se asigna una dirección IP pública a la máquina virtual.
- La máquina virtual se coloca en el grupo back-end de un equilibrador de carga estándar, con o sin reglas de salida.
- Se asigna un recurso de Azure NAT Gateway a la subred de la máquina virtual.
Las máquinas virtuales creadas mediante conjuntos de escalado de máquinas virtuales en modo de orquestación flexible no tienen acceso de salida predeterminado.
Para más información sobre las conexiones de salida en Azure, vea Acceso de salida predeterminado en Azure y Uso de traducción de direcciones de red (SNAT) de origen para conexiones de salida.
Confirmación de que Accelerated Networking esté habilitado
Linux
En el Azure Portal, busque y seleccione máquinas virtuales.
En la página Máquinas virtuales, seleccione la nueva máquina virtual.
En la página Información general de la máquina virtual, seleccione Conectar y, después, Conectar a través de Bastion.
En la pantalla de conexión de Bastion, cambie Tipo de autenticación a Clave privada SSH del archivo local.
Escriba el nombre de usuario que usó al crear la máquina virtual. En este ejemplo, el usuario se denomina azureuser, reemplace por el nombre de usuario que creó.
En Archivo local, seleccione el icono de carpeta y vaya al archivo de clave privada que se generó al crear la máquina virtual. Normalmente, el archivo de clave privada se denomina
id_rsaoid_rsa.pem.Seleccione Conectar.
Se abre una nueva ventana del explorador con la conexión de Bastion a la máquina virtual.
En un shell en la máquina virtual remota, escriba
uname -ry confirme que la versión de kernel es una de las siguientes o una posterior:- Ubuntu 16.04: 4.11.0-1013.
- SLES SP3: 4.4.92-6.18.
- RHEL: 3.10.0-693, 2.6.32-573. RHEL 6.7-6.10 son compatibles si la versión 4.5+ de Mellanox VF se instala antes que Linux Integration Services 4.3+.
Nota:
Es posible que se admitan otras versiones del kernel. Para obtener una lista actualizada, consulte las tablas de compatibilidad para cada distribución en máquinas virtuales Linux y FreeBSD compatibles con Hyper-V y confirme que SR-IOV es compatible. Encontrará más detalles en las notas de la versión de Linux Integration Services para Hyper-V y Azure. *
Use el comando
lspcipara confirmar que el dispositivo Mellanox VF está expuesto a la máquina virtual. La salida devuelta debe ser similar a la del ejemplo siguiente:0000:00:00.0 Host bridge: Intel Corporation 440BX/ZX/DX - 82443BX/ZX/DX Host bridge (AGP disabled) (rev 03) 0000:00:07.0 ISA bridge: Intel Corporation 82371AB/EB/MB PIIX4 ISA (rev 01) 0000:00:07.1 IDE interface: Intel Corporation 82371AB/EB/MB PIIX4 IDE (rev 01) 0000:00:07.3 Bridge: Intel Corporation 82371AB/EB/MB PIIX4 ACPI (rev 02) 0000:00:08.0 VGA compatible controller: Microsoft Corporation Hyper-V virtual VGA 0001:00:02.0 Ethernet controller: Mellanox Technologies MT27500/MT27520 Family [ConnectX-3/ConnectX-3 Pro Virtual Function]Use el comando
ethtool -S eth0 | grep vf_para comprobar si hay actividad en la función virtual (VF). Si las redes aceleradas están habilitadas y activas, recibirá una salida similar a la del siguiente ejemplo:vf_rx_packets: 992956 vf_rx_bytes: 2749784180 vf_tx_packets: 2656684 vf_tx_bytes: 1099443970 vf_tx_dropped: 0Cierre la conexión de Bastion a la máquina virtual.
Windows
Una vez creada la VM en Azure, conéctese a ella y confirme que el controlador de Ethernet está instalado en Windows.
En el Azure Portal, busque y seleccione máquinas virtuales.
En la página Máquinas virtuales, seleccione la nueva máquina virtual.
En la página Información general de la máquina virtual, seleccione Conectar y, después, Conectar a través de Bastion.
Escriba las credenciales que usó al crear la máquina virtual y, a continuación, seleccione Conectar.
Se abre una nueva ventana del explorador con la conexión de Bastion a la máquina virtual.
En la máquina virtual remota, haga clic con el botón derecho en Inicio y seleccione Administrador de dispositivos.
En la ventana Administrador de dispositivos, expanda el nodo Adaptadores de red.
Compruebe que el Adaptador Ethernet virtual ConnectX-4 Lx de Mellanox aparezca como se muestra en la siguiente imagen:

La presencia del adaptador confirma que las redes aceleradas están habilitadas para la máquina virtual.
Compruebe que los paquetes fluyen a través de la interfaz VF desde la salida del siguiente comando:
PS C:\ > Get-NetAdapter | Where-Object InterfaceDescription –like "*Mellanox*Virtual*" | Get-NetAdapterStatistics Name ReceivedBytes ReceivedUnicastPackets SentBytes SentUnicastPackets ---- ------------- ---------------------- --------- ------------------ Ethernet 2 492447549 347643 7468446 34991Nota:
Si el adaptador Mellanox no se inicia, abra un símbolo del sistema del administrador en la máquina virtual remota e introduzca el siguiente comando:
netsh int tcp set global rss = enabledCierre la conexión de Bastion a la máquina virtual.