Authoring a C# Windows Runtime component for use from a C++/WinRT app
This topic walks you through the process of adding a simple C# component to your C++/WinRT project.
Visual Studio makes it easy to author and deploy your own custom Windows Runtime types inside a Windows Runtime component (WRC) project written with C# or Visual Basic, and then to reference that WRC from a C++ application project, and to consume those custom types from that application.
Internally, your Windows Runtime types can use any .NET functionality that's allowed in a UWP application.
Note
For more info, see Windows Runtime components with C# and Visual Basic and .NET for UWP apps overview.
Externally, the members of your type can expose only Windows Runtime types for their parameters and return values. When you build your solution, Visual Studio builds your .NET WRC project, and then executes a build step that creates a Windows metadata (.winmd) file. This is your Windows Runtime component (WRC), which Visual Studio includes in your app.
Note
.NET automatically maps some commonly used .NET types, such as primitive data types and collection types, to their Windows Runtime equivalents. These .NET types can be used in the public interface of a Windows Runtime component, and will appear to users of the component as the corresponding Windows Runtime types. See Windows Runtime components with C# and Visual Basic.
Prerequisites
- Windows 10
- Microsoft Visual Studio
Create a Blank App
In Visual Studio, create a new project using the Blank App (C++/WinRT) project template. Make sure that you're using the (C++/WinRT) template, and not the (Universal Windows) one.
Set the name of the new project to CppToCSharpWinRT so that your folder structure will match the walkthrough.
Add a C# Windows Runtime Component to the Solution
In Visual Studio, create the component project: In Solution Explorer, open the shortcut menu for the CppToCSharpWinRT solution and choose Add, and then choose New Project to add a new C# project to the solution. In the Installed Templates section of the Add New Project dialog box, choose Visual C#, and then choose Windows, and then Universal. Choose the Windows Runtime Component (Universal Windows) template and enter SampleComponent for the project name.
Note
On the New Universal Windows Platform Project dialog box, choose Windows 10 Creators Update (10.0; Build 15063) as the Minimum Version. Please see the Application Minimum Version section below for more information.
Add the C# GetMyString method
In the SampleComponent project, change the name of the class from Class1 to Example. Then add two simple members to the class, a private int field and an instance method named GetMyString:
public sealed class Example { int MyNumber; public string GetMyString() { return $"This is call #: {++MyNumber}"; } }
Note
By default, the class is marked public sealed. All the Windows Runtime classes you expose from your component must be sealed.
Note
Optional: To enable IntelliSense for the newly added members, in Solution Explorer, open the shortcut menu for the SampleComponent project, and then choose Build.
Reference the C# SampleComponent from the CppToCSharpWinRT project
In Solution Explorer, in the C++/WinRT project, open the shortcut menu for References, and then choose Add Reference to open the Add Reference dialog. Choose Projects, and then choose Solution. Select the check box for the SampleComponent project and choose OK to add a reference.
Note
Optional: To enable IntelliSense for the C++/WinRT project, in Solution Explorer, open the shortcut menu for the CppToCSharpWinRT project, and then choose Build.
Edit MainPage.h
Open MainPage.h in the CppToCSharpWinRT project and then add two items. First add #include "winrt/SampleComponent.h" at the end of the #include statements, then a winrt::SampleComponent::Example field to the MainPage struct.
// MainPage.h
...
#include "winrt/SampleComponent.h"
namespace winrt::CppToCSharpWinRT::implementation
{
struct MainPage : MainPageT<MainPage>
{
...
winrt::SampleComponent::Example myExample;
...
};
}
Note
In Visual Studio, MainPage.h is listed under MainPage.xaml.
Edit MainPage.cpp
In MainPage.cpp, change the Mainpage::ClickHandler implementation to call the C# method GetMyString.
void MainPage::ClickHandler(IInspectable const&, RoutedEventArgs const&)
{
//myButton().Content(box_value(L"Clicked"));
hstring myString = myExample.GetMyString();
myButton().Content(box_value(myString));
}
Run the project
You can now build and run the project. Each time you click the button, the number in the button will increment.
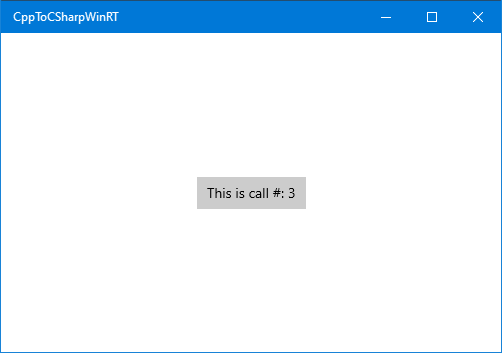
Tip
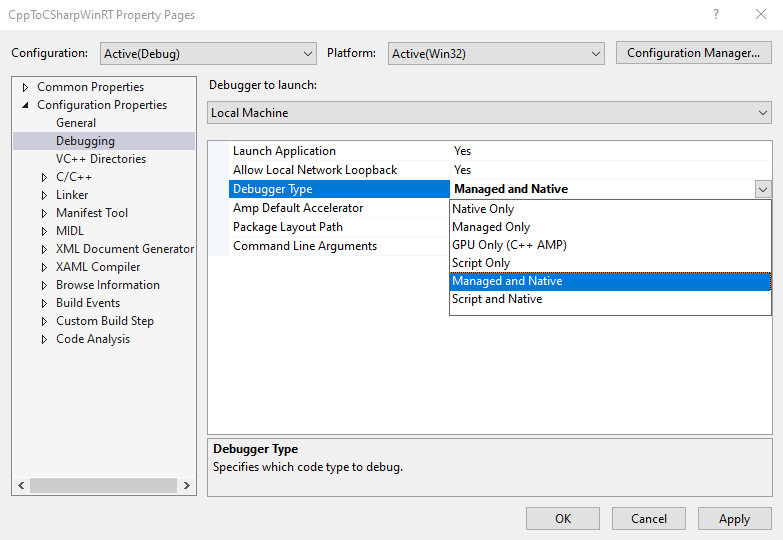
In Visual Studio, create the component project: In Solution Explorer, open the shortcut menu for the CppToCSharpWinRT project and choose Properties, and then choose Debugging under Configuration Properties. Set the Debugger Type to Managed and Native if you want to debug both the C# (managed) and C++ (native) code.
Application Minimum Version
The Application Minimum of the C# project version will control the version of .NET used to compile the application. For example, choosing Windows 10 Fall Creators Update (10.0; Build 16299) or later will enable .NET Standard 2.0 and Windows Arm64 processor support.
Tip
We recommend using Application Minimum versions lower than 16299 to avoid extra build configuration if .NET Standard 2.0 or Arm64 support is not necessary.
Configure for Windows 10 Fall Creators Update (10.0; Build 16299)
Follow these steps to enable .NET Standard 2.0 or Windows Arm64 support in the C# projects referenced from your C++/WinRT project.
In Visual Studio, go to the Solution Explorer and open the shortcut menu for the CppToCSharpWinRT project. Choose Properties and set the Universal Windows App Min version to Windows 10 Fall Creators Update (10.0; Build 16299) (or higher). Do the same for the SampleComponent project.
In Visual Studio, open the shortcut menu for the CppToCSharpWinRT project and choose Unload Project to open CppToCSharpWinRT.vcxproj in the text editor.
Copy and paste the following XML to the first PropertyGroup in CPPWinRTCSharpV2.vcxproj.
<!-- Start Custom .NET Native properties -->
<DotNetNativeVersion>2.2.12-rel-31116-00</DotNetNativeVersion>
<DotNetNativeSharedLibrary>2.2.8-rel-31116-00</DotNetNativeSharedLibrary>
<UWPCoreRuntimeSdkVersion>2.2.14</UWPCoreRuntimeSdkVersion>
<!--<NugetPath>$(USERPROFILE)\.nuget\packages</NugetPath>-->
<NugetPath>$(ProgramFiles)\Microsoft SDKs\UWPNuGetPackages</NugetPath>
<!-- End Custom .NET Native properties -->
The values for DotNetNativeVersion, DotNetNativeSharedLibrary, and UWPCoreRuntimeSdkVersion may vary depending on the version of Visual Studio. To set them to the correct values, open the %ProgramFiles(x86)%\Microsoft SDKs\UWPNuGetPackages and look at the sub-directory for each value in the table below. The %ProgramFiles(x86)%\Microsoft SDKs\UWPNuGetPackages\Microsoft.Net.Native.Compiler directory will have a sub-directory that contains an installed version of .NET native that starts with 2.2. In the example below, it is 2.2.12-rel-31116-00.
MSBuild Variable Directory Example DotNetNativeVersion %ProgramFiles(x86)%\Microsoft SDKs\UWPNuGetPackages\Microsoft.Net.Native.Compiler2.2.12-rel-31116-00DotNetNativeSharedLibrary %ProgramFiles(x86)%\Microsoft SDKs\UWPNuGetPackages\runtime.win10-x64.microsoft.net.native.sharedlibrary2.2.8-rel-31116-00UWPCoreRuntimeSdkVersion %ProgramFiles(x86)%\Microsoft SDKs\UWPNuGetPackages\Microsoft.Net.UWPCoreRuntimeSdk2.2.14
Note
There are multiple supported architectures for Microsoft.Net.Native.SharedLibrary. Replace x64 with the appropriate architecture. For example, the arm64 architecture would be in the %ProgramFiles(x86)%\Microsoft SDKs\UWPNuGetPackages\runtime.win10-arm64.microsoft.net.native.sharedlibrary directory.
Next, immediately after the first PropertyGroup, add the following (unaltered).
<!-- Start Custom .NET Native targets -->
<!-- Import all of the .NET Native / CoreCLR props at the beginning of the project -->
<Import Condition="'$(WindowsTargetPlatformMinVersion)' >= '10.0.16299.0'" Project="$(NugetPath)\Microsoft.Net.UWPCoreRuntimeSdk\$(UWPCoreRuntimeSdkVersion)\build\Microsoft.Net.UWPCoreRuntimeSdk.props" />
<Import Condition="'$(WindowsTargetPlatformMinVersion)' >= '10.0.16299.0'" Project="$(NugetPath)\runtime.win10-x86.Microsoft.Net.UWPCoreRuntimeSdk\$(UWPCoreRuntimeSdkVersion)\build\runtime.win10-x86.Microsoft.Net.UWPCoreRuntimeSdk.props" />
<Import Condition="'$(WindowsTargetPlatformMinVersion)' >= '10.0.16299.0'" Project="$(NugetPath)\runtime.win10-x64.Microsoft.Net.UWPCoreRuntimeSdk\$(UWPCoreRuntimeSdkVersion)\build\runtime.win10-x64.Microsoft.Net.UWPCoreRuntimeSdk.props" />
<Import Condition="'$(WindowsTargetPlatformMinVersion)' >= '10.0.16299.0'" Project="$(NugetPath)\runtime.win10-arm.Microsoft.Net.UWPCoreRuntimeSdk\$(UWPCoreRuntimeSdkVersion)\build\runtime.win10-arm.Microsoft.Net.UWPCoreRuntimeSdk.props" />
<Import Condition="'$(WindowsTargetPlatformMinVersion)' >= '10.0.16299.0'" Project="$(NugetPath)\Microsoft.Net.Native.Compiler\$(DotNetNativeVersion)\build\Microsoft.Net.Native.Compiler.props" />
<Import Condition="'$(WindowsTargetPlatformMinVersion)' >= '10.0.16299.0'" Project="$(NugetPath)\runtime.win10-x86.Microsoft.Net.Native.Compiler\$(DotNetNativeVersion)\build\runtime.win10-x86.Microsoft.Net.Native.Compiler.props" />
<Import Condition="'$(WindowsTargetPlatformMinVersion)' >= '10.0.16299.0'" Project="$(NugetPath)\runtime.win10-x64.Microsoft.Net.Native.Compiler\$(DotNetNativeVersion)\build\runtime.win10-x64.Microsoft.Net.Native.Compiler.props" />
<Import Condition="'$(WindowsTargetPlatformMinVersion)' >= '10.0.16299.0'" Project="$(NugetPath)\runtime.win10-arm.Microsoft.Net.Native.Compiler\$(DotNetNativeVersion)\build\runtime.win10-arm.Microsoft.Net.Native.Compiler.props" />
<Import Condition="'$(WindowsTargetPlatformMinVersion)' >= '10.0.16299.0'" Project="$(NugetPath)\runtime.win10-arm64.Microsoft.Net.Native.Compiler\$(DotNetNativeVersion)\build\runtime.win10-arm64.Microsoft.Net.Native.Compiler.props" />
<Import Condition="'$(WindowsTargetPlatformMinVersion)' >= '10.0.16299.0'" Project="$(NugetPath)\runtime.win10-x86.Microsoft.Net.Native.SharedLibrary\$(DotNetNativeSharedLibrary)\build\runtime.win10-x86.Microsoft.Net.Native.SharedLibrary.props" />
<Import Condition="'$(WindowsTargetPlatformMinVersion)' >= '10.0.16299.0'" Project="$(NugetPath)\runtime.win10-x64.Microsoft.Net.Native.SharedLibrary\$(DotNetNativeSharedLibrary)\build\runtime.win10-x64.Microsoft.Net.Native.SharedLibrary.props" />
<Import Condition="'$(WindowsTargetPlatformMinVersion)' >= '10.0.16299.0'" Project="$(NugetPath)\runtime.win10-arm.Microsoft.Net.Native.SharedLibrary\$(DotNetNativeSharedLibrary)\build\runtime.win10-arm.Microsoft.Net.Native.SharedLibrary.props" />
<Import Condition="'$(WindowsTargetPlatformMinVersion)' >= '10.0.16299.0'" Project="$(NugetPath)\runtime.win10-arm64.Microsoft.Net.Native.SharedLibrary\$(DotNetNativeSharedLibrary)\build\runtime.win10-arm64.Microsoft.Net.Native.SharedLibrary.props" />
<!-- End Custom .NET Native targets -->
At the end of the project file, just before the closing Project tag, add the following (unaltered).
<!-- Import all of the .NET Native / CoreCLR targets at the end of the project -->
<Import Condition="'$(WindowsTargetPlatformMinVersion)' >= '10.0.16299.0'" Project="$(NugetPath)\runtime.win10-x86.Microsoft.Net.UWPCoreRuntimeSdk\$(UWPCoreRuntimeSdkVersion)\build\runtime.win10-x86.Microsoft.Net.UWPCoreRuntimeSdk.targets" />
<Import Condition="'$(WindowsTargetPlatformMinVersion)' >= '10.0.16299.0'" Project="$(NugetPath)\runtime.win10-x64.Microsoft.Net.UWPCoreRuntimeSdk\$(UWPCoreRuntimeSdkVersion)\build\runtime.win10-x64.Microsoft.Net.UWPCoreRuntimeSdk.targets" />
<Import Condition="'$(WindowsTargetPlatformMinVersion)' >= '10.0.16299.0'" Project="$(NugetPath)\runtime.win10-arm.Microsoft.Net.UWPCoreRuntimeSdk\$(UWPCoreRuntimeSdkVersion)\build\runtime.win10-arm.Microsoft.Net.UWPCoreRuntimeSdk.targets" />
<Import Condition="'$(WindowsTargetPlatformMinVersion)' >= '10.0.16299.0'" Project="$(NugetPath)\Microsoft.Net.Native.Compiler\$(DotNetNativeVersion)\build\Microsoft.Net.Native.Compiler.targets" />
<Import Condition="'$(WindowsTargetPlatformMinVersion)' >= '10.0.16299.0'" Project="$(NugetPath)\runtime.win10-x86.Microsoft.Net.Native.Compiler\$(DotNetNativeVersion)\build\runtime.win10-x86.Microsoft.Net.Native.Compiler.targets" />
<Import Condition="'$(WindowsTargetPlatformMinVersion)' >= '10.0.16299.0'" Project="$(NugetPath)\runtime.win10-x64.Microsoft.Net.Native.Compiler\$(DotNetNativeVersion)\build\runtime.win10-x64.Microsoft.Net.Native.Compiler.targets" />
<Import Condition="'$(WindowsTargetPlatformMinVersion)' >= '10.0.16299.0'" Project="$(NugetPath)\runtime.win10-arm.Microsoft.Net.Native.Compiler\$(DotNetNativeVersion)\build\runtime.win10-arm.Microsoft.Net.Native.Compiler.targets" />
<Import Condition="'$(WindowsTargetPlatformMinVersion)' >= '10.0.16299.0'" Project="$(NugetPath)\runtime.win10-arm64.Microsoft.Net.Native.Compiler\$(DotNetNativeVersion)\build\runtime.win10-arm64.Microsoft.Net.Native.Compiler.targets" />
<Import Condition="'$(WindowsTargetPlatformMinVersion)' >= '10.0.16299.0'" Project="$(NugetPath)\runtime.win10-x86.Microsoft.Net.Native.SharedLibrary\$(DotNetNativeSharedLibrary)\build\runtime.win10-x86.Microsoft.Net.Native.SharedLibrary.targets" />
<Import Condition="'$(WindowsTargetPlatformMinVersion)' >= '10.0.16299.0'" Project="$(NugetPath)\runtime.win10-x64.Microsoft.Net.Native.SharedLibrary\$(DotNetNativeSharedLibrary)\build\runtime.win10-x64.Microsoft.Net.Native.SharedLibrary.targets" />
<Import Condition="'$(WindowsTargetPlatformMinVersion)' >= '10.0.16299.0'" Project="$(NugetPath)\runtime.win10-arm.Microsoft.Net.Native.SharedLibrary\$(DotNetNativeSharedLibrary)\build\runtime.win10-arm.Microsoft.Net.Native.SharedLibrary.targets" />
<Import Condition="'$(WindowsTargetPlatformMinVersion)' >= '10.0.16299.0'" Project="$(NugetPath)\runtime.win10-arm64.Microsoft.Net.Native.SharedLibrary\$(DotNetNativeSharedLibrary)\build\runtime.win10-arm64.Microsoft.Net.Native.SharedLibrary.targets" />
<!-- End Custom .NET Native targets -->
Reload the project file in Visual Studio. To do this, in the Visual Studio Solution Explorer, open the shortcut menu for the CppToCSharpWinRT project and choose Reload Project.
Building for .NET Native
It is recommended to build and test your application with the C# component built against .NET native. In Visual Studio, open the shortcut menu for the CppToCSharpWinRT project and choose Unload Project to open CppToCSharpWinRT.vcxproj in the text editor.
Next, set the UseDotNetNativeToolchain property to true in the Release and Arm64 configurations in the C++ project file.
In the Visual Studio Solution Explorer, open the shortcut menu for the CppToCSharpWinRT project and choose Reload Project.
<PropertyGroup Condition="'$(Configuration)'=='Release'" Label="Configuration">
...
<UseDotNetNativeToolchain>true</UseDotNetNativeToolchain>
</PropertyGroup>
<PropertyGroup Condition="'$(Platform)'=='Arm64'" Label="Configuration">
<UseDotNetNativeToolchain Condition="'$(UseDotNetNativeToolchain)'==''">true</UseDotNetNativeToolchain>
</PropertyGroup>
Referencing other C# nuget packages
If the C# component is referencing other nuget packages, the application's project file may need list file dependencies from the nuget package as deployment content. For example, if the C# component references the Newtonsoft.Json nuget package, the same nuget package and file dependency should also be referenced in the application project.
In the SampleComponent.csproj file, add the nuget package reference:
<PackageReference Include="Newtonsoft.Json">
<Version>13.0.1</Version>
</PackageReference>
In the CppToCSharpWinRT project, locate the packages.config file and add the appropriate nuget reference. This will install the nuget package into the solution's package folder.
In packages.config, add the same nuget package reference:
<package id="Newtonsoft.Json" version="13.0.1" targetFramework="native" developmentDependency="true" />
Then add the following to the application project file to reference the appropriate file dependency from the solution's package folder. For example, in CppToCSharpWinRT.vcxproj add the following:
<ItemGroup>
<None Include="..\packages\Newtonsoft.Json.13.0.1\lib\netstandard2.0\Newtonsoft.Json.dll">
<Link>%(Filename)%(Extension)</Link>
<DeploymentContent>true</DeploymentContent>
</None>
</ItemGroup>