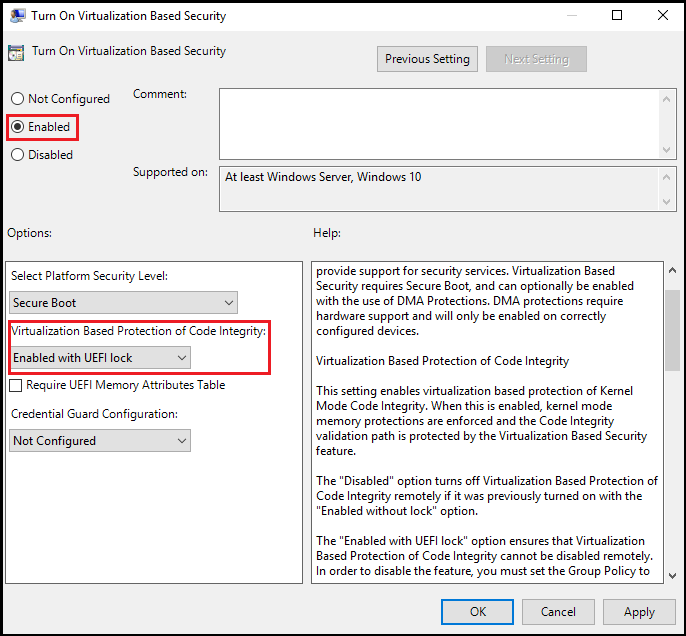
Enable virtualization-based protection of code integrity
Warning
Some applications and hardware device drivers may be incompatible with memory integrity. This incompatibility can cause devices or software to malfunction and in rare cases may result in a boot failure (blue screen). Such issues may occur after memory integrity has been turned on or during the enablement process itself. If compatibility issues occur, see Troubleshooting for remediation steps.
Memory integrity is a Virtualization-based security (VBS) feature available in Windows. Memory integrity and VBS improve the threat model of Windows and provide stronger protections against malware trying to exploit the Windows kernel. VBS uses the Windows hypervisor to create an isolated virtual environment that becomes the root of trust of the OS that assumes the kernel can be compromised. Memory integrity is a critical component that protects and hardens Windows by running kernel mode code integrity within the isolated virtual environment of VBS. Memory integrity also restricts kernel memory allocations that could be used to compromise the system.
Note
- Memory integrity is sometimes referred to as hypervisor-protected code integrity (HVCI) or hypervisor enforced code integrity, and was originally released as part of Device Guard. Device Guard is no longer used except to locate memory integrity and VBS settings in Group Policy or the Windows registry.
- Memory integrity works better with Intel Kabylake and higher processors with Mode-Based Execution Control, and AMD Zen 2 and higher processors with Guest Mode Execute Trap capabilities. Older processors rely on an emulation of these features, called Restricted User Mode, and will have a bigger impact on performance. When nested virtualization is enabled, memory integrity works better when the VM is version >= 9.3.
Memory integrity features
- Protects modification of the Control Flow Guard (CFG) bitmap for kernel mode drivers.
- Protects the kernel mode code integrity process that ensures that other trusted kernel processes have a valid certificate.
How to turn on memory integrity
To enable memory integrity on Windows devices with supporting hardware throughout an enterprise, use any of these options:
Enable memory integrity using Windows Security
Memory integrity can be turned on in Windows Security settings and found at Windows Security > Device security > Core isolation details > Memory integrity. For more information, see Device protection in Windows Security.
Beginning with Windows 11 22H2, Windows Security shows a warning if memory integrity is turned off. The warning indicator also appears on the Windows Security icon in the Windows Taskbar and in the Windows Notification Center. The user can dismiss the warning from within Windows Security.
Validate enabled VBS and memory integrity features
Use Win32_DeviceGuard WMI class
Windows 10, Windows 11, and Windows Server 2016 and higher have a WMI class for VBS-related properties and features: Win32_DeviceGuard. This class can be queried from an elevated Windows PowerShell session by using the following command:
Get-CimInstance -ClassName Win32_DeviceGuard -Namespace root\Microsoft\Windows\DeviceGuard
Note
Mode Based Execution Control property will only be listed as available starting with Windows 10 version 1803 and Windows 11 version 21H2. This value is reported for both Intel's Mode-Based Execution Control and AMD's Guest Mode Execute Trap capabilities.
The output of this command provides details of the available hardware-based security features and those features that are currently enabled.
InstanceIdentifier: A string that is unique to a particular device and set by WMI.
Version: This field lists the version of this WMI class. The only valid value now is 1.0.
AvailableSecurityProperties: This field helps to enumerate and report state on the relevant security properties for VBS and memory integrity.
Value Description 0 If present, no relevant properties exist on the device. 1 If present, hypervisor support is available. 2 If present, Secure Boot is available. 3 If present, DMA protection is available. 4 If present, Secure Memory Overwrite is available. 5 If present, NX protections are available. 6 If present, SMM mitigations are available. 7 If present, MBEC/GMET is available. 8 If present, APIC virtualization is available. CodeIntegrityPolicyEnforcementStatus: This field indicates the code integrity policy enforcement status.
Value Description 0 Off 1 Audit. 2 Enforced. RequiredSecurityProperties: This field describes the required security properties to enable VBS.
Value Description 0 Nothing is required. 1 If present, hypervisor support is needed. 2 If present, Secure Boot is needed. 3 If present, DMA protection is needed. 4 If present, Secure Memory Overwrite is needed. 5 If present, NX protections are needed. 6 If present, SMM mitigations are needed. 7 If present, MBEC/GMET is needed. SecurityServicesConfigured: This field indicates whether Credential Guard or memory integrity is configured.
Value Description 0 No services are configured. 1 If present, Credential Guard is configured. 2 If present, memory integrity is configured. 3 If present, System Guard Secure Launch is configured. 4 If present, SMM Firmware Measurement is configured. 5 If present, Kernel-mode Hardware-enforced Stack Protection is configured. 6 If present, Kernel-mode Hardware-enforced Stack Protection is configured in Audit mode. 7 If present, Hypervisor-Enforced Paging Translation is configured. SecurityServicesRunning: This field indicates whether Credential Guard or memory integrity is running.
Value Description 0 No services running. 1 If present, Credential Guard is running. 2 If present, memory integrity is running. 3 If present, System Guard Secure Launch is running. 4 If present, SMM Firmware Measurement is running. 5 If present, Kernel-mode Hardware-enforced Stack Protection is running. 6 If present, Kernel-mode Hardware-enforced Stack Protection is running in Audit mode. 7 If present, Hypervisor-Enforced Paging Translation is running. SmmIsolationLevel: This field indicates the SMM isolation level.
UsermodeCodeIntegrityPolicyEnforcementStatus: This field indicates the user mode code integrity policy enforcement status.
Value Description 0 Off 1 Audit. 2 Enforced. VirtualizationBasedSecurityStatus: This field indicates whether VBS is enabled and running.
Value Description 0 VBS isn't enabled. 1 VBS is enabled but not running. 2 VBS is enabled and running. VirtualMachineIsolation: This field indicates whether virtual machine isolation is enabled.
VirtualMachineIsolationProperties: This field indicates the set of virtual machine isolation properties that are available.
Value Description 1 AMD SEV-SNP 2 Virtualization-based Security 3 Intel TDX
Use msinfo32.exe
Another method to determine the available and enabled VBS features is to run msinfo32.exe from an elevated PowerShell session. When you run this program, the VBS features are displayed at the bottom of the System Summary section.
Troubleshooting
- If a device driver fails to load or crashes at runtime, you might be able to update the driver using Device Manager.
- If you experience a critical error during boot or your system is unstable after turning on memory integrity, you can recover using the Windows Recovery Environment (Windows RE).
First, disable any policies that are used to enable VBS and memory integrity, for example Group Policy.
Then, boot to Windows RE on the affected computer, see Windows RE Technical Reference.
After logging in to Windows RE, set the memory integrity registry key to off:
reg add "HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\DeviceGuard\Scenarios\HypervisorEnforcedCodeIntegrity" /v "Enabled" /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /fFinally, restart your device.
Note
If you turned on memory integrity with UEFI lock, you will need to disable Secure Boot to complete the Windows RE recovery steps.
Memory integrity deployment in virtual machines
Memory integrity can protect a Hyper-V virtual machine, just as it would a physical machine. The steps to enable memory integrity are the same from within the virtual machine.
Memory integrity protects against malware running in the guest virtual machine. It doesn't provide extra protection from the host administrator. From the host, you can disable memory integrity for a virtual machine:
Set-VMSecurity -VMName <VMName> -VirtualizationBasedSecurityOptOut $true
Requirements for running memory integrity in Hyper-V virtual machines
- The Hyper-V host must run at least Windows Server 2016 or Windows 10 version 1607.
- The Hyper-V virtual machine must be Generation 2, and running at least Windows Server 2016 or Windows 10.
- Memory integrity and nested virtualization can be enabled at the same time. To enable the Hyper-V role on the virtual machine, you must first install the Hyper-V role in a Windows nested virtualization environment.
- Virtual Fibre Channel adapters aren't compatible with memory integrity. Before attaching a virtual Fibre Channel Adapter to a virtual machine, you must first opt out of Virtualization-based security using
Set-VMSecurity. - The AllowFullSCSICommandSet option for pass-through disks isn't compatible with memory integrity. Before configuring a pass-through disk with AllowFullSCSICommandSet, you must first opt out of Virtualization-based security using
Set-VMSecurity.