Enable DNS Logging and Diagnostics
Learn how to enable enhanced DNS logging, auditing, and analytic events for the DNS Server role in Windows Server. DNS logging and diagnostics provide detailed information about DNS server operations, including zone changes, dynamic updates, and DNSSEC operations. DNS logging and diagnostics can help you monitor DNS server performance, troubleshoot DNS issues, and track DNS server activity.
Prerequisites
Before you enable DNS logging and diagnostics, ensure that you have:
A Windows Server with the DNS Server role installed, including the DNS Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT).
Administrative privileges on the server.
A basic understanding of DNS server operations.
View DNS server logs
DNS audit logs are enabled by default, and don't significantly affect DNS server performance. DNS server audit events enable change tracking on the DNS server. An audit event is logged each time server, zone, or resource record settings are changed. Audit events include operational events such as dynamic updates, zone transfers, and DNSSEC zone signing and unsigning. To view DNS server logs:
Select the Start button, type Event viewer, open Event viewer from the best match list.
In Event Viewer, navigate to Applications and Services > Logs > Microsoft > Windows > DNS-Server.
Select Audit from the navigation pane to view DNS audit logs.
Audit events
The following table summarizes DNS server audit events.
| Event ID | Type | Category | Level | Event text |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 513 | Zone delete |
Zone operations | Informational | The zone %1 was deleted. |
| 514 | Zone updated |
Zone operations | Informational | The zone %1 was updated. The %2 setting has been set to %3. |
| 515 | Record create |
Zone operations | Informational | A resource record of type %1, name %2, TTL %3 and RDATA %5 was created in scope %7 of zone %6. |
| 516 | Record delete |
Zone operations | Informational | A resource record of type %1, name %2 and RDATA %5 was deleted from scope %7 of zone %6. |
| 517 | RRSET delete |
Zone operations | Informational | All resource records of type %1, name %2 were deleted from scope %4 of zone %3. |
| 518 | Node delete |
Zone operations | Informational | All resource records at Node name %1 were deleted from scope %3 of zone %2. |
| 519 | Record create - dynamic update |
Dynamic update | Informational | A resource record of type %1, name %2, TTL %3 and RDATA %5 was created in scope %7 of zone %6 via dynamic update from IP Address %8. |
| 520 | Record delete - dynamic update |
Dynamic update | Informational | A resource record of type %1, name %2 and RDATA %5 was deleted from scope %7 of zone %6 via dynamic update from IP Address %8. |
| 521 | Record scavenge |
Aging | Informational | A resource record of type %1, name %2, TTL %3 and RDATA %5 was scavenged from scope %7 of zone %6. |
| 522 | Zone scope create |
Zone operations | Informational | The scope %1 was created in zone %2. |
| 523 | Zone scope delete |
Zone operations | Informational | The scope %1 was created in zone %2. |
| 525 | Zone sign |
Online signing | Informational | The zone %1 was signed with following properties... |
| 526 | Zone unsign |
Online signing | Informational | The zone %1 was unsigned. |
| 527 | Zone re-sign |
Online signing | Informational | The zone %1 was re-signed with following properties... |
| 528 | Key rollover start |
DNSSEC operations | Informational | Rollover was started on the type %1 with GUID %2 of zone %3. |
| 529 | Key rollover end |
DNSSEC operations | Informational | Rollover was completed on the type %1 with GUID %2 of zone %3. |
| 530 | Key retire |
DNSSEC operations | Informational | The type %1 with GUID %2 of zone %3 was marked for retiral. The key will be removed after the rollover completion. |
| 531 | Key rollover triggered |
DNSSEC operations | Informational | Manual rollover was triggered on the type %1 with GUID %2 of zone %3. |
| 533 | Key poke rollover |
DNSSEC operations | Warning | The keys signing key with GUID %1 on zone %2 that was waiting for a Delegation Signer(DS) update on the parent has been forced to move to rollover completion. |
| 534 | Export DNSSEC |
DNSSEC operations | Informational | DNSSEC setting metadata was exported %1 key signing key metadata from zone %2. |
| 535 | Import DNSSEC |
DNSSEC operations | Informational | DNSSEC setting metadata was imported on zone %1. |
| 536 | Cache purge |
DNSSEC operations | Informational | A record of type %1, QNAME %2 was purged from scope %3 in cache. |
| 537 | Forwarder reset |
Cache operations | Informational | The forwarder list on scope %2 has been reset to %1. |
| 540 | Root hints |
Configuration | Informational | The root hints have been modified. |
| 541 | Server setting |
Configuration | Informational | The setting %1 on scope %2 has been set to %3. |
| 542 | Server scope create |
Configuration | Informational | The scope %1 of DNS server was created. |
| 543 | Server scope delete |
Configuration | Informational | The scope %1 of DNS server was deleted. |
| 544 | Add trust point DNSKEY |
Configuration | Informational | The DNSKEY with Key Protocol %2, Base64 Data %4 and Crypto Algorithm %5 has been added at the trust point %1. |
| 545 | Add trust point DS |
Configuration | Informational | The DS with Key Tag: %2, Digest Type: %3, Digest: %5 and Crypto Algorithm: %6 has been added at the trust point %1. |
| 546 | Remove trust point |
Configuration | Informational | The trust point at %1 of type %2 has been removed. |
| 547 | Add trust point root |
DNSSEC operations | Informational | The trust anchor for the root zone has been added. |
| 548 | Restart server |
DNSSEC operations | Informational | A request to restart the DNS server service has been received. |
| 549 | Clear debug logs |
DNSSEC operations | Informational | The debug logs have been cleared from %1 on DNS server. |
| 550 | Write dirty zones |
DNSSEC operations | Informational | The in-memory contents of all the zones on DNS server have been flushed to their respective files. |
| 551 | Clear statistics |
Server operations | Informational | All the statistical data for the DNS server has been cleared. |
| 552 | Start scavenging |
Server operations | Informational | A resource record scavenging cycle has been started on the DNS Server. |
| 553 | Enlist directory partition |
Server operations | Informational | 1% |
| 554 | Abort scavenging |
Server operations | Informational | The resource record scavenging cycle has been terminated on the DNS Server. |
| 555 | Prepare for demotion |
Server operations | Informational | The DNS server has been prepared for demotion by removing references to it from all zones stored in the Active Directory. |
| 556 | Write root hints |
Server operations | Informational | The information about the root hints on the DNS server has been written back to the persistent storage. |
| 557 | Listen address |
Server operations | Informational | The addresses on which DNS server will listen has been changed to %1. |
| 558 | Active refresh trust points |
Server operations | Informational | An immediate RFC 5011 active refresh has been scheduled for all trust points. |
| 559 | Pause zone |
Server operations | Informational | The zone %1 is paused. |
| 560 | Resume zone |
Server operations | Informational | The zone %1 is resumed. |
| 561 | Reload zone |
DNSSEC operations | Informational | The data for zone %1 has been reloaded from %2. |
| 562 | Refresh zone |
Zone operations | Informational | The data for zone %1 has been refreshed from the primary server %2. |
| 563 | Expire zone |
Zone operations | Informational | The secondary zone %1 has been expired and new data has been requested from the primary server %2. |
| 564 | Update from DS |
Zone operations | Informational | The zone %1 has been reloaded from the Active Directory. |
| 565 | Write and notify |
Zone operations | Informational | The content of the zone %1 has been written to the disk and the notification has been sent to all the notify servers. |
| 566 | Force aging |
Zone operations | Informational | All DNS records at the node %1 in the zone %2 will have their aging time stamp set to the current time.%3 |
| 567 | Scavenge servers |
Zone operations | Informational | The Active Directory-integrated zone %1 has been updated. Only %2 can run scavenging. |
| 568 | Transfer primary key server |
Zone operations | Informational | The key management role for zone %1 has been %2.%3 |
| 569 | Add SKD |
Zone operations | Informational | A %1 singing key (%2) descriptor has been added on the zone %3 with following properties: KeyId=%4; KeyType=%5; CurrentState=%6; KeyStorageProvider=%7; StoreKeysInAD=%8; CryptoAlgorithm=%9; KeyLength=%10; DnsKeySignatureValidityPeriod=%11; DSSignatureValidityPeriod=%12; ZoneSignatureValidityPeriod=%13; InitialRolloverOffset=%14; RolloverPeriod=%15; RolloverType=%16; NextRolloverAction=%17; LastRolloverTime=%18; NextRolloverTime=%19; CurrentRolloverStatus=%20; ActiveKey=%21; StandbyKey=%22; NextKey=%23. The zone will be resigned with the %2 generated with these properties. |
| 570 | Modify SKD |
Zone operations | Informational | A %1 singing key (%2) descriptor with GUID %3 has been updated on the zone %4. The properties of this %2 descriptor have been set to: KeyId=%5; KeyType=%6; CurrentState=%7; KeyStorageProvider=%8; StoreKeysInAD=%9; CryptoAlgorithm=%10; KeyLength=%11; DnsKeySignatureValidityPeriod=%12; DSSignatureValidityPeriod=%13; ZoneSignatureValidityPeriod=%14; InitialRolloverOffset=%15; RolloverPeriod=%16; RolloverType=%17; NextRolloverAction=%18; LastRolloverTime=%19; NextRolloverTime=%20; CurrentRolloverStatus=%21; ActiveKey=%22; StandbyKey=%23; NextKey=%24. The zone will be resigned with the %2 generated with these properties. |
| 571 | Delete SKD |
DNSSEC operations | Informational | A %1 singing key (%2) descriptor %4 has been removed from the zone %3. |
| 572 | Modify SKD state |
DNSSEC operations | Informational | The state of the %1 signing key (%2) %3 has been modified on zone %4. The new active key is %5, standby key is %6 and next key is %7. |
| 573 | Add delegation |
DNSSEC operations | Informational | A delegation for %1 in the scope %2 of zone %3 with the name server %4 has been added. |
| 574 | Create client subnet record |
DNSSEC operations | Informational | The client subnet record with name %1 value %2 has been added to the client subnet map. |
| 575 | Delete client subnet record |
DNSSEC operations | Informational | The client subnet record with name %1 has been deleted from the client subnet map. |
| 576 | Update client subnet record |
Zone operations | Informational | The client subnet record with name %1 has been updated from the client subnet map. The new client subnets that it refers to are %2. |
| 577 | Create server level policy |
Policy operations | Informational | A server level policy %6 for %1 has been created on server %2 with following properties: ProcessingOrder:%3; Criteria:%4; Action:%5. |
| 578 | Create zone level policy |
Policy operations | Informational | A zone level policy %8 for %1 has been created on zone %6 on server %2 with following properties: ProcessingOrder:%3; Criteria:%4; Action:%5; Scopes:%7. |
| 579 | Create forwarding policy |
Policy operations | Informational | A forwarding policy %6 has been created on server %2 with following properties: ProcessingOrder:%3; Criteria:%4; Action:%5; Scope:%1. |
| 580 | Delete server level policy |
Policy operations | Informational | The server level policy %1 has been deleted from server %2. |
| 581 | Delete zone level policy |
Policy operations | Informational | The zone level policy %1 has been deleted from zone %3 on server %2. |
| 582 | Delete forwarding policy |
Policy operations | Informational | The forwarding policy %1 has been deleted from server %2. |
Enable analytical event logging
Enhanced DNS logging and diagnostics in Windows Server includes DNS Audit events and DNS Analytic events. DNS audit logs are enabled by default, and don't significantly affect DNS server performance.
DNS analytical logs aren't enabled by default and typically will only affect DNS server performance at high DNS query rates. For example, a DNS server running on modern hardware that's receiving 100,000 queries per second (QPS) can experience a performance degradation of 5% when analytic logs are enabled. There's no apparent performance impact for query rates of 50,000 QPS and lower. However, we recommend you monitor DNS server performance whenever logging is enabled.
To enable DNS diagnostic logging:
From the Applications and Services > Logs > Microsoft > Windows > DNS-Server node, right-select DNS-Server, select View, then select Show Analytic and Debug Logs. The Analytical log is displayed.
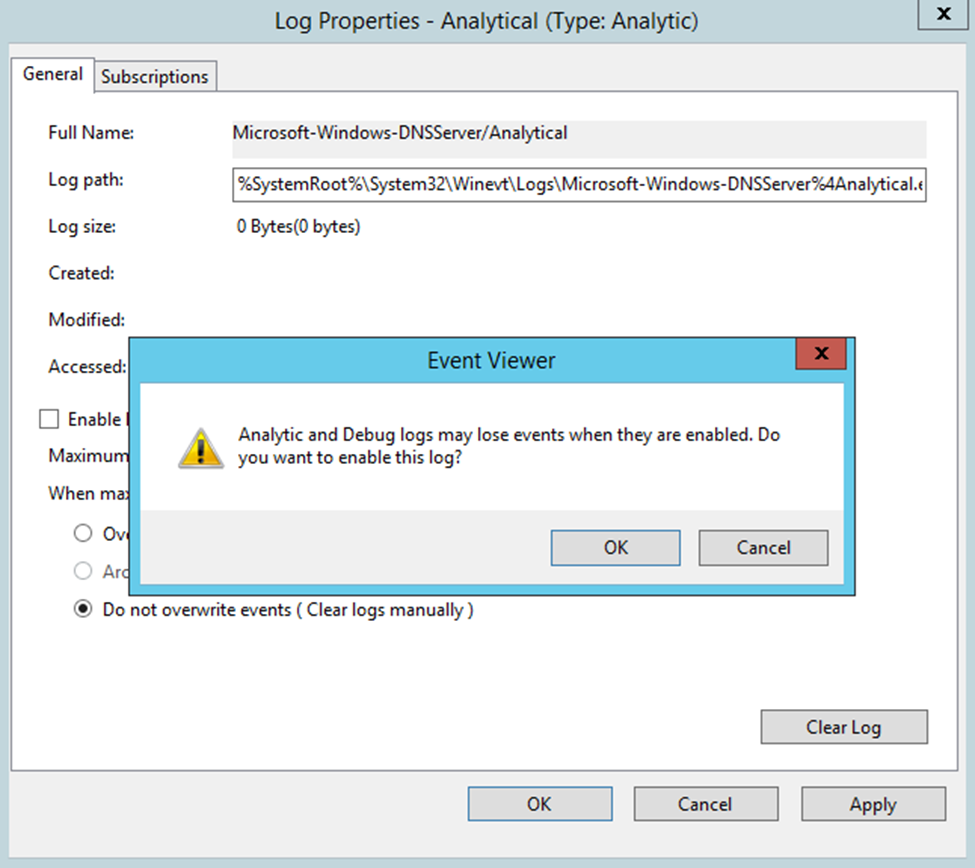
Right-click Analytical and then select Properties.
If you want to query and view the logs from event viewer, choose When maximum event log size is reached, select Do not overwrite events (Clear logs manually), select the Enable logging checkbox, and then select OK when asked whether you want to enable this log.
If you want to enable circular logging, choose Overwrite as needed (oldest events first) and select Enable logging. After selecting OK, a query error will display. Logging is taking place even though this error is displayed. The error only means you can't view the events that are currently being logged in event viewer.
Select OK to enable the DNS Server Analytic event log.
Analytic logs are by default written to the file %SystemRoot%\System32\Winevt\Logs\Microsoft-Windows-DNSServer%4Analytical.etl. Events displayed in the DNS server audit and analytic event logs are treated in the next section.
Analytic events
DNS server analytic events enable activity tracking on the DNS server. An analytic event is logged each time the server sends or receives DNS information. The following table summarizes DNS server analytic events.
| Event ID | Type | Category | Level | Event text |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 257 | Response success |
Lookup | Informational | RESPONSE_SUCCESS: TCP=%1; InterfaceIP=%2; Destination=%3; AA=%4; AD=%5; QNAME=%6; QTYPE=%7; XID=%8; DNSSEC=%9; RCODE=%10; Port=%11; Flags=%12; Scope=%13; Zone=%14; PolicyName=%15; PacketData=%17 |
| 258 | Response failure |
Lookup | Error | RESPONSE_FAILURE: TCP=%1; InterfaceIP=%2; Reason=%3; Destination=%4; QNAME=%5; QTYPE=%6; XID=%7; RCODE=%8; Port=%9; Flags=%10; Zone=%11; PolicyName=%12; PacketData=%14 |
| 259 | Ignored query |
Lookup | Error | IGNORED_QUERY: TCP=%1; InterfaceIP=%2; Reason=%3; QNAME=%4; QTYPE=%5; XID=%6; Zone=%7; PolicyName=%8 |
| 260 | Query out |
Recursive query | Informational | RECURSE_QUERY_OUT: TCP=%1; Destination=%2; InterfaceIP=%3; RD=%4; QNAME=%5; QTYPE=%6; XID=%7; Port=%8; Flags=%9; ServerScope=%10; CacheScope=%11; PolicyName=%12; PacketData=%14 |
| 261 | Response in |
Recursive query | Informational | RECURSE_RESPONSE_IN: TCP=%1; Source=%2; InterfaceIP=%3; AA=%4; AD=%5; QNAME=%6; QTYPE=%7; XID=%8; Port=%9; Flags=%10; ServerScope=%11; CacheScope=%12; PacketData=%14 |
| 262 | Recursive query |
Error | RECURSE_QUERY_TIMEOUT: TCP=%1; InterfaceIP=%2; Destination=%3; QNAME=%4; QTYPE=%5; XID=%6; Port=%7; Flags=%8; ServerScope=%9; CacheScope=%10 |
|
| 263 | Update in |
Dynamic update | Informational | DYN_UPDATE_RECV: TCP=%1; InterfaceIP=%2; Source=%3; QNAME=%4; XID=%5; Port=%6; Flags=%7; SECURE=%8; PacketData=%10 |
| 264 | Update response |
Dynamic Update | Informational | DYN_UPDATE_RESPONSE: TCP=%1; InterfaceIP=%2; Destination=%3; QNAME=%4; XID=%5; ZoneScope=%6; Zone=%7; RCODE=%8; PolicyName=%9; PacketData=%11 |
| 265 | IXFR request out |
Zone XFR | Informational | IXFR_REQ_OUT: TCP=%1; InterfaceIP=%2; Source=%3; QNAME=%4; XID=%5; ZoneScope=%6; Zone=%7; PacketData=%9 |
| 266 | IXFR request in |
Zone XFR | Informational | IXFR_REQ_RECV: TCP=%1; InterfaceIP=%2; Source=%3; QNAME=%4; XID=%5; ZoneScope=%6; Zone=%7; PacketData=%9 |
| 267 | 267 IXFR response out |
Zone XFR | Informational | IXFR_RESP_OUT: TCP=%1; InterfaceIP=%2; Destination=%3; QNAME=%4; XID=%5; ZoneScope=%6; Zone=%7; RCODE=%8; PacketData=%10 |
| 268 | IXFR response in |
Zone XFR | Informational | IXFR_RESP_RECV: TCP=%1; InterfaceIP=%2; Destination=%3; QNAME=%4; XID=%5; ZoneScope=%6; Zone=%7; RCODE=%8; PacketData=%10 |
| 269 | AXFR request out |
Zone XFR | Informational | AXFR_REQ_OUT: TCP=%1; Source=%2; InterfaceIP=%3; QNAME=%4; XID=%5; ZoneScope=%6; Zone=%7; PacketData=%9 |
| 270 | AXFR request in |
Zone XFR | Informational | AXFR_REQ_RECV: TCP=%1; Source=%2; InterfaceIP=%3; QNAME=%4; XID=%5; ZoneScope=%6; Zone=%7; PacketData=%9 |
| 271 | AXFR response out |
Zone XFR | Informational | AXFR_RESP_OUT: TCP=%1; InterfaceIP=%2; Destination=%3; QNAME=%4; XID=%5; ZoneScope=%6; Zone=%7; RCODE=%8 |
| 272 | AXFR response in |
Zone XFR | Informational | AXFR_RESP_RECV: TCP=%1; InterfaceIP=%2; Destination=%3; QNAME=%4; XID=%5; ZoneScope=%6; Zone=%7; RCODE=%8 |
| 273 | XFR notification in |
Zone XFR | Informational | XFR_NOTIFY_RECV: Source=%1; InterfaceIP=%2; QNAME=%3; ZoneScope=%4; Zone=%5; PacketData=%7 |
| 274 | XFR notification out |
Zone XFR | Informational | XFR_NOTIFY_OUT: Destination=%1; InterfaceIP=%2; QNAME=%3; ZoneScope=%4; Zone=%5; PacketData=%7 |
| 275 | XFR notify ACK in |
Zone XFR | Informational | XFR_NOTIFY_ACK_IN: Source=%1; InterfaceIP=%2; PacketData=%4 |
| 276 | XFR notify ACK out |
Zone XFR | Informational | XFR_NOTIFY_ACK_OUT: Destination=%1; InterfaceIP=%2; Zone=%3; PacketData=%5 |
| 277 | Update forward |
Dynamic update | Informational | DYN_UPDATE_FORWARD: TCP=%1; ForwardInterfaceIP=%2; Destination=%3; QNAME=%4; XID=%5; ZoneScope=%6; Zone=%7; RCODE=%8; PacketData=%10 |
| 278 | Update response in |
Dynamic update | Informational | DYN_UPDATE_RESPONSE_IN: TCP=%1; InterfaceIP=%2; Source=%3; QNAME=%4; XID=%5; ZoneScope=%6; Zone=%7; RCODE=%8; PacketData=%10 |
| 279 | Internal lookup CNAME |
Lookup | Informational | INTERNAL_LOOKUP_CNAME: TCP=%1; InterfaceIP=%2; Source=%3; RD=%4; QNAME=%5; QTYPE=%6; Port=%7; Flags=%8; XID=%9; PacketData=%11 |
| 280 | Internal lookup |
Lookup | Informational | INTERNAL_LOOKUP_ADDITIONAL: TCP=%1; InterfaceIP=%2; Source=%3; RD=%4; QNAME=%5; QTYPE=%6; Port=%7; Flags=%8; XID=%9; PacketData=%11 |
Event Tracing
DNS logs are compatible with Event Tracing for Windows (ETW) consumer applications such as logman, tracelog, and message analyzer. For more information about using event tracing, see About Event Tracing.
You can use ETW consumers such as tracelog.exe with DNS server audit and analytic events by specifying a GUID of {EB79061A-A566-4698-9119-3ED2807060E7}.
You can get tracelog.exe by downloading and installing the Windows Driver Kit (WDK). Tracelog.exe is included when you install the WDK, Visual Studio, and the Windows SDK for desktop apps. For information about downloading the kits, see Windows Hardware Downloads. For example, when you download and install Windows Driver Kit (WDK) and accept the default installation path, tracelog.exe is available at: C:\Program Files (x86)\WindowsKits\10\bin\10.0.26100.0\x64\tracelog.exe.
For more information about using tracelog.exe, see Tracelog Command Syntax.
The following examples demonstrate how to use tracelog.exe with DNS audit and analytic event logs:
The following command enables both analytical and audit logging:
tracelog.exe -start Dns -guid #{EB79061A-A566-4698-9119-3ED2807060E7} -level 5 -matchanykw 0xFFFFFFFF -f C:\analytic_audit.etl
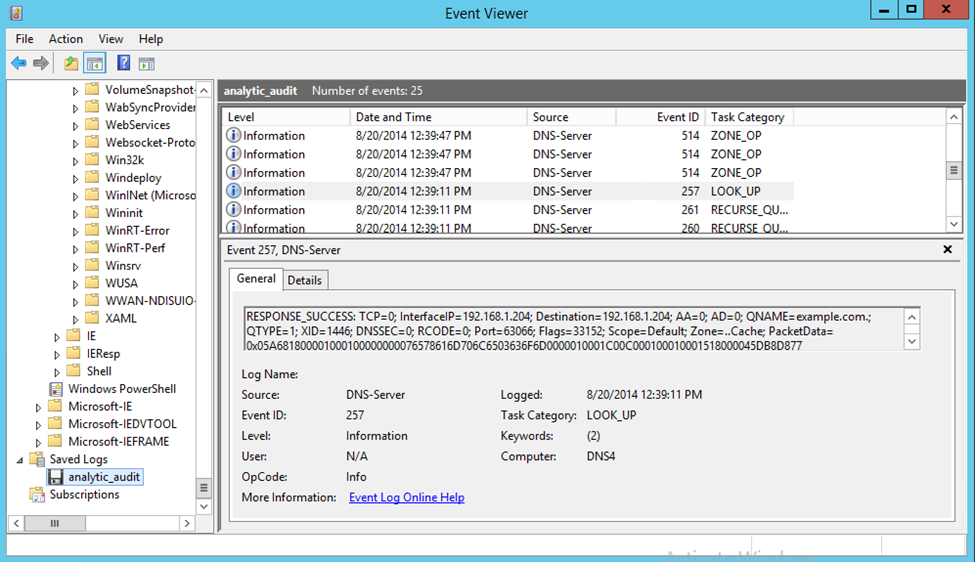
While the trace is active, all analytical and audit events are recorded in the C:\analytic_audit.etl file that was specified on the command line. You can stop tracing by issuing a stop command:
tracelog –stop Dns
After stopping the trace, you can view the .etl file in Event Viewer by selecting Action and then selecting Open Saved Log.
The following example enables only the analytical channel and matches only the keywords to 0x7FFFF:
tracelog.exe -start Dns -guid #{EB79061A-A566-4698-9119-3ED2807060E7} -level 5 -matchanykw 0x7FFFF -f C:\analytic.etl
A logging level of 5 is used in the previous examples. The following table shows the available logging levels.
| Logging level | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 (None) | Logging OFF |
| 1 (Critical) | Only critical events are logged, for example process exit or termination. If no logging level is given, level 1 is used by default. |
| 2 (Error) | Only severe error events are logged, for example failures to complete a required task. |
| 3 (Warning) | Errors that can cause a service issue, but are acceptable or recoverable. For example, the first attempt to contact a forwarder fails. |
| 4 (Informational) | High-level events are recorded in the event log. These events might include one message for each major task performed by the service. Use this setting to begin an investigation when the location of the problem is in doubt. For example, a scavenger thread was started. |
| 5 (Verbose) | All events are logged. Level 5 provides a complete log of the operation of the service. Use this level when the problem is traced to a particular category or a small set of categories. |
Performance considerations
DNS server performance can be affected when logging is enabled, however the enhanced DNS logging and diagnostics feature in Windows Server is designed to lower the impact on performance. This article discusses DNS server performance considerations when logging is enabled.
Debug logging
Before the introduction of DNS analytic logs, DNS debug logging was an available method to monitor DNS transactions. DNS debug logging isn't the same as the enhanced DNS logging and diagnostics feature discussed in this article. Debug logging is a tool that also can be used for DNS logging and diagnostics. The DNS debug log provides detailed data about all DNS information sent and received by the DNS server. The information gathered is similar to the data that can be gathered using packet capture tools such as network monitor.
Debug logging can affect overall server performance and also consumes disk space. We recommended you enable debug logging temporarily only when detailed DNS transaction information is needed.
To select and enable debug logging options on the DNS server, follow these steps:
Select Start, type DNS Manager, and then select DNS Manager from the best match list.
In the console tree, right-click the applicable DNS server, then select Properties.
Select the Debug Logging tab.
From the Properties dialog box, check the Log packets for debugging box, and then select the events that you want the DNS server to record for debug logging.
The following DNS debug logging options are available:
Direction of packets
Send - Packets sent by the DNS server are logged in the DNS server log file.
Receive - Packets received by the DNS server are logged in the log file.
Content of packets
Standard queries - Specifies that packets containing standard queries (per RFC 1034) are logged in the DNS server log file.
Updates - Specifies that packets containing dynamic updates (per RFC 2136) are logged in the DNS server log file.
Notifies - Specifies that packets containing notifications (per RFC 1996) are logged in the DNS server log file.
Transport protocol
UDP - Specifies that packets sent and received over UDP are logged in the DNS server log file.
TCP - Specifies that packets sent and received over TCP are logged in the DNS server log file.
Type of packet
Request - Specifies that request packets are logged in the DNS server log file (a request packet is characterized by a QR bit set to 0 in the DNS message header).
Response - Specifies that response packets are logged in the DNS server log file (a response packet is characterized by a QR bit set to 1 in the DNS message header).
Enable filtering based on IP address Provides filtering of packets logged in the DNS server log file. This option allows logging of packets sent from specific IP addresses to a DNS server, or from a DNS server to specific IP addresses.
File name - Lets you specify the name and location of the DNS server log file.
For example:
dns.log specifies that the DNS server log file should be saved as dns.log in the
<systemroot>zSystem32Dns directory. Remember to replace<systemroot>with the actual path to the Windows directory on your computer.temp\dns.log specifies that the DNS server log file should be saved as dns.log in the
<systemroot>\Temp directory. Remember to replace<systemroot>with the actual path to the Windows directory on your computer.
Log file maximum size limit Lets you set the maximum file size for the DNS server log file. When the specified maximum size of the DNS server log file is reached, the DNS server overwrites the oldest packet information with new information. Note: If left unspecified, the DNS server log file's size can take up a large amount of hard disk space.
By default, all debug logging options are disabled. When selectively enabled, the DNS Server service can perform trace-level logging of selected types of events or messages for general troubleshooting and debugging of the server.
Debug logging can be resource intensive, affecting overall server performance, and consuming disk space. Therefore, it should only be used temporarily when more detailed information about server performance is needed.
Dns.log contains debug logging activity. By default, the log is located in the <windir>\System32\Dns folder.