Federation Server Farm Using SQL Server
This topology for Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS) differs from the federation server farm using Windows Internal Database (WID) deployment topology in that it does not replicate the data to each federation server in the farm. Instead, all federation servers in the farm can read and write data into a common database that is stored on a server running Microsoft SQL Server that is located in the corporate network.
Deployment considerations
This section describes various considerations about the intended audience, benefits, and limitations that are associated with this deployment topology.
Who should use this topology?
Large organizations with more than 100 trust relationships that need to provide both their internal users and external users with single sign-on (SSO) access to federated application or services
Organizations that already use SQL Server and want to take advantage of their existing tools and expertise
What are the benefits of using this topology?
Support for larger numbers of trust relationships (more than 100)
Support for token replay detection (a security feature) and artifact resolution (part of the Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) 2.0 protocol)
Support for the full benefits of SQL Server, such as database mirroring, failover clustering, reporting, and management tools
What are the limitations of using this topology?
- This topology does not provide database redundancy by default. Although a federation server farm with WID topology automatically replicates the WID database on each federation server in the farm, the federation server farm with SQL Server topology contains only one copy of the database
Note
SQL Server supports many different data and application redundancy options including failover clustering, database mirroring, and several different types of SQL Server replication.
The Microsoft Information Technology (IT) department uses SQL Server database mirroring in high-safety (synchronous) mode and failover clustering to provide high-availability support for the SQL Server instance. SQL Server transactional (peer-to-peer) and merge replication have not been tested by the AD FS product team at Microsoft. For more information about SQL Server, see High Availability Solutions Overview or Selecting the Appropriate Type of Replication.
Supported SQL Server Versions
The following SQL server versions are supported with AD FS installed with Windows Server 2012:
SQL Server 2008 / R2
SQL Server 2012
Server placement and network layout recommendations
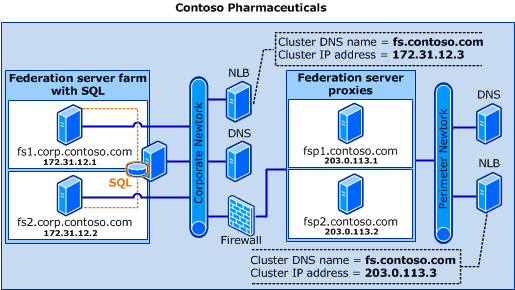
Similar to the federation server farm with WID topology, all of the federation servers in the farm are configured to use one cluster Domain Name System (DNS) name (which represents the Federation Service name) and one cluster IP address as part of the Network Load Balancing (NLB) cluster configuration. This helps the NLB host allocate client requests to the individual federation servers. Federation server proxies can be used to proxy client requests to the federation server farm.
The following illustration shows how the fictional Contoso Pharmaceuticals company deployed its federation server farm with SQL Server topology in the corporate network. It also shows how that company configured the perimeter network with access to a DNS server, an additional NLB host that uses the same cluster DNS name (fs.contoso.com) that is used on the corporate network NLB cluster, and with two federation server proxies (fsp1 and fsp2).
For more information about how to configure your networking environment for use with federation servers or federation server proxies, see either Name Resolution Requirements for Federation Servers or Name Resolution Requirements for Federation Server Proxies.