Troubleshooting Windows HLK Test Failures
We recommend that you use this guide as your starting point to troubleshoot Windows Hardware Lab Kit (Windows HLK) test failures. This article describes possible test failures and provides step-by-step instructions on how to troubleshoot them. You must perform the troubleshooting steps in the prescribed order.
Troubleshooting steps:
1. Install latest updates and filters
Verify that you have the latest updates and filters for Windows HLK. The test failure might already be resolved by a published filter or update. You can get the latest Windows HLK content at Windows Hardware Lab Kit Filters.
Watch a video demonstration.
2. Review the Status icons
In Windows HLK Studio, review the test status icons on the Results tab. The status icons are described below. To follow the test failure categories that are listed in 5. Identify the failure category, you must know what each icon represents.
| Status Icon | Meaning | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Queued | The test is queued but not running. If the test is in this mode for a long time, it can indicate a network infrastructure or Windows HLK infrastructure problem. In most cases, this does not indicate an issue with the test itself. | |
| Running | The test is running. On the Tests tab, the Length column indicates the expected test runtime. This information is also available in the test reference topic for the specific test. If a device encounters issues during testing, the tests can run for three to four times the expected runtime. | |
| Passed | The test passed. | |
| Passed with Filters | The test passed. | |
| Failed | The test failed. | |
| Failed with Filters | The test failed. | |
| Failed due to system crash | The system crashed during the test run. You can right-click on this test to view Bugcheck information. For more information about reviewing system crashes, see Troubleshooting Windows HLK Test Failures (system crashes). |
|
| Canceled | A user canceled the test, or a task has been canceled because the preceding task failed. |
Note
If the status icon suggests that you have a Windows HLK infrastructure problem, see Troubleshooting the Windows HLK Environment.
3. Make sure that the test was run correctly
Make sure that the test was run correctly, as described in the following sections:
Watch a video demonstration.
Verify tests that require special configuration
You should check whether the test requires a special configuration and if it does, verify that all special configuration requirements are met.
Some Windows HLK tests require additional files that are not included in the Windows HLK because of size or security reasons. Windows HLK Studio denotes these tests as requiring special configuration. These tests fail if the supplemental data is not installed.
Tests that require special configuration are denoted by a toolbox icon (![]() ) in the Type column in the Test pane and the Results pane in Windows HLK Studio. Special configuration details are described in the test reference topic for each test. For specific test reference documentation, see HLK Test Reference, or from in Windows HLK Studio, select the specific test on the Test tab or the Result tab, and then press F1.
) in the Type column in the Test pane and the Results pane in Windows HLK Studio. Special configuration details are described in the test reference topic for each test. For specific test reference documentation, see HLK Test Reference, or from in Windows HLK Studio, select the specific test on the Test tab or the Result tab, and then press F1.
Note
The online version of the help content is generally the most current.
Verify manual tests that require user interaction
You should determine whether the test requires user interaction.
Tests that require user interaction are denoted by a person icon (![]() ) in the Type column in the Test pane and the Results pane in Windows HLK Studio. For instructions on how to run a manual test, see the Running the test section in the test reference topic for the particular test. For specific test reference documentation, see HLK Test Reference, or from in Windows HLK Studio, select the specific test on the Test tab or the Result tab, and then press F1.
) in the Type column in the Test pane and the Results pane in Windows HLK Studio. For instructions on how to run a manual test, see the Running the test section in the test reference topic for the particular test. For specific test reference documentation, see HLK Test Reference, or from in Windows HLK Studio, select the specific test on the Test tab or the Result tab, and then press F1.
Run multi-device test as a single test
If the test was run as a multi-device test, rerun the test as a single test.
Multi-device testing is a Windows HLK feature that is supported by some tests. This feature reduces the time that a test runs by testing multiple devices at the same time (instead of scheduling a separate test run for each device.) Although this is a good way to reduce overall test time, it makes troubleshooting difficult because the results for all devices are logged in the same log files.
If a test fails during a multi-device test run, we recommend that you rerun the test separately against each device and troubleshoot each test run accordingly. To run a test individually in Windows HLK Studio, select the context-menu item Run Tests Individually. This menu item is available in the Results pane for tests that run as multi-device tests.
4. Check for configuration changes
Confirm that the Windows HLK infrastructure or the device configuration did not change after you selected the test target. Windows HLK gets the Windows HLK Client system configuration information when you select the test target. If you change the system or device configuration after you select the test target, you must then re-select the test target.
Warning
Be aware that re-selecting the test target invalidates and removes all previous test results. We highly recommend that you do not make any device or infrastructure changes after you have started testing.
Watch a video demonstration.
5. Identify the failure category
The Results tab in Windows HLK Studio lists test tasks in the order in which they were run. Failed tests include error options that you can use to help troubleshoot test failures. For more information about the Results tab, see Manage Test Results using Result Tab.
The following table describes test categories and their indicators; the failure category column links to troubleshooting assistance in this article. To access test errors, execution logs, tasks logs, and additional associated files, right-click the failed test on the Windows HLK Studio Results tab.
| Failure category | Status icon | Identifiers | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Failed |
Task Error, Task Log Task Log Task Error |
Task <> is Marked as Failed from the Log File Failed to determine Pass/Fail of the task <> Task will be marked as failed anyway. Cause : The Execute Task with <> Failed with ExitCode <Error Code> |
|
Failed |
Windows Event Log, Windows crash dump files |
A system event log entry and (if enabled) a crash dump file are created during a system crash. The Task Error probably states: Task Cancelled Because of an Unexpected Reboot. You can right-click on a test associated with a system crash to view associated Bugcheck information. |
|
Failed |
Windows Event Log, user-mode crash dump files |
When a user mode component crashes, an Application event log entry is created on the Windows HLK Client; if it is enabled, a user mode dump file is also created. |
|
Failed |
Task Execution Log |
This problem is indicated in the Task Execution Log. |
|
Running |
No indicators |
If the Windows HLK Client is not responding, tests can run indefinitely. |
|
Test was ended by the user on the Windows HLK Client. |
Failed |
Task Error |
This kind of error does not usually produce a log file. |
For additional information about specific error messages, see Windows HLK Studio task error message reference.
The following sections fully describe the failure categories that are listed in the preceding table:
Test failed because of test results
Test result failures are the most common kind of failure. If you receive a test result failure, review the following information:
The Task Log file and Additional Files from the Results tab in Windows HLK Studio.
The Troubleshooting section in the test reference topic. Select the test in Windows HLK Studio and then press F1.
The associated technology-specific troubleshooting guide that contains general troubleshooting guidance for all tests in a particular feature or technology area. For a list of technology-specific troubleshooting guides, see Troubleshooting Windows HLK.
Test fails with no failing task and Execution Logs are disabled
A known HLK client issue can cause a test to fail when there are no failing tasks, but one or more of the tasks is marked as cancelled. The test result should be checked for Execution Logs.
To check for execution logs
In Windows HLK Studio, right click a task result from the failing test result.
Use the Infrastructure menu item to view the types of logs.
Check whether the Execution Logs option is disabled (greyed out).
If the Execution Logs are missing this failure is likely caused by the known issue. The work-around is to re-run the test, so that logs are copied back to the controller.
System crashed
When Windows encounters a condition that compromises safe system operation, the system halts. This condition is commonly called a bug check, a system crash, a kernel error, a Stop error, or BSOD. A hardware device, its driver, or related software can cause this error.
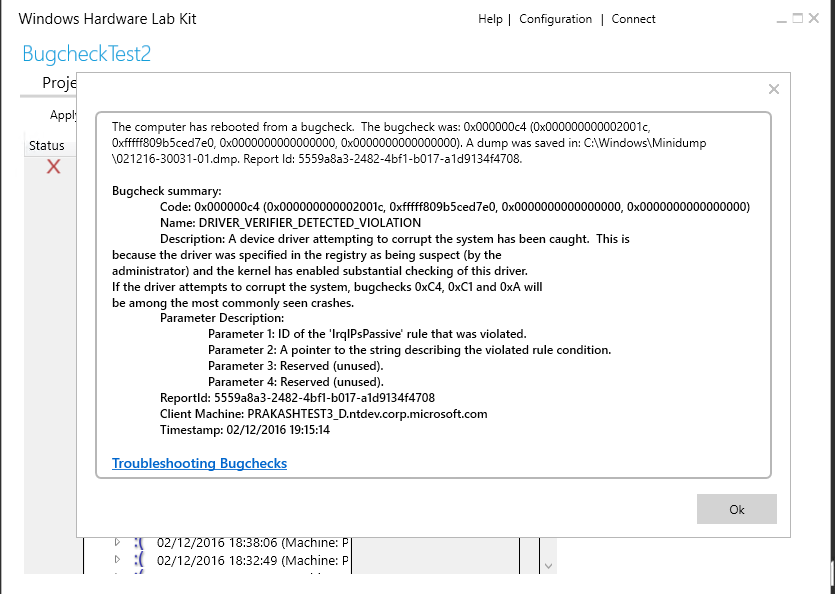
Bugcheck summary information
The system crash icon (![]() ) indicates that the system crashed during the test run. You can right-click on a test associated with a system crash to view associated Bugcheck information:
) indicates that the system crashed during the test run. You can right-click on a test associated with a system crash to view associated Bugcheck information:
When Windows crashes, it writes an event to the Windows System Event Log. To start the Event Viewer and view the event, do the following on the client system:
On the Start screen, type Event Logs.
Under Settings, click View Event Log.
In the Event Log Viewer, select Windows Logs.
Select the specific log of interest. To troubleshoot most user-mode failures, including problems with Windows HLK tests, select Application Log. For kernel-mode issues, select System Log.
In the Windows System Event Log file, look for an event that is similar to the following:
Level = Critical Source = Kernel-Power Event ID 41 Description: The system has rebooted without cleanly shutting down first. This error could be caused if the system stopped responding, crashed, or lost power unexpectedly.
Analyzing crash dump files
In addition to the Bugcheck summary information dialog, you can debug a system crash by using the crash dump file and the Windows debugger. For information on how to analyze crash dump files see Crash Dump Files and Analyzing a Kernel-Mode Dump File. For Windows debugging tools, see Troubleshooting Windows HLK.
You must determine whether the crash is caused by the driver that you are trying to certify or whether it is a Windows problem. You can identify this by using the Windows debugger !analyze extension. In the kernel debugger, use the !analyze -v command to review data on the failing component.
For more information about how to use the !analyze extension, see Using the !analyze Extension. For advanced troubleshooting assistance, see Debugging Techniques. For more information about bug checks, see Interpreting a Bug Check Code. For a list of bug check error codes, see Bug Check Code Reference.
If the problem is caused by Windows, collect the dump file and debugging data and follow the instructions in Windows HLK Support.
Test crashed
Tests in this category show up as test failures that have no Task Logs files. Start the Windows Event Viewer on the client computer. (To start Windows Event Viewer, on the Start screen, type Event Logs and then select View Event Log under Settings.) In the Windows Event Viewer, in the Windows Application event log, look for an event that is similar to the following:
Level = ErrorSource = Application ErrorEvent ID = 1000Description: Faulting application name: Testname.exe, …
Collect the-user mode crash dumps as described in Collecting User-Mode Dumps, and submit them as instructed in Windows HLK Support.
Test was cancelled because it ran too long
Windows HLK automatically cancels a test run if the test is still running after three times the expected runtime. Windows HLK Studio displays the estimated test run time for each test.
You can identify tests that were cancelled because they ran too long by using the following criteria:
Test does not have associated Task Logs.
Test does not have a Task Error in Windows HLK Studio.
In the WttEa.log file, under Infrastructure\Execution Log, look for the error: Run Test Failed Because the Task With TaskTimeout, as shown in the following example:
1872 3868 2012:3:3 3:43:7:898 Error: 0x8201adb1, Error 0x8201adb1 CExecutionTask::Cleanup()::(null)::CAUSE:INFORMATION: Task "Run Test" Failed Because the Task With TaskTimeout Flag Was running after the Timeout period 10800000 MilliSeconds File=d:\branches\fbl\tools\wtt\rel25\dtm\sdktools\wtt\jobs\runtime\wttexecutionagent\coreea\executiontask\src\executiontask.cpp Line=1686
To view the Wttea.log file by using Windows HLK Studio
In Windows HLK Studio, click the Results tab.
Right-click the failed test.
Click Infrastructure, click Execution Logs, and then click WttEa.log.
Verify that the basic functionality of the device still works.
Client system is unresponsive
Use the Job Monitor in Windows HLK Manager to view the Last Heartbeat column in the Machine window. If the last heartbeat has not registered for a long time, a communication problem probably exists between the Windows HLK Controller and the Windows HLK Client. If there is no heartbeat from the Windows HLK Client, it can take a long time for a test to be cancelled. To troubleshoot this problem, consider the following issues:
Network problems. See Troubleshooting the Windows HLK Environment.
Client system is unresponsive. This state is indicated in the following ways:
The mouse pointer moves, but it cannot perform any actions.
All video is frozen; the mouse pointer does not move; paging continues.
The mouse, keyboard, and disk are all unresponsive.
If the test appears to be making progress but the progress is slow, review console logging to determine the cause.
Enable the system for debugging and follow the instructions in Forcing a System Crash and Debugging a Stalled System.
Driver developers should investigate these issues by using a kernel debugger. If the test is nonresponsive, start the kernel debugger before Windows HLK cancels the test run. In the kernel debugger, look for any unresponsive threads in the test process.
6. Contact Windows HLK Support
See Windows HLK Support for instructions on how to report the following problems to Windows HLK Support:
An inaccurate status icon is reported.
You cannot determine the cause of the failure.
The failure is caused by a system crash that you cannot resolve.
The failure is caused by a Windows problem.
How to get the test name
To get the test name in Windows HLK Studio, perform the following steps:
On the Results tab in Windows HLK Studio, right-click the test name.
Type Ctrl-C to copy the test data into the clipboard.
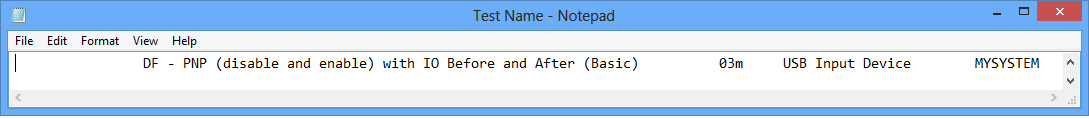
Paste the test data into Notepad or other text editor. The data will be similar to Figure 2. Sample Test Data, where DF - PNP (disable and enable) with IO Before and After (Basic) is the test name, 03m is the anticipated test runtime, USB Input Device is the device under test, and MYSYSTEM is the name of the Windows HLK Client.
Windows HLK Studio task error message reference
This section describes task error messages that Windows HLK Studio returns for some test failures.
Task <> is Marked as Failed from the Log File
This is the most common error message. Review the Task Log file.
Failed to determine Pass/Fail of the task <> Task will be marked as failed anyway.
This error usually means that the test generated a log, but did not log anything other than comments. Some log failures do not result in a Task Error. The Log indicates a failure or the Log is incomplete.
Cause : The Execute Task with <> Failed with ExitCode <Error Code>
Not all Tasks return logs; failure is indicated by exe exit code. This code can be any error typ. Determine whether the error code makes sense for a win32 error or a HRESULT error.
Task cancelled because of an unexpected reboot
This is a general error that can have various causes, including but not limited to the system under test rebooting or crashing.
Troubleshooting graphics tests
Graphics Support CABs
Graphics Feature on Demand (FOD) packages are required to be present on the test client for all graphics testing. The DLLs for the\\BUILD OS are available for download on the MSDN on the HLK Supplemental Content download page. The cabs can be deployed on a running client, or injected into the OS image prior to deploying to the client.
For example, to install on a running client, use the following command:
dism /online /add-package /packagepath:<path to package>\Microsoft-OneCore-Graphics-Tools-Package.cab