Convert an existing custom device image to a Generation 2 virtual machine
To support Windows 11, your custom device images must be based on Generation 2 (Gen2) virtual machines (VMs). If you already have custom device images based on Generation 1 (Gen1) virtual machines, you can convert those custom device images by following the steps below. After you've completed these steps, all future Cloud PCs provisioned from the converted device image will be based on Generation 2 virtual machines.
Windows 365 won't prevent you from provisioning new Cloud PCs from existing custom images based on Generation 1 VMs. However, when you want to add new custom images, Windows 365 will only accept Generation 2-based images. Generation 2 VMs are required to support Windows 11.
There are four main steps to this process:
- Create a new virtual machine
- Convert the Master Boot Record to the GUID partition
- Convert the disk to a fixed size and VHD format
- Upload the converted virtual machine to Azure
Create a new virtual machine
- Make sure that Hyper-V is installed on your management PC. For information on how to install Hyper-V, see Install Hyper-V on Windows.
- Download your existing custom image virtual hard drive (VHD) file from the Azure storage blob URL to your PC where you have Hyper-V available. The VHD file is the exact size of the OS disk, which can be a large file size. Make sure to use a fast, stable internet connection to download the VHD file, and prepare for long download times. For information on how to download a managed disk, see Download a VHD from Azure. You can also download the VHD by using Azure Storage Explorer directly, both as managed disk or storage blob VHDs.
- Switch to your local PC and open Hyper-V Manager.
- Under Actions, select New > Virtual Machine.
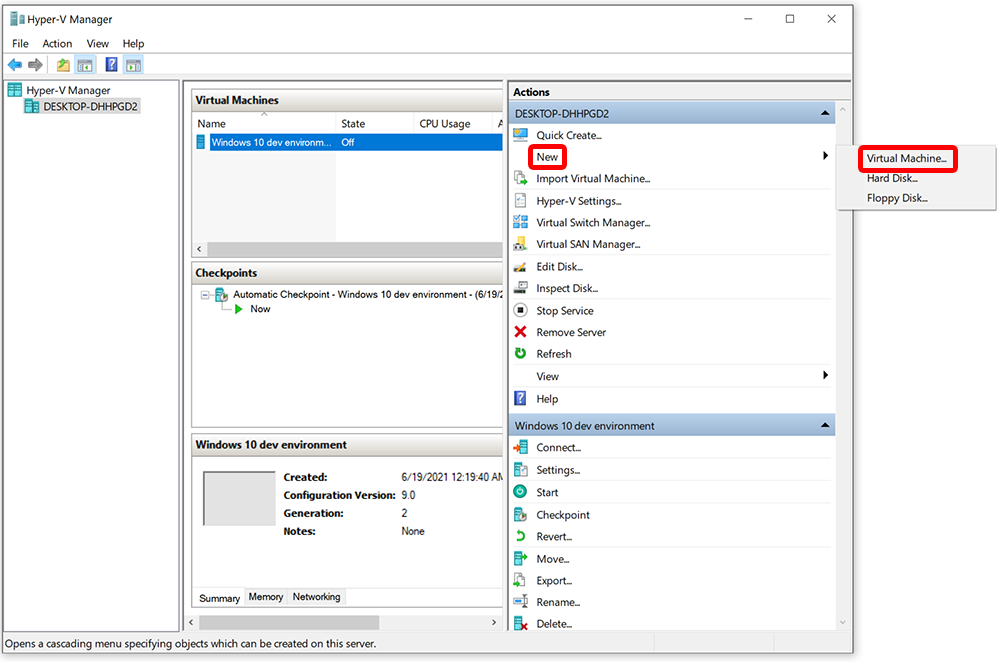
- On the Before You Begin page, select Next.
- On the Specify Name and Location page, type a friendly name, like CustomFinanceImageg2, and then select Next.

- On the Specify Generation page, select Generation 1 (not Generation 2). Generation 2 is needed here to mount the disk and change the partition model to GUID Partition Table (GPT). Select Next.
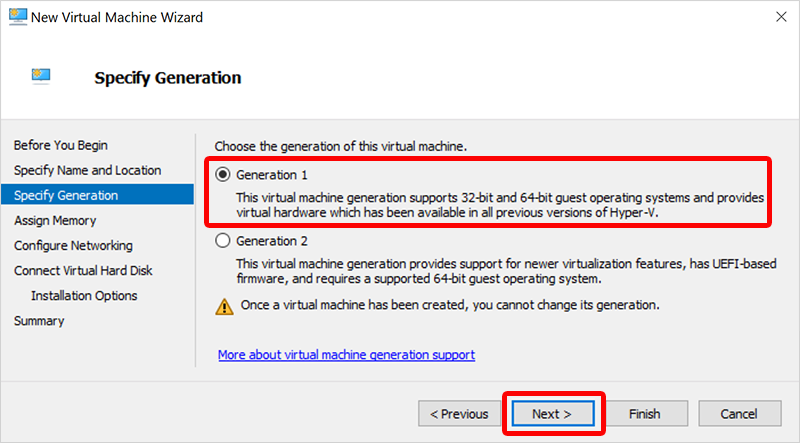 Hyper-V only supports Generation 2 images in VHDX and Generation 1 images in VHD. Azure only supports Generation 2 images in VHD. Therefore, we're creating a Generation 1 VHD image here in order to convert it to a Generation 2 VHD image.
Hyper-V only supports Generation 2 images in VHDX and Generation 1 images in VHD. Azure only supports Generation 2 images in VHD. Therefore, we're creating a Generation 1 VHD image here in order to convert it to a Generation 2 VHD image. - On the Assign Memory page, set Startup memory to at least 1024 MB, preferably 4096 MB. Select Next.

- On the Configure Networking page, select Default Switch > Next.
- On the Connect Virtual Hard Disk page, select Use an existing virtual hard disk.

- For Location, select Browse and select the VHD that you downloaded earlier.
- Select Next and on the Summary page select Finish.
Convert the Master Boot Record to the GUID partition
- Create a WinPE media ISO. For instructions on how to create an ISO, see Create bootable WinPE media. Alternatively, boot from a Windows 11 ISO and press Shift + F10 to display a CMD prompt.
- In Hyper-V Manager, under Virtual Machines, select the new VM, and then under Actions select Settings.
- In the left navigation pane, under IDE Controller 1, select DVD Drive.
- Under DVD Drive, under Controller, select IDE Controller 1.
- Select Image file and browse to the new ISO file you created.
- Select OK.
- Under Actions, select Start.
- Wait for the wpeinit command prompt to open.
- To convert the Master Boot Record (MBR) to the GUID Partition Table (GPT) partition, run the following two commands in the wpeinit window. The GPT is the new standard for Generation 2 based VMs.
- To determine the correct disk for conversion and validate it, run
mbr2gpt /validate /disk:0. - To convert the disk to the GUID Partition Table (GPT), run
mbr2gpt /convert /disk:0For more information on MBR2GPT, see the MBR2GPT.exe documentation.
- To determine the correct disk for conversion and validate it, run
- After the commands run successfully, move on to the next step.
Convert the disk to a fixed size and VHD format
- Shut down the virtual machine.
- In Hyper-V Manager, select the new virtual machine > Edit disk (under Actions).
- On the Before You Begin page, select Next.
- On the Locate Disk page, Browse to the location of the converted disk > Next.
- On the Choose Action page, select Compact > Finish.
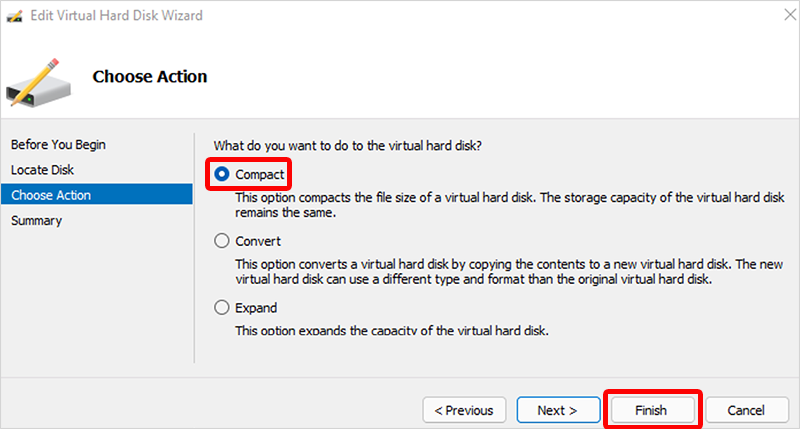
- After the process completes, select the new virtual machine again > Edit disk.
- On the Before You Begin page, select Next.
- On the Locate Disk page, Browse to the location of the converted disk > Next.
- On the Choose Action page, select Convert > Next.
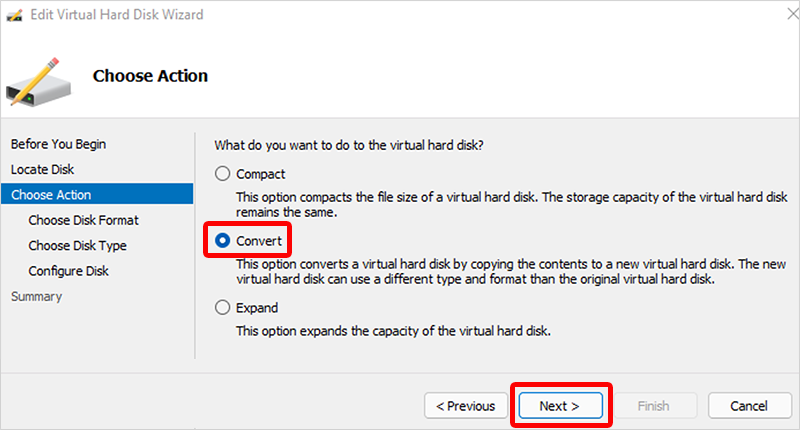
- On the Choose Disk Format page, select VHD > Next.
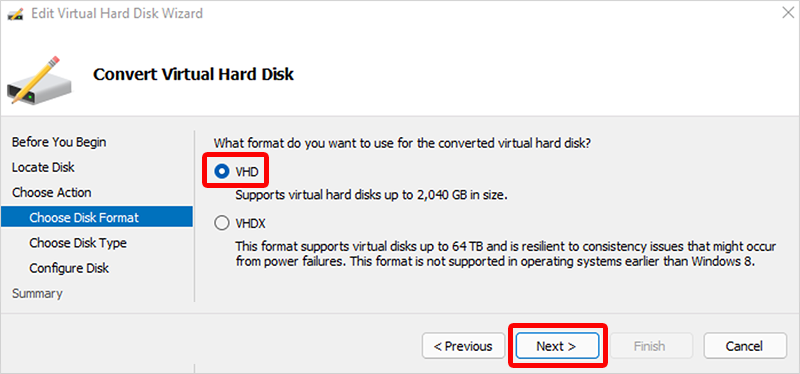
- On the Choose Disk Type page, select Fixed size > Next.
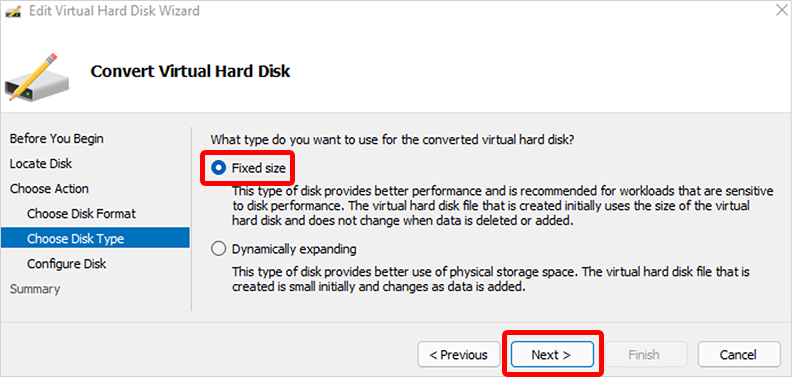
- On the Configure Disk page, Browse to a new location for the disk to be created > Next.
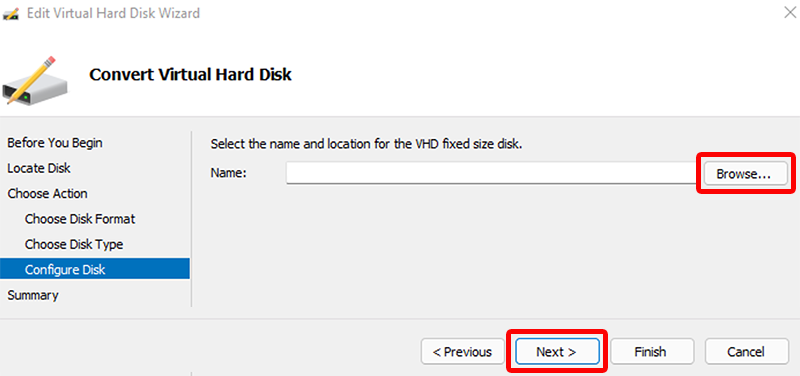
- On the Summary page, confirm all of the details are correct and select Finish.
- After the process completes, dismount the WinPE ISO by following these steps:
- In Hyper-V Manager, under Virtual Machines, select the new VM, and then under Actions select Settings.
- In the left navigation pane, select IDE Controller 1.
- Under DVD Drive, under Controller, select IDE Controller 1.
- Select OK.
Upload the converted VHD to Azure
- Upload the converted VHD back to Azure. You can use Azure Storage Explorer. For other upload options, see Upload a generalized Windows VHD and use it to create new VMs in Azure.
Note
Make sure that the VHD remains VHD in fixed size. VHDX as format isn’t supported on Azure.
- Go to the Azure portal, open Images > Create.
- Fill in the required fields and make sure to select Gen 2 for VM generation.
- Select Review + Create.
- (Optional) After the image is created, you can upload it. For instructions on how to upload, see Upload a VHD to Azure or copy a managed disk to another region - Azure PowerShell.
- You can now add the device image to Windows 365. For information on how to upload custom images, see Add a custom device image.