Windows LAPS troubleshooting guidance
This guide provides the fundamental concepts to use when troubleshooting Windows Local Administrator Password Solution (Windows LAPS) issues.
Windows LAPS is a Windows feature that automatically manages and backs up the password of a local administrator account on your Microsoft Entra joined or Windows Server Active Directory-joined devices. You also can use Windows LAPS to automatically manage and back up the Directory Services Repair Mode (DSRM) account password on your Windows Server Active Directory domain controllers. An authorized administrator can retrieve the DSRM password and use it. For more information, see What is Windows LAPS?
Note
- This article is for Windows LAPS (the new feature), not for the legacy LAPS or the older version of LAPS.
- This article lists only some of the top possible root causes. Other causes may also exist but remain undiscovered.
- The following list contains the most common event IDs and might not include all Windows LAPS events.
Troubleshooting Windows LAPS using Windows events
To view Windows LAPS events, go to Applications and Services Logs > Microsoft > Windows > LAPS > Operational in Event Viewer.
Note
- Windows LAPS processing starts with Event ID 10003 and ends with Event ID 10004.
- If the processing of the current cycle fails for any reason, Event ID 10005 is logged.
Windows LAPS has two scenarios:
Windows LAPS Active Directory
Client machines are configured to store the password in Active Directory.
Windows LAPS Azure Microsoft Entra ID
Client machines are configured to store the password in Microsoft Entra ID.
The following table lists the event IDs that are logged in different scenarios:
| Event ID | Scenario |
|---|---|
| 10006 | Windows LAPS Active Directory |
| 10011 | Windows LAPS Active Directory |
| 10012 | Windows LAPS Active Directory |
| 10013 | Windows LAPS Active Directory and Microsoft Entra ID |
| 10017 | Windows LAPS Active Directory |
| 10019 | Windows LAPS Active Directory and Microsoft Entra ID |
| 10025 | Windows LAPS Microsoft Entra ID |
| 10026 | Windows LAPS Microsoft Entra ID |
| 10027 | Windows LAPS Active Directory and Microsoft Entra ID |
| 10028 | Windows LAPS Microsoft Entra ID |
| 10032 | Windows LAPS Microsoft Entra ID |
| 10034 | Windows LAPS Active Directory |
| 10035 | Windows LAPS Active Directory |
| 10048 | Windows LAPS Active Directory and Microsoft Entra ID |
| 10049 | Windows LAPS Active Directory and Microsoft Entra ID |
| 10056 | Windows LAPS Active Directory |
| 10057 | Windows LAPS Active Directory |
| 10059 | Windows LAPS Microsoft Entra ID |
| 10065 | Windows LAPS Active Directory |
Event ID 10006
LAPS password encryption is required but the Active Directory domain is not yet at 2016 domain functional level. The password was not updated and no changes will be made until this is corrected
By default, Windows LAPS encrypts the password of the managed account on the client machine. To support the encryption, the domain functional level should be Windows Server 2016.
Resolution
- Raise the domain functional level if needed.
- Disable the Enable password encryption Group Policy for client machines.
Note
We don't recommend disabling the password encryption stored on the domain controller.
Event ID 10011
LAPS failed when querying Active Directory for the current computer state
Windows LAPS periodically (every hour) queries Active Directory for the computer state, and the client machine uses the Netlogon service to discover a domain controller on it.
Resolution
If you're in an environment where you have connectivity only to a writable domain controller, open the network ports between the client machine and the domain controller.
For more information, see Service overview and network port requirements for Windows.
Event ID 10012
The Active Directory schema has not been updated with the necessary LAPS attributes
To introduce Windows LAPS, you need to extend the schema with Windows LAPS attributes. Or, if you're using Windows LAPS in legacy LAPS emulation mode, you need to extend the schema with the legacy LAPS attributes. This issue occurs for one of the following reasons:
Root cause 1
The schema hasn't been extended with the new Windows LAPS attributes.
Root cause 2
A transient Active Directory replication exists between the local domain controller (DC) and the primary domain controller (PDC).
Root cause 3
An Active Directory replication issue on the local domain controller.
Resolution to root cause 1
Run the Update-LapsADSchema PowerShell cmdlet to update the Active Directory schema by using Schema Admin privileges.
If you're using the legacy LAPS emulation, extend the schema with the Update-AdmPwdADSchema PowerShell cmdlet (this action requires installing the legacy LAPS product first).
Resolution to root cause 2
Due to the replication latency, the schema attributes haven't been replicated to the local domain controller. You can use the LDP or ADSIEDIT snap-in to identify if the Windows LAPS schema attributes have been replicated. Force Active Directory replication of the schema partition with the schema master by using the following command:
repadmin /replicate DC2.contoso.com PDC.contoso.com CN=Schema,CN=Configuration,DC=contoso,dc=com /force
Note
- Replace
DC2.contoso.comwith the name of the DC identified by Event ID 10055 in the Windows LAPS event logs. - Replace
PDC.contoso.comwith the name of the PDC in your environment. You can identify the PDC by using thenltest /dsgetdc:contoso.com /pdc /forcecommand.
Resolution to root cause 3
There's an Active Directory replication issue between the local domain controller and other domain controllers in the domain. You can view Event ID 10055 in Windows LAPS event logs to verify the name of the domain controller and run the repadmin /showreps command to identify any replication errors.
For more information, see Troubleshooting Active Directory Replication Problems.
Event ID 10013
LAPS failed to find the currently configured local administrator account
Windows LAPS reads the local administrator's name from Group Policy or the Intune setting Name of administrator account to manage. If this setting isn't configured, it will look for the local account with a security identifier (SID) ending with 500 (administrator). If Windows LAPS can't find the account, Event ID 10013 is logged.
In the current version of Windows LAPS, there's no feature to create the managed user.
Resolution
Verify and make sure the managed user is present in local users by using one of the following methods:
- Use lusrmgr.msc to open Local Users and Groups.
- Run the
net usercommand.Note
Make sure there are no trailing spaces at the beginning and the end of the account.
Event ID 10017
LAPS failed to update Active Directory with the new password. The current password has not been modified
This is a status event at the end of a Windows LAPS processing cycle. This event has no root cause, so you need to review the earlier processing of the events where Windows LAPS has encountered an issue.
Resolution
- Open an elevated PowerShell command prompt and run the
Invoke-lapsPolicyProcessingcmdlet. - Open Event Viewer and go to Applications and Services Logs > Microsoft > Windows > LAPS > Operational.
- Filter for the latest processing of events starting from Event ID 10003 through Event ID 10005.
- Fix any errors prior to Event ID 10017.
Event ID 10019
LAPS failed to update the local admin account with the new password
Windows LAPS can't update the password of the locally managed user account on the local machine. Windows LAPS found the managed user, but had trouble changing the password.
Resolution
- Identify if there's a resource issue like a memory leak or out of memory issue. Reboot the machine to verify if you observe a similar error.
- A third-party application or filter driver that's managing the same managed user doesn't allow Windows LAPS to manage the password.
Event ID 10025
Azure discovery failed
The device (Microsoft Entra joined or hybrid joined) that's configured with Windows LAPS to store passwords in Microsoft Entra ID should discover the Enterprise Registration Endpoint.
Resolution
- Verify that you can connect successfully to the registration endpoint (
https://enterpriseregistration.windows.net). If you open Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome and connect to the registration endpoint (https://enterpriseregistration.windows.net), you get a message "Endpoint not found". This message means you can connect to the Enterprise Registration Endpoint. - If you're using a proxy server, verify that your proxy is configured under the system context. You can open an elevated command prompt and run the
netsh winhttp show proxycommand to display the proxy.
Event ID 10026
LAPS was unable to authenticate to Azure using the device identity
This issue occurs if there's an issue with the device's Primary Refresh Token (PRT).
Resolution
- Verify that you have enabled the Windows LAPS feature in your Azure tenant.
- Verify that the machine isn't deleted or disabled in your Azure tenant.
- Open a command prompt, run the
dsregcmd /statuscommand and check the following sections for any errors:Device statusSSO dataDiagnostic data
- Verify the error message by using the dsregcmd command and troubleshoot the issue.
- Troubleshoot Microsoft Entra hybrid joined devices by using Troubleshoot Microsoft Entra hybrid joined devices.
- Use the Device Registration Troubleshooter Tool to identify and fix any device registration issues.
- If you receive an error message, see Microsoft Entra authentication and authorization error codes for the description of the error and further troubleshooting.
Event ID 10027
LAPS was unable to create an acceptable new password. Please verify that the LAPS password length and complexity policy is compatible with the domain and local password policy settings
Windows LAPS can't update the password of the locally managed user account on the local machine. Windows LAPS found the managed user, but had trouble changing the password.
Resolution
Check the password policy on the machine by running the
net accountscommand in a command prompt. Validate any of the password policies if they don't meet the criteria of Windows LAPS configured password policy, like the password complexity, password length, or password age.Identify if the setting is applied via a local Group Policy Object (GPO), a Domain GPO, or Local Security Settings by running the
GPRESULT /hcommand. Modify the GPO or security settings to match the Windows LAPS GPO password settings. The settings are configured via the Password Settings setting in GPO or Intune (MDM).Note
Your password policies configured in Active Directory, local GPO, or security settings should match the Windows LAPS password settings, or should contain settings lower than those in the Windows LAPS Password Settings configuration.
Check if you have any third-party password filters that might be blocking setting the password.
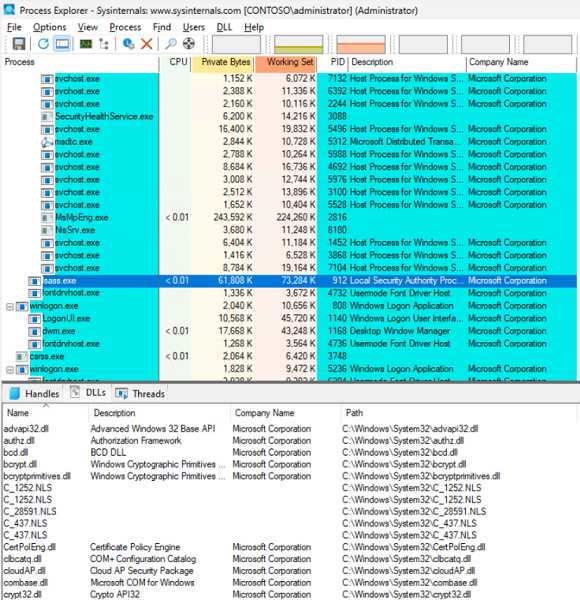
Download Process Explorer.
Extract and run Process Explorer as an administrator.
Select the LSASS.exe process on the left pane.
Select View > Show Lower Pane.
Select View > Lower Pane View > DLLs.
The lower pane displays the loaded DLLs or modules. Identify if there are any third-party modules by using the Company Name field (any modules other than Microsoft).
Review the DLL list to identify if the name of the third-party DLL (module) has some keywords like "security," "password," or "policies." Uninstall or stop the application or service that might be using this DLL.
Machine joined to Microsoft Entra ID
Microsoft Entra ID or hybrid joined devices can be managed by using mobile device management (MDM) (Intune), local GPOs, or any similar third-party software.
- Check the password policy on the machine by running the
net accountscommand in a command prompt. Validate any of the password policies if they don't meet the criteria of Windows LAPS configured password policy, like the password complexity, password length, or password age. - Identify if the conflicting policy is applied via Intune, local GPO, or a similar third-party software like Intune to manage the password policies on the machine.
Event ID 10028
LAPS failed to update Azure Active Directory with the new password
The Windows LAPS client machine periodically updates passwords. This event appears if the client machine configured with Windows LAPS can't update the password to Microsoft Entra ID.
Resolution
- Verify that you have enabled the Windows LAPS feature in your Azure tenant.
- Verify that the machine isn't deleted or disabled in your Azure tenant.
- Open a command prompt and run the
dsregcmd /statuscommand to check the following sections for any errors:Device statusSSO dataDiagnostic data
- Verify the error message by using the dsregcmd command and troubleshoot the issue.
- Use Troubleshoot Microsoft Entra hybrid joined devices to troubleshoot Microsoft Entra hybrid joined devices.
- Use the Device Registration Troubleshooter Tool to identify and fix any device registration issues.
- If you receive an error message, see Microsoft Entra authentication and authorization error codes for the description of the error and further troubleshooting.
Event ID 10032
LAPS was unable to authenticate to Azure using the device identity
There might be issues related to Microsoft Entra authentication when using device PRT.
Resolution
- Verify that you have enabled Windows LAPS feature in your Azure tenant.
- Verify that the machine isn't deleted or disabled in your Azure tenant.
- Open a command prompt and run the
dsregcmd /statuscommand to check the following sections for any errors:Device statusSSO dataDiagnostic data
- Verify the error message by using the dsregcmd command and troubleshoot the issue.
- Use Troubleshoot Microsoft Entra hybrid joined devices to troubleshoot Microsoft Entra hybrid joined devices.
- Use the Device Registration Troubleshooter Tool to identify and fix any device registration issues.
- If you receive an error message, see Microsoft Entra authentication and authorization error codes for the description of the error and further troubleshooting.
Event ID 10034
The configured encryption principal is an isolated (ambiguous) name. This must be corrected before the configured account's password can be managed. Please specify the name in either user@domain.com or domain\user format.
The encryption principal is configured via the Configure authorized password decryptors setting by using GPO or MDM (Intune). It appears that the setting isn't configured properly.
Resolution
Correct the Intune or GPO configuration. This setting accepts two values:
- SID of a domain group or user
- Group name in <Domain Name>\<Group Name>, <Domain Name>\<User Name>, or <User Name>@<Domain Name>
Note
Verify that there are no trailing spaces at the beginning and the end of the setting.
Event ID 10035
The configured encryption principal name could not be mapped to a known account. This must be corrected before the configured account's password can be managed.
The encryption principal is configured via the Configure authorized password decryptors setting by using GPO or MDM (Intune). The setting accepts an SID or a domain group name in either <Domain Name>\<Group Name>, <Domain Name>\<User Name>, or <User Name>@<Domain Name>. The error occurs when the Windows LAPS client can't resolve an SID to a name or a name to an SID.
Resolution
- Verify that the domain group exists in Active Directory and hasn't been deleted.
- If the group is newly created, wait for the Active Directory replication to converge on the local domain controller of the client machine.
- Use the Sysinternal tool PsGetSid to manually resolve the SID or name.
- Download PsGetSid.
- Extract the downloaded file and open an elevated command prompt on the client machine where you're experiencing the issue.
- Run the
psgetsid -accepteula <SID> or <Name>command. Use the SID or name mentioned in Event ID 10035.
- Check if there are any Active Directory replication errors in the forest and troubleshoot them. For more information, see Troubleshooting Active Directory Replication Problems.
Event ID 10048
The currently pending post-authentication reset timer has been retried the maximum allowed number attempts and will no longer be scheduled
The post-authentication retry is the number of retry operations tried reset the password with the appropriate directory (Microsoft Entra ID or Active Directory). If this number exceeds the maximum of 100 on a boot, this event is triggered.
Resolution
- Identity if there's a problem connecting to the appropriate directory, such as Active Directory or Microsoft Entra ID.
- Troubleshoot any other errors during the processing of Windows LAPS events.
Event ID 10049
LAPS attempted to reboot the machine as a post-authentication action but the operation failed
Windows LAPS can be configured for a post-authentication action by using the Post-authentication actions setting with GPO or MDM (Intune). In this scenario, the setting is configured to reboot the machine if it detects a post-authentication action. This event denotes that the machine can't reboot.
Resolution
- Identify if there's any application blocking a shutdown of the machine.
- Identify if you have necessary privileges to shut down the machine.
Event ID 10056
LAPS failed to locate a writable domain controller
Windows LAPS client uses Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) modify operation to write passwords to Active Directory from the Windows LAPS client. Windows LAPS needs to discover a writable domain controller in the domain to write the password of the managed account.
Resolution
Open a command prompt on the client machine and run the command:
nltest /dsgetdc:<Domain Name> /force /writableIf you get error 1355 (domain controller for the domain cannot be found), it means you need to troubleshoot the writable DC discovery issue.
If you're in an environment where you have connectivity only to a writable domain controller, open the network ports between the client machine and the domain controller. For more information, see Service overview and network port requirements for Windows.
Event ID 10057
LAPS was unable to bind over LDAP to the domain controller with an <Error Code>:
During a scheduled background processing, Windows LAPS needs to connect to a domain controller. This processing is done using the machine context. This error appears if there's any Active Directory authentication issue between the client machine and the domain controller.
Resolution
Verify that the machine account isn't deleted in Active Directory.
Validate any secure channel issues between the client and the domain controller by running an elevated command:
nltest /sc_query:<Domain Name>Rejoin the machine to the domain.
Note
Ensure that you know the local administrator's password.
Event ID 10059
Azure returned a failure code
The event also contains an HTTP error. The error occurs when connecting, authenticating, or updating the password to Microsoft Entra ID.
Resolution
- Verify that you can successfully connect to the Microsoft Entra registration endpoint (
https://enterpriseregistration.windows.net). - Verify that you have enabled the Windows LAPS feature in your Azure tenant.
- Verify that the machine isn't deleted or disabled in your Azure tenant.
- Open a command prompt and run the
dsregcmd /statuscommand to check the following sections for any errors:Device statusSSO dataDiagnostic data
- Verify the error message by using the dsregcmd command and troubleshoot the issue.
- Use Troubleshoot Microsoft Entra hybrid joined devices to troubleshoot Microsoft Entra hybrid joined devices.
- Use the Device Registration Troubleshooter Tool to identify and fix any device registration issues.
- If you receive an error message, see Microsoft Entra authentication and authorization error codes for the description of the error and further troubleshooting.
Event ID 10065
LAPS received an LDAP_INSUFFICIENT_RIGHTS error trying to update the password using the legacy LAPS password attribute. You should update the permissions on this computer's container using the Update-AdmPwdComputerSelfPermission cmdlet, for example:
This error occurs because the Windows LAPS client machine needs to write passwords of the managed user.
This issue can also occur if you move the machine to a different organizational unit (OU), and the destination OU doesn't have the Self Permission to the computer.
Resolution
If you haven't run the Windows LAPS PowerShell cmdlet to assign the Self Permission to the computer account, run the following cmdlet:
Set-LapsADComputerSelfPermission -identity <OU Name>For example:
Set-LapsADComputerSelfPermission -Identity LAPSOU Set-LapsADComputerSelfPermission -Identity OU=LAPSOU,DC=contoso,DC=ComNote
You can use a distinguished name (DN) if you have the same name for the OU but in different hierarchies.
Verify that the computer account has the Self Permission on the OU where the machine account exists.
Logon to a domain controller with a domain administrator privilege
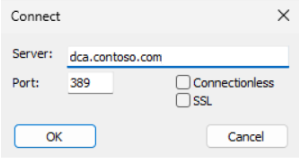
Open LDP.exe.
Select Connection > Connect and configure the server and port as follows:
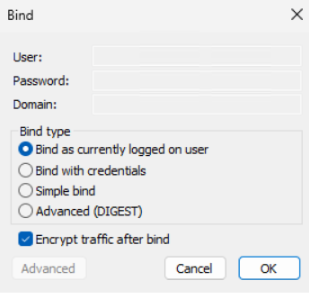
Select Connection > Bind, configure the following settings, and then select OK.
Select View > Tree. Then, from the drop-down list of BaseDN, select the domain where your client machine is located.
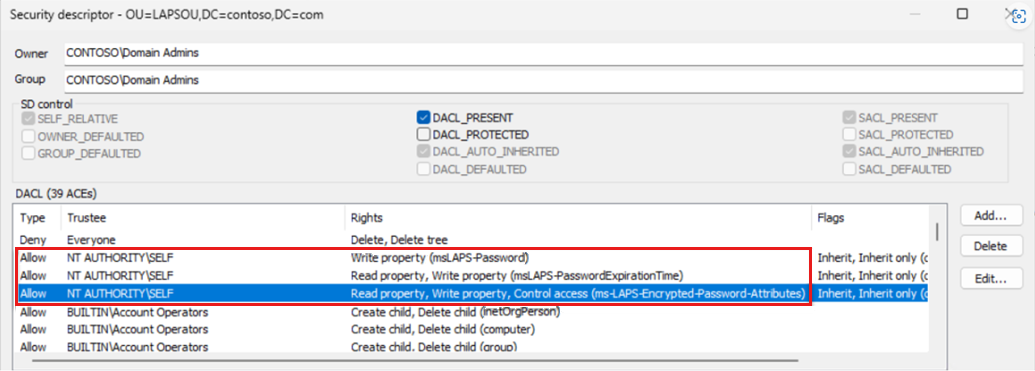
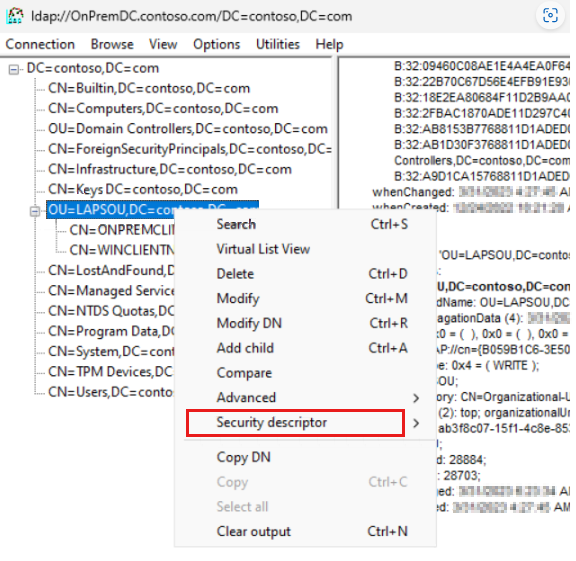
Browse the domain tree to identify the OU where you have the client machines located. Right-click the OU, and select Security descriptor > Edit.
Sort the Trustee column and find the following user rights for
NT AUTHORITY\SELFpermissions for themsLAPS-Passwordattribute.