Implement security to protect Azure SQL
Understanding and effectively managing server and database firewall rules, as well as Microsoft Defender for SQL, is essential to ensure protection to your Azure SQL resources during migration and beyond.
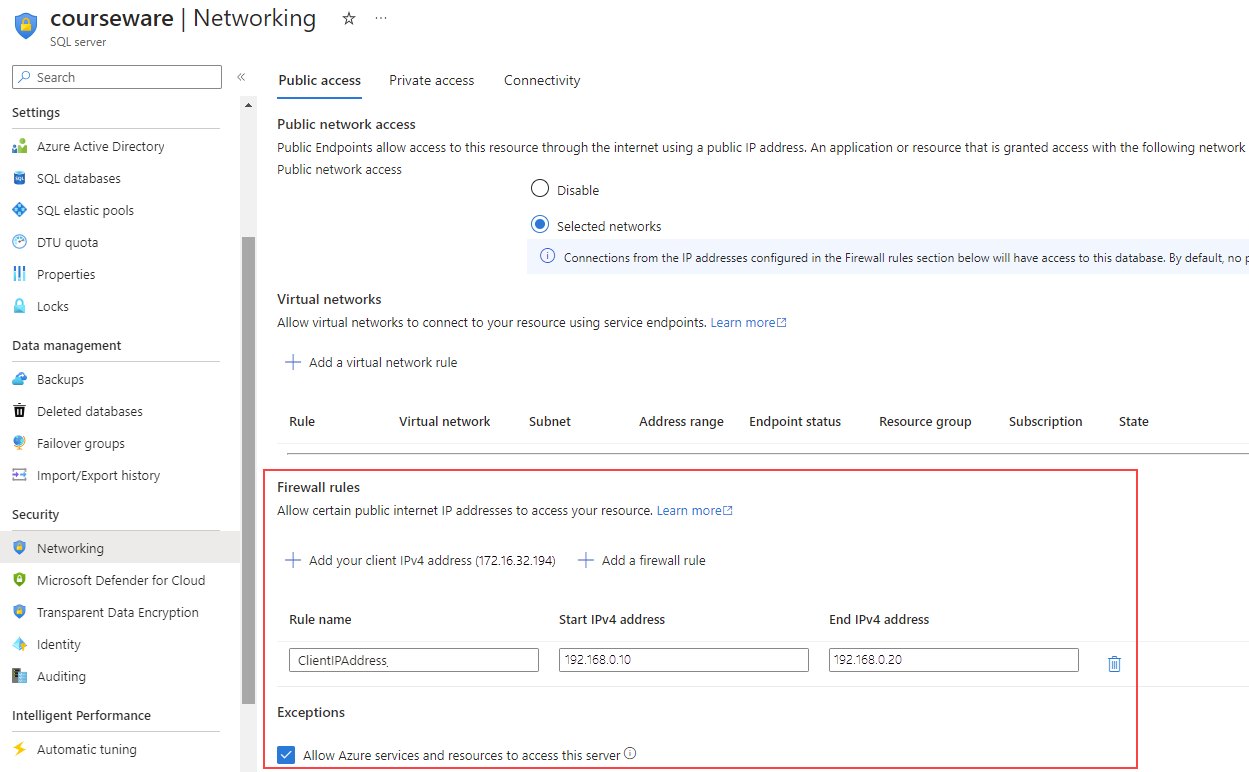
Configure server and database firewall rules
In Azure SQL Database, you can configure firewall rules both at the server level and the database level.
Server-level firewall rules
Server-level firewall rules control access to Azure SQL Database on a broader level, determining which IP addresses can connect to the server. In contrast,
Server-level firewall rules permit users to connect to all server databases, while database-level firewalls control access for specific IP addresses to individual databases.
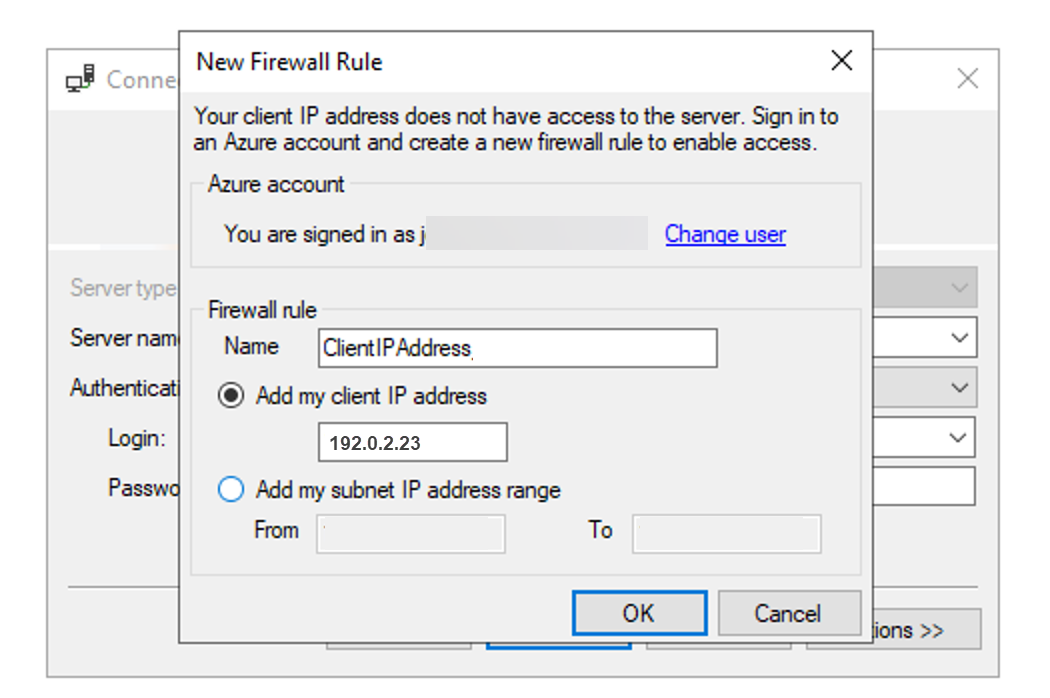
You can configure server-level firewall rules through the Azure portal or by using the sp_set_firewall_rule stored procedure within the master database.
Note
The Allow Azure Services and resources to access this server server setting counts as a single firewall rule when enabled. By default, block all access and only open it when needed.
Database-level firewall rules
Database-level rules offer more specific control within individual databases. You can configure database-level firewall rules through T-SQL only using the sp_set_database_firewall_rule stored procedure from within the user database.
When connecting, Azure SQL Database checks for a database-level firewall rule specific to the provided database name. If that rule isn't found, it checks the server-level IP firewall rules, which apply to all databases on the server. If either rule exists, the connection is established.
If neither rule exists, and the user is using SQL Server Management Studio or Azure Data Studio to connect, they'll be prompted to create a firewall rule.
To learn more about server-level firewall rules and database-level firewall rules, see Azure SQL Database and Azure Synapse IP firewall rules.
Microsoft Defender for SQL
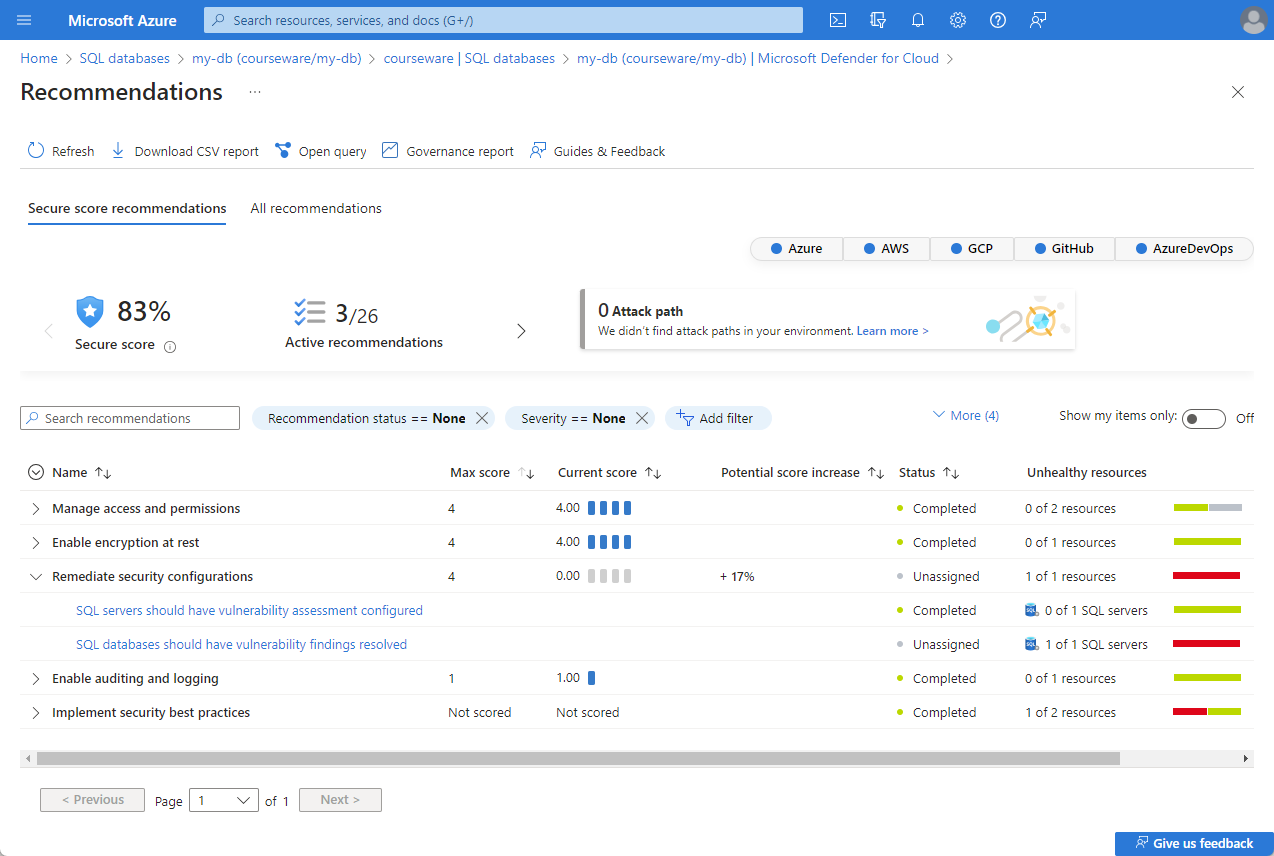
Microsoft Defender for SQL is a comprehensive security solution for Azure SQL Database, Azure SQL Managed Instance, and SQL Server on Azure VM. It continuously monitors and assesses your database's security, offering customized recommendations to strengthen it.
Also, it provides advanced security capabilities, including SQL vulnerability assessment and Advanced Threat Protection, to proactively protect your data state. This all-in-one solution helps you maintain a high level of security in your SQL environment.
There are two different ways you can enable Microsoft Defender for SQL.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Subscription Level (Recommended) | Enable it at the subscription level for comprehensive protection of all databases in Azure SQL Database and Azure SQL Managed Instance. You can disable them individually if needed. |
| Resource Level | Alternatively, you can enable it at the resource level if you prefer to manage protection for specific databases manually. |
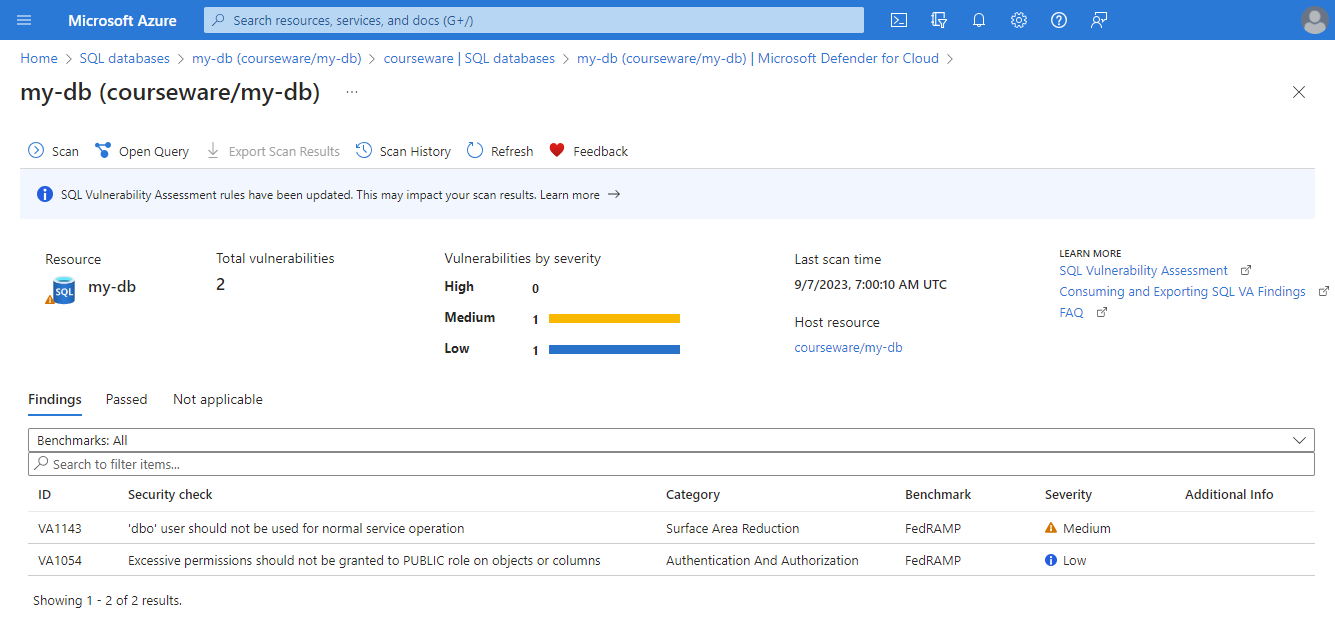
SQL Vulnerability Assessment
SQL vulnerability assessment uses a knowledge base of rules based on Microsoft's best practices. It flags security vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, excessive permissions, and unprotected sensitive data.
You have two configuration choices for SQL Vulnerability Assessment:
Express Configuration: It's the default option and doesn't require external storage for baseline and scan results.
Classic Configuration: It needs you to manage an Azure storage account for storing baseline and scan result data.
Advanced Threat Protection
Advanced Threat Protection enhances the security of Azure SQL by detecting and responding to unusual or potentially harmful database access attempts.
It provides security alerts for suspicious database activities, potential vulnerabilities, SQL injection attacks, and abnormal access patterns, integrated with Microsoft Defender for Cloud. This integration offers insights and recommended actions for investigating and mitigating threats, making it accessible to nonsecurity experts.
For a list of alerts, see the Alerts for SQL Database and Azure Synapse Analytics in Microsoft Defender for Cloud.