Understand distributed availability group for migration
If you want to minimize the amount of downtime during the migration, you can use the SQL Server Always On availability group (AG) feature to extend an on-premises database into the cloud.
A distributed availability group (AG) can be used to migrate a standalone instance of SQL Server or an Always On availability group to SQL Server on Azure Virtual Machines (VMs).
If you're migrating a database (or multiple databases) from a standalone instance, using a distributed AG is a straightforward solution that doesn't require either a Windows Server Failover Cluster or an availability group listener on the source or target. However, if you're migrating an availability group, both a cluster and a listener are required on the source and target.
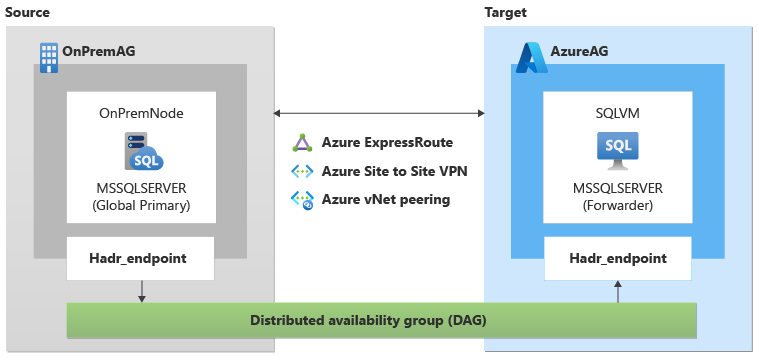
You can use Transact-SQL to add a replica of the database using your already existing on-premises SQL Server using the Add Azure Replica wizard. It must have an existing Always On availability group and have an existing connection between your on-premises network and Azure.
Note
The Add Azure Replica wizard only works with Azure Virtual Machines running in classic deployment model. The best practice is to create virtual machines with Resource Manager, as a result you can only add a replica using Transact-SQL.