Exercise - Implement infrastructure resiliency with Kubernetes
In the previous unit, you implemented resiliency by adding failure-handling code using .NET native resilience extension. However, this change only applies to the service that you changed. Updating a large app with many services would be nontrivial.
Instead of using code-based resiliency, this unit uses an approach called infrastructure-based resiliency that spans the entire app. You will:
- Redeploy the app without any resiliency into Kubernetes.
- Deploy Linkerd in your Kubernetes cluster.
- Configure the app to use Linkerd for resiliency.
- Explore the app behavior with Linkerd.
Redeploy the app
Before applying Linkerd, revert the app to a state before code-based resiliency was added. To revert, follow these steps:
In the bottom panel, select to the TERMINAL tab and run the following git commands to undo your changes:
cd Store git checkout Program.cs git checkout Store.csproj cd .. dotnet publish /p:PublishProfile=DefaultContainer
Install Kubernetes
In your codespace, install Kubernetes and k3d. k3d is a tool that runs a single-node Kubernetes cluster inside a Virtual Machine (VM) on your local machine. It's useful for testing Kubernetes deployments locally and runs well inside a codespace.
Run these commands to install Kubernetes and MiniKube:
curl -fsSL https://pkgs.k8s.io/core:/stable:/v1.28/deb/Release.key | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/kubernetes-apt-keyring.gpg
echo 'deb [signed-by=/etc/apt/kubernetes-apt-keyring.gpg] https://pkgs.k8s.io/core:/stable:/v1.28/deb/ /' | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/kubernetes.list
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y kubectl
curl -s https://raw.githubusercontent.com/k3d-io/k3d/main/install.sh | bash
k3d cluster create devcluster --config k3d.yml
Deploy the eShop services to Docker Hub
The local images of your services that you build need to be hosted in a container registry to be deployable into Kubernetes. In this unit, you use Docker Hub as your container registry.
Run these commands to push your images to Docker Hub:
sudo docker login
sudo docker tag products [your username]/productservice
sudo docker tag store [your username]/storeimage
sudo docker push [your username]/productservice
sudo docker push [your username]/storeimage
Convert your docker-compose file to Kubernetes manifests
At the moment, you define how your app runs in docker. Kubernetes uses a different format for defining how your app runs. You can use a tool called Kompose to convert your docker-compose file to Kubernetes manifests.
You need to edit these files to use the images you pushed to Docker Hub.
In the codespace, open the file backend-deploy.yml.
Change this line:
containers: - image: [YOUR DOCKER USER NAME]/productservice:latestReplace the placeholder [YOUR DOCKER USER NAME] with your actual Docker username.
Repeat these steps for the frontend-deploy.yml file.
Change this line:
containers: - name: storefrontend image: [YOUR DOCKER USER NAME]/storeimage:latestReplace the placeholder [YOUR DOCKER USER NAME] with your actual Docker username.
Deploy the eShop app into Kubernetes:
kubectl apply -f backend-deploy.yml,frontend-deploy.ymlYou should see output similar to the following messages:
deployment.apps/productsbackend created service/productsbackend created deployment.apps/storefrontend created service/storefrontend createdCheck that all the services are running:
kubectl get podsYou should see output similar to the following messages:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE backend-66f5657758-5gnkw 1/1 Running 0 20s frontend-5c9d8dbf5f-tp456 1/1 Running 0 20sSwitch to the PORTS tab, to view the eShop running on Kubernetes select the globe icon next to Front End (32000) port.
Install linkerd
The dev container needs Linkerd CLI to be installed. Run the following command to confirm that Linkerd prerequisites are satisfied:
curl -sL run.linkerd.io/install | sh
export PATH=$PATH:/home/vscode/.linkerd2/bin
linkerd check --pre
A variation of the following output appears:
kubernetes-api
--------------
√ can initialize the client
√ can query the Kubernetes API
kubernetes-version
------------------
√ is running the minimum Kubernetes API version
√ is running the minimum kubectl version
pre-kubernetes-setup
--------------------
√ control plane namespace does not already exist
√ can create non-namespaced resources
√ can create ServiceAccounts
√ can create Services
√ can create Deployments
√ can create CronJobs
√ can create ConfigMaps
√ can create Secrets
√ can read Secrets
√ can read extension-apiserver-authentication configmap
√ no clock skew detected
pre-kubernetes-capability
-------------------------
√ has NET_ADMIN capability
√ has NET_RAW capability
linkerd-version
---------------
√ can determine the latest version
√ cli is up-to-date
Status check results are √
Deploy Linkerd to Kubernetes
First, run the following command to install the Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs):
linkerd install --crds | kubectl apply -f -
Then, run the following command:
linkerd install --set proxyInit.runAsRoot=true | kubectl apply -f -
In the preceding command:
linkerd installgenerates a Kubernetes manifest with the necessary control plane resources.- The generated manifest is piped to
kubectl apply, which installs those control plane resources in the Kubernetes cluster.
The first line of the output shows that the control plane was installed in its own linkerd namespace. The remaining output represents the objects being created.
namespace/linkerd created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/linkerd-linkerd-identity created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/linkerd-linkerd-identity created
serviceaccount/linkerd-identity created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/linkerd-linkerd-controller created
Validate the Linkerd deployment
Run the following command:
linkerd check
The preceding command analyzes the configurations of the Linkerd CLI and control plane. If Linkerd is configured correctly, the following output is displayed:
kubernetes-api
--------------
√ can initialize the client
√ can query the Kubernetes API
kubernetes-version
------------------
√ is running the minimum Kubernetes API version
√ is running the minimum kubectl version
linkerd-existence
-----------------
√ 'linkerd-config' config map exists
√ heartbeat ServiceAccount exist
√ control plane replica sets are ready
√ no unschedulable pods
√ controller pod is running
√ can initialize the client
√ can query the control plane API
linkerd-config
--------------
√ control plane Namespace exists
√ control plane ClusterRoles exist
√ control plane ClusterRoleBindings exist
√ control plane ServiceAccounts exist
√ control plane CustomResourceDefinitions exist
√ control plane MutatingWebhookConfigurations exist
√ control plane ValidatingWebhookConfigurations exist
√ control plane PodSecurityPolicies exist
linkerd-identity
----------------
√ certificate config is valid
√ trust anchors are using supported crypto algorithm
√ trust anchors are within their validity period
√ trust anchors are valid for at least 60 days
√ issuer cert is using supported crypto algorithm
√ issuer cert is within its validity period
√ issuer cert is valid for at least 60 days
√ issuer cert is issued by the trust anchor
linkerd-api
-----------
√ control plane pods are ready
√ control plane self-check
√ [kubernetes] control plane can talk to Kubernetes
√ [prometheus] control plane can talk to Prometheus
√ tap api service is running
linkerd-version
---------------
√ can determine the latest version
√ CLI is up to date
control-plane-version
---------------------
√ control plane is up to date
√ control plane and CLI versions match
linkerd-addons
--------------
√ 'linkerd-config-addons' config map exists
linkerd-grafana
---------------
√ grafana add-on service account exists
√ grafana add-on config map exists
√ grafana pod is running
Status check results are √
Tip
To see a list of Linkerd components that were installed, run this command: kubectl -n linkerd get deploy
Configure the app to use Linkerd
Linkerd is deployed, but it isn't configured. The app's behavior is unchanged.
Linkerd is unaware of service internals and can't determine whether it's appropriate to retry a failed request. For example, it would be a bad idea to retry a failed HTTP POST for a payment. A service profile is necessary for this reason. A service profile is a custom Kubernetes resource that defines routes for the service. It also enables per-route features, such as retries and timeouts. Linkerd only retries routes configured in the service profile manifest.
For brevity, implement Linkerd only on the aggregator and coupon services. To implement Linkerd for those two services, you will:
- Modify the eShop deployments so Linkerd creates its proxy container in the pods.
- To configure retries on the coupon service's route, add a service profile object to the cluster.
Modify the eShop deployments
The services must be configured to use Linkerd proxy containers.
Add the
linkerd.io/inject: enabledannotation to the backend-deploy.yml file under template metadata.template: metadata: annotations: linkerd.io/inject: enabled labels:Add the
linkerd.io/inject: enabledannotation to the frontend-deploy.yml file in the same place.Update the deployments in the Kubernetes cluster:
kubectl apply -f backend-deploy.yml,frontend-deploy.yml
Apply the Linkerd service profile for the product service
The service profile manifest for the product service is:
apiVersion: linkerd.io/v1alpha2
kind: ServiceProfile
metadata:
name: backend
namespace: default
spec:
routes:
- condition:
method: GET
pathRegex: /api/Product
name: GET /v1/products
isRetryable: true
retryBudget:
retryRatio: 0.2
minRetriesPerSecond: 10
ttl: 120s
The preceding manifest is configured so:
- Any idempotent HTTP GET route matching the pattern
/api/Productcan be retried. - Retries can add no more than an extra 20 percent to the request load, plus another 10 "free" retries per second.
Run the following command to use the service profile in the Kubernetes cluster:
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: linkerd.io/v1alpha2
kind: ServiceProfile
metadata:
name: backend
namespace: default
spec:
routes:
- condition:
method: GET
pathRegex: /api/Product
name: GET /v1/products
isRetryable: true
retryBudget:
retryRatio: 0.2
minRetriesPerSecond: 10
ttl: 120s
EOF
The following output appears:
serviceprofile.linkerd.io/backend created
Install monitoring on the service mesh
Linkerd has extensions to give you extra features. Install the viz extension and view the status of the app in Linkerd's dashboard.
In the terminal, run this command to install the extension:
linkerd viz install | kubectl apply -f -View the dashboard with this command:
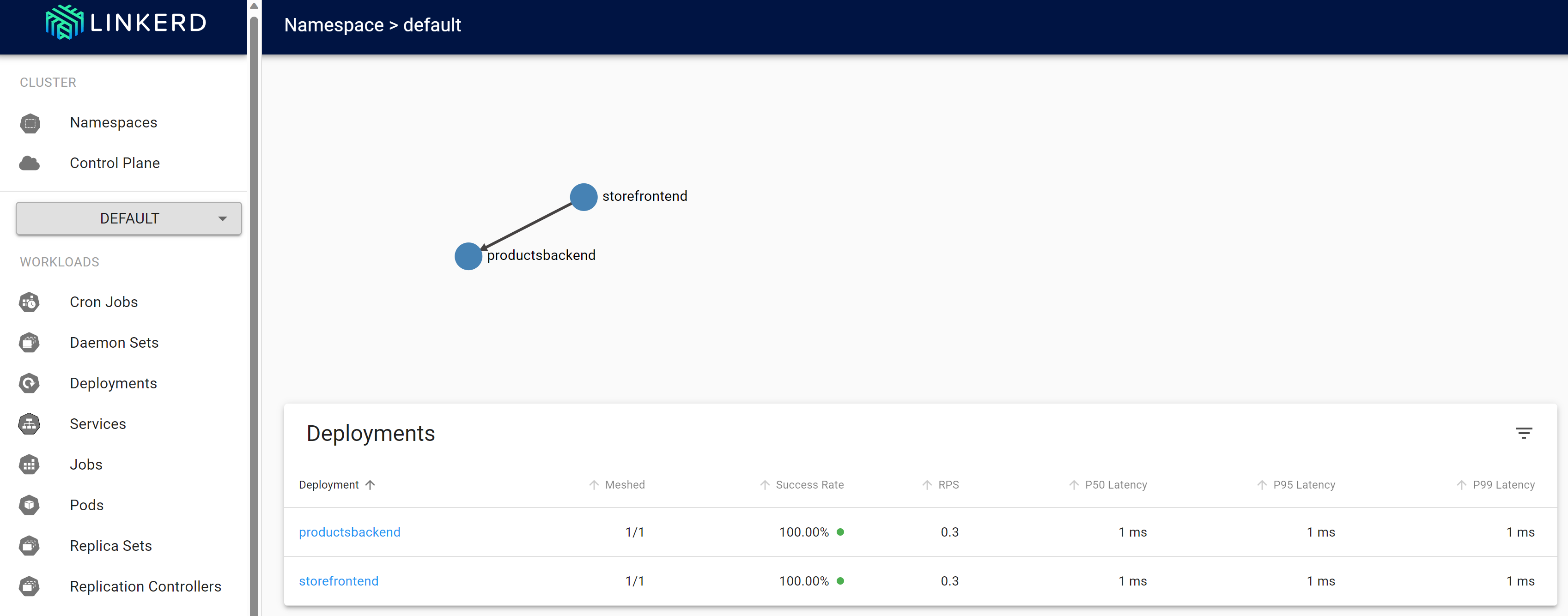
linkerd viz dashboardGo to the PORTS tab and to see a new port forwarded with a process of linkerd viz dashboard running. Select the Open in Browser to open the dashboard.
In the Linkerd dashboard, select Namespaces.
Under HTTP Metrics, select default.
Test Linkerd resiliency
After the redeployed containers are healthy, use the following steps to test the app's behavior with Linkerd:
Check the status of the running pods with this command:
kubectl get pods --all-namespacesStop all the product service pods:
kubectl scale deployment productsbackend --replicas=0Go to the eShop web app and try to view the products. There's a delay until the error message, "There's a problem loading our products. Please try again later."
Restart the product service pods:
kubectl scale deployment productsbackend --replicas=1The app should now display the products.
Linkerd follows a different approach to resiliency than what you saw with code-based resilience. Linkerd transparently retried the operation multiple times in quick succession. The app didn't need to be changed to support this behavior.
Additional information
For more information about Linkerd configuration, see the following resources:
- Configuring retries - Linkerd documentation
- Configuring timeouts - Linkerd documentation
- How we designed retries in Linkerd 2.2 - Linkerd blog