Implement application resiliency
The resiliency features of .NET are built upon the Polly project and made available through Microsoft.Extensions. You can add a standard resilience strategy that uses sensible defaults by adding a single line of code to your app.
Add resilience to your app
To add resilience to an app built using a microservices architecture, using HTTP requests between individual services, take these steps:
- Add the
Microsoft.Extensions.Http.Resiliencepackage to your project. - Add a resilience handler to your HttpClient service calls.
- Configure the resilience strategy.
Add the NuGet package to your project
Run the following command to add the resiliency NuGet package:
dotnet add package Microsoft.Extensions.Http.Resilience
Running this command from the terminal in the apps project folder will add the package reference to the project file.
In your application's startup class then add the following using statement:
using Microsoft.Extensions.Http.Resilience;
Add a resilience strategy
You can now add a standard resilience strategy to your HttpClient service. .NET provides this out-of-the-box configuration combining a number of strategies.

The request handler goes through each of the above strategies in order form left to right:
- Total request timeout strategy: This sets a total amount of time that the request can take. You can think of this as setting the upper time limit for all the other strategies.
- Retry strategy: This strategy controls the options on number of retries, backoff, and jitter. These options can't exceed the total timeout set in the previous strategy.
- Circuit breaker strategy: This strategy opens the circuit if the failure ratio exceeds the threshold.
- Attempt timeout strategy: This strategy sets a timeout for each individual request. If the request takes longer than this time then an exception is thrown.
You can add this standard strategy, with all the default values by adding this extension method:
.AddStandardResilienceHandler();
For example if you have declared a WebApplication, and you want to add a resilience strategy to the HttpClient service use this code:
builder.Services.AddHttpClient<ServiceBeingCalled>(httpClient =>
{
httpClient.BaseAddress = new Uri("https://service.endpoint/");
}).AddStandardResilienceHandler();
The first line of the above code adds a standard resilience handler to the HTTPClient. This will use all the default settings for the retry and circuit breaker strategies.
Configure the resilience strategy
You can change the default values of any of the strategies by specifying new options, for example:
.AddStandardResilienceHandler( options =>
{
options.RetryOptions.RetryCount = 10;
options.RetryOptions.BaseDelay = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1);
});
This code changes the retry strategy defaults to have a maximum number of retires of 10, to use a linear back off, and use a base delay of 1 second.
The options you choose have to be compatible with each other. For example, if the total time remains as its default of 30 seconds, then the retry options above will cause an exception. This is an error because the exponential backoff setting would cause the total time to complete the 10 retries to be 2046 seconds. This is a runtime exception, not a compile time error.
The following table lists the options available for each of the strategies.
| Total request timeout options | Description |
|---|---|
| TotalTimeout | The total amount of time that the request can take. The default is 30 seconds. |
| OnTimeout | A callback function that's invoked when the request times out. The default is null. |
| Retry options | Description |
|---|---|
| RetryCount | The maximum number of retries. The default is 3. |
| BackoffType | The type of backoff to use. You can choose between linear and exponential. The default is exponential. |
| UseJitter | Whether to add jitter to the backoff. Jitter adds randomness to the delay to help reduce spikes in load. The default is true. |
| BaseDelay | The delay between retries. The default is 2 seconds. |
| Circuit breaker options | Description |
|---|---|
| BreakDuration | The duration of the circuit break. The default is 5 seconds. |
| FailureRatio | The ratio of failed requests to successful requests that will open the circuit. The default is 0.1. |
| SamplingDuration | The duration of time that the failure ratio is calculated over. The default is 30 seconds. |
| OnClosed | A callback function that's invoked when the circuit is closed. The default is null. |
| OnHalfOpened | A callback function that's invoked when the circuit is half-open. The default is null. |
| OnOpened | A callback function that's invoked when the circuit is opened. The default is null. |
| Attempt timeout options | Description |
|---|---|
| Timeout | The amount of time that the request can take. The default is 2 seconds. |
| OnTimeout | A callback function that's invoked when the request times out. The default is null. |
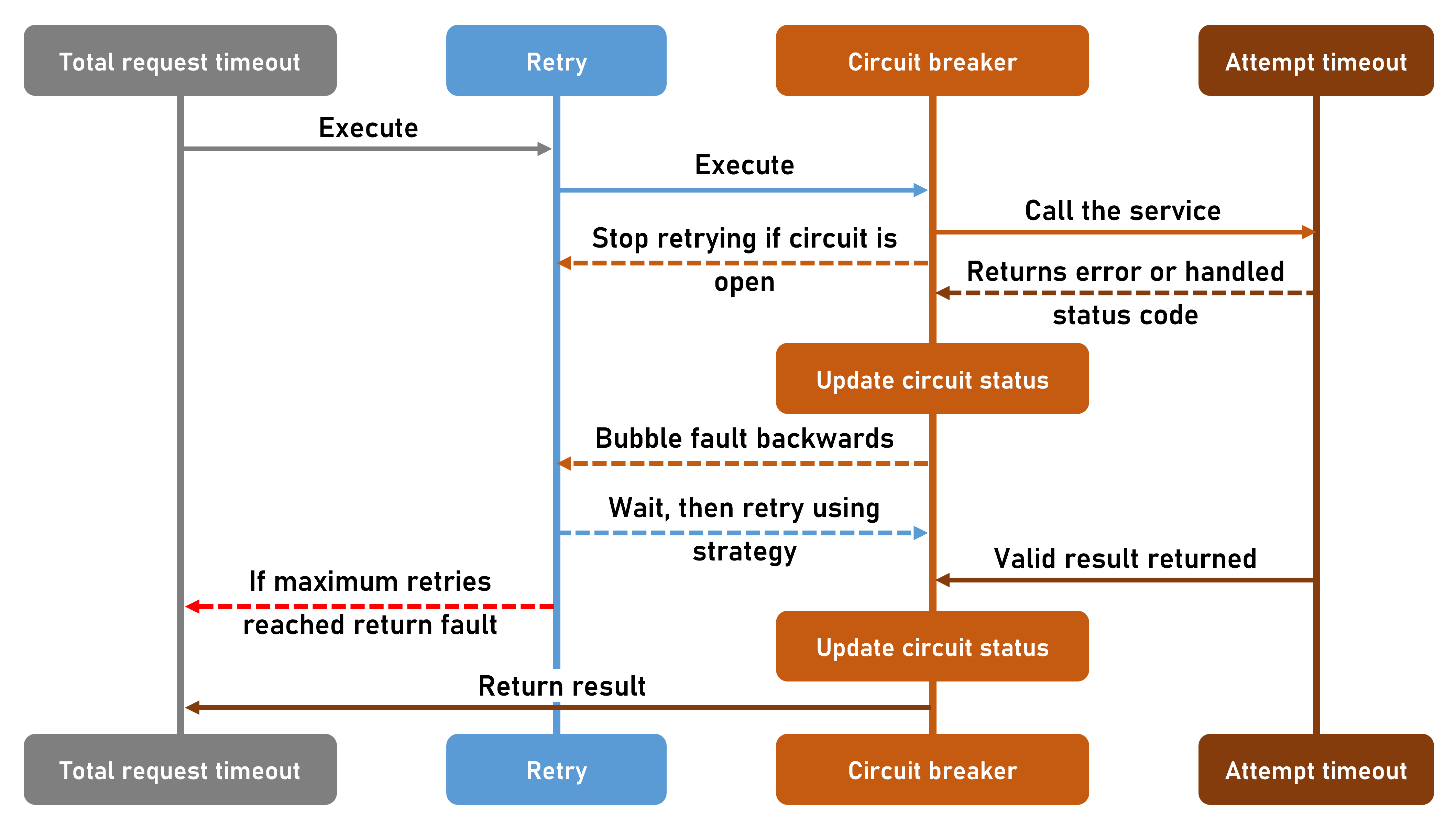
The sequence diagram above shows how each of the strategies work together in a standard resiliency strategy. To begin with the limiting factor of how long a request can take is controlled by the total timeout strategy. The retry strategy must then be set to have a maximum number of retries that will complete within the total timeout. The circuit breaker strategy will open the circuit if the failure ratio exceeds the threshold set for it. The attempt timeout strategy sets a timeout for each individual request. If the request takes longer than this time then an exception is thrown.