Set up, configure, and troubleshoot GitHub Copilot
This unit explains how to sign up for GitHub Copilot, how to configure GitHub Copilot by using VS Code, and how to troubleshoot GitHub Copilot by using VS Code.
Sign up for GitHub Copilot
Before you can start using GitHub Copilot, you need to set up a free trial or subscription for your account.
To get started, select your GitHub profile photo, and then select Settings. Copilot is on the left menu under Code, planning, and automation.
After you sign up, you need to install an extension for your preferred environment. GitHub Copilot supports GitHub.com (which doesn't need an extension), VS Code, Visual Studio, JetBrains IDEs, and Neovim as an unobtrusive extension.
For this module, you'll just review extensions and configurations for VS Code. The exercise that you'll complete in the next unit uses VS Code.
If you're using a different environment, you can find specific links to set up other environments in the "References" section at the end of this module.
Configure GitHub Copilot in VS Code
Add the VS Code extension for GitHub Copilot
- In Visual Studio Marketplace, go to the GitHub Copilot extension page and select Install.
- A popup dialog asks you to open VS Code. Select Open.
- In VS Code, on the Extension: GitHub Copilot tab, select Install.
- If you didn't previously authorize VS Code in your GitHub account, you're prompted to sign in to GitHub in VS Code. Select Sign in to GitHub.
GitHub Copilot can autocomplete code as you type when you use VS Code. After installation, you can enable or disable GitHub Copilot, and you can configure advanced settings within VS Code.
Enable or disable GitHub Copilot in VS Code
On the bottom pane of the VS Code window, select the status icon, and then select Enable or Disable.

When you're disabling GitHub Copilot, VS Code asks whether you want to disable completions globally or for the language of the file that you're currently editing.
- To disable GitHub Copilot completions globally, select Disable completions.
- To disable GitHub Copilot completions for a specified language, select Disable completions for LANGUAGE.
Enable or disable inline suggestions in VS Code
On the File menu, select Preferences > Settings.
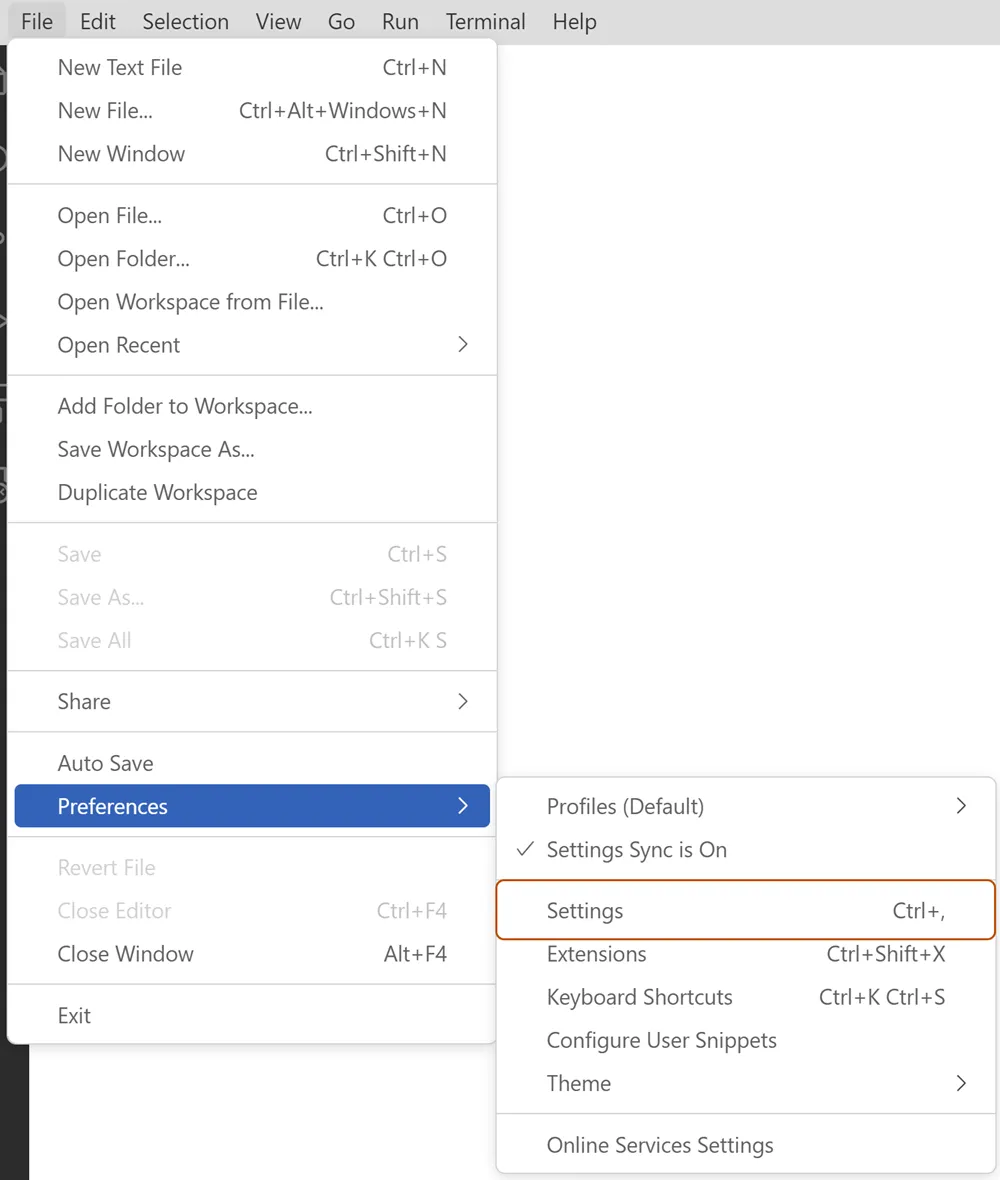
On the left-side pane of the Settings tab, select Extensions, and then select GitHub Copilot.
Under Editor: Enable Auto Completions, select or clear the checkbox to enable or disable inline suggestions.
Additionally, you can choose to enable or disable inline suggestions and specify for which languages you want to enable or disable GitHub Copilot.
Troubleshoot GitHub Copilot in VS Code
In VS Code, the log files are useful for diagnosing connection problems. The GitHub Copilot extension stores the log files in the standard log location for VS Code extensions. You can find the log files by opening the command palette and then entering either Developer: Open Log File or Developer: Open Extensions Logs Folder.
In rare cases, errors might not be logged in the regular locations. If you encounter errors and nothing is in the logs, you might try to view the logs from the process that's running VS Code and the extension. This process enables you to view the Electron logs. You can find these logs by selecting Help > Toggle Developer Tools in VS Code.
Network restrictions, firewalls, or your proxy might cause problems when you're connecting to GitHub Copilot. If a problem occurs, use the following steps to open a new editor with the relevant information that you can inspect yourself or share with the support team:
Open the VS Code command palette, and then:
- For Mac, use
Shift+Command+P. - For Windows or Linux, use
Ctrl+Shift+P.
- For Mac, use
Enter Diagnostics, and then select GitHub Copilot: Collect Diagnostics from the list.
For more information on how to troubleshoot in other environments, check out the "References" section at the end of this module.