When should you use Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL
Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL is a fully managed NoSQL database service for modern and AI app development. It provides guaranteed single-digit millisecond response times, 99.999-percent availability and vector database capabilities, backed by SLAs with automatic and instant scalability.
For enterprise scenarios, Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL has a comprehensive suite of financially backed service level agreements (SLAs) that cover throughput, consistency, availability, and latency.
Common use cases for the Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL
As a fast NoSQL database with a flexible API and vector indexing and search capabilities, Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL is well suited for many types and sizes of applications. From the very small scale, to high-performance applications with global ambition. Speed and flexibility make Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL great for Generative AI, web, retail, IoT, gaming, and mobile applications. Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL is a good fit for applications that require flexibility, low cost, fast response times, and the ability to scale to massive volume or velocity.
Generative AI
Generative AI applications can be diverse and unpredictable. These workloads require a database platform that is cost-efficient, responsive and scalable. Users can store vectors directly in their documents with traditional schema-free data and high-dimensional vectors as other properties. This colocation of data and vectors allows for efficient indexing and searching, as the vectors are stored in the same logical unit as the data they represent. Keeping vectors and data together simplifies data management, AI application architectures, and the efficiency of vector-based operations.
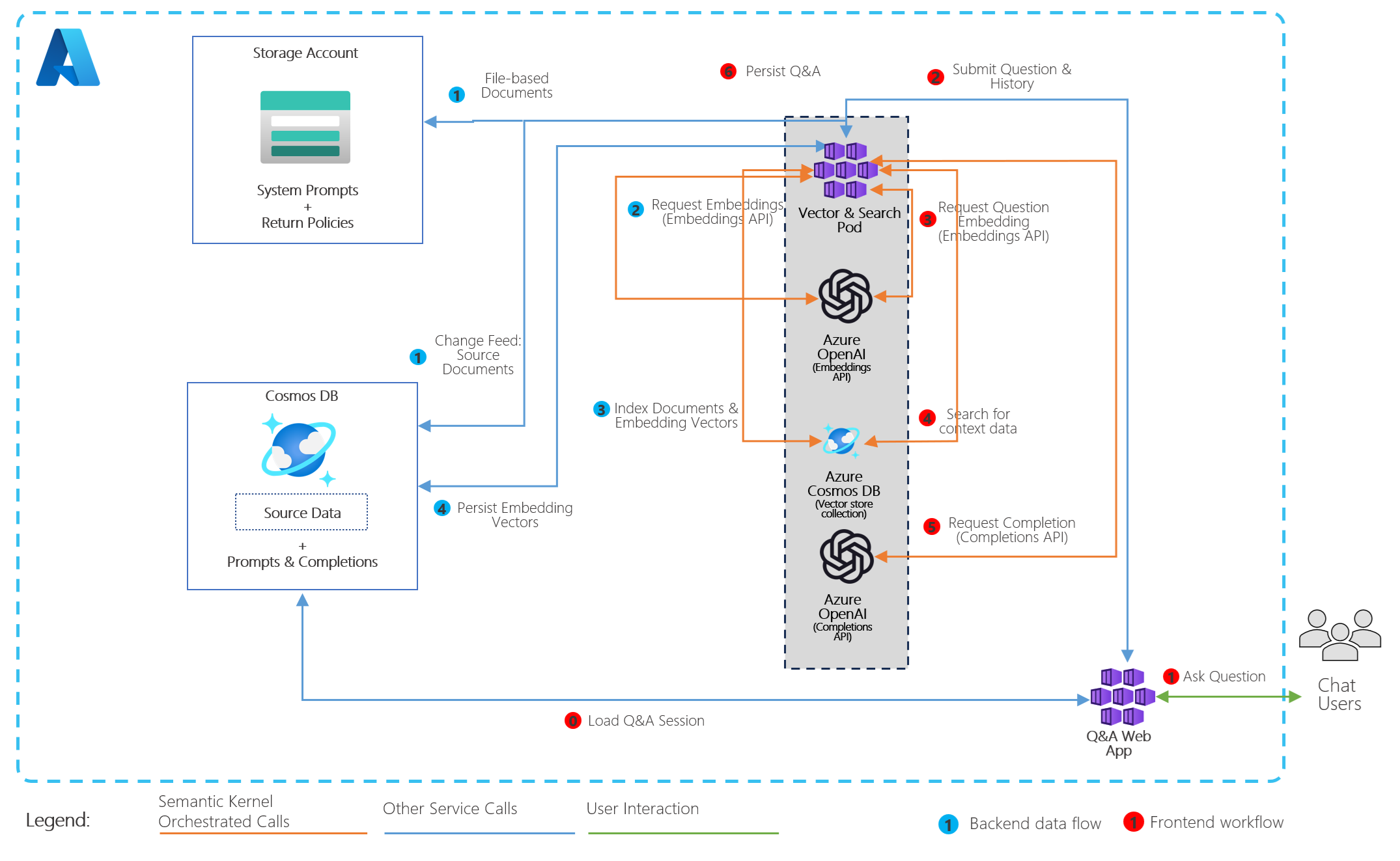
In this example, customers are taking transactional and operational data and vectorizing it to be used for vector search by multiple AI Agents serving customers. Azure Cosmos DB's Change Feed is used to handle ingestion and vectorization of new or updated data, making it available in near real-time for users. Customers interacting with these agents generate prompts and completions which are also stored as their chat history in Azure Comsos DB and used to provide a semantic cache for improved cost and performance.
Retail/marketing
Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL is a great fit for retail and marketing workloads that can experience dramatic and unexpected swings in usage at any point throughout the year. The elastic scale of Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL ensures that the database platform can handle requests during peak usage, and save money during nonpeak times.
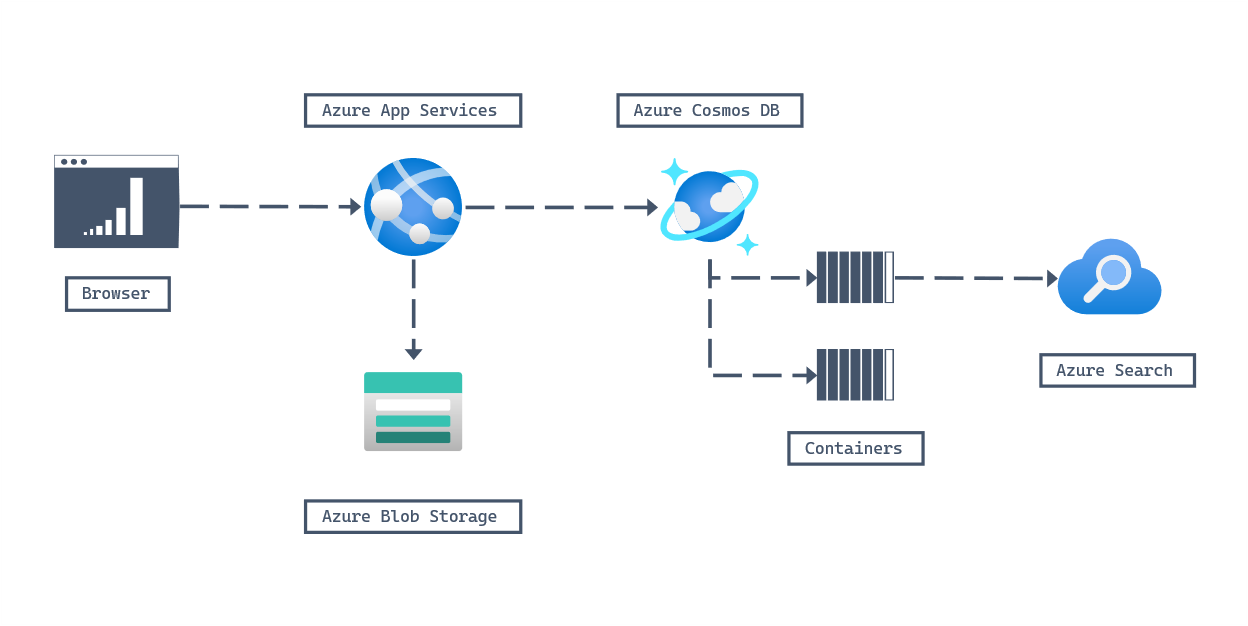
In this example, a JavaScript web application, built on content stored in Azure Blob Storage, uses Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL as it's backing database. Multiple accounts are used to manage different facets of the solution such as the shopping cart, inventory, or catalog. The solution then uses Azure Search to index the Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL data, providing a rich search experience to end users.
Web/mobile
Many modern social applications generate a plethora of user-generated content that is diverse in quantity, shape, and volume. Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL is a great candidate for this workload as this API can store data of varying schemas. Consider the NoSQL API for data that may have schemas that change or evolve over time as the company's initiatives expand into new areas.
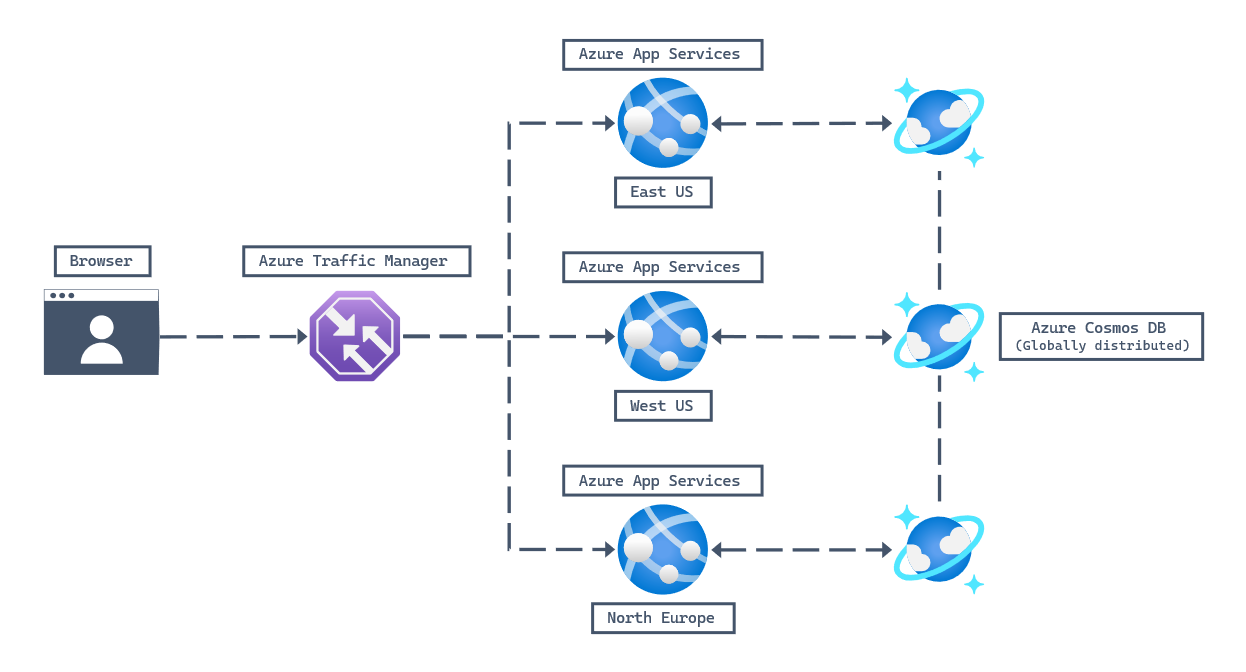
In this example, a user is using a URL to access a web site in their browser. The URL points to Azure Traffic Manager, which then uses a built-in algorithm to determine which Azure App Service endpoint to redirect the user to. Since Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL is capable of global distribution, you only need one account that is replicated across multiple regions.
Module Scenario
Consider the scenario from the beginning of this module:
Suppose you work as the lead developer at a retail company. Your team is building your online storefront with support for AI Agents to provide a rich experience for users. You're designing the new storefront to be accessible across various devices including mobile. The team expects a spike in demand when the storefront is published and various "grand opening" sales begin.
One key part of your store's success is the ability for the company to notify users of shipping updates regardless of what device they place the order on or are currently using. Your team has worked hard on a sophisticated system to manage detailed order status tracking. The tight integration of Azure Cosmos DB with other Azure services, let's you consider building solutions that use order data in Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL to send notification to your user's mobile devices. The notifications alert them when their package ships, or is out for delivery.
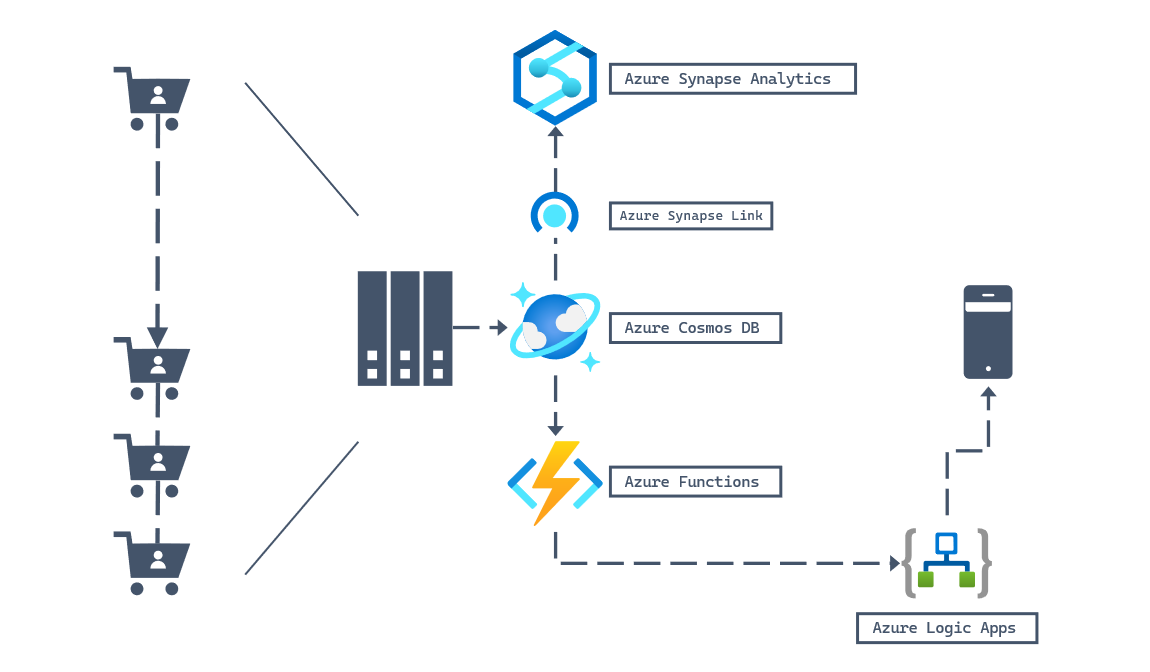
This example is similar to the example from the introduction of this module. To build on the first example, your team has decided to introduce Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL as the database of choice. Now, your team can use Azure Synapse Link to prepare and aggregate data for deeper analysis using Azure Synapse Analytics. Your team can also use services such as Azure Functions to react to data events with Azure Cosmos DB, and then trigger an Azure Logic Apps workflow that sends notifications to mobile devices.