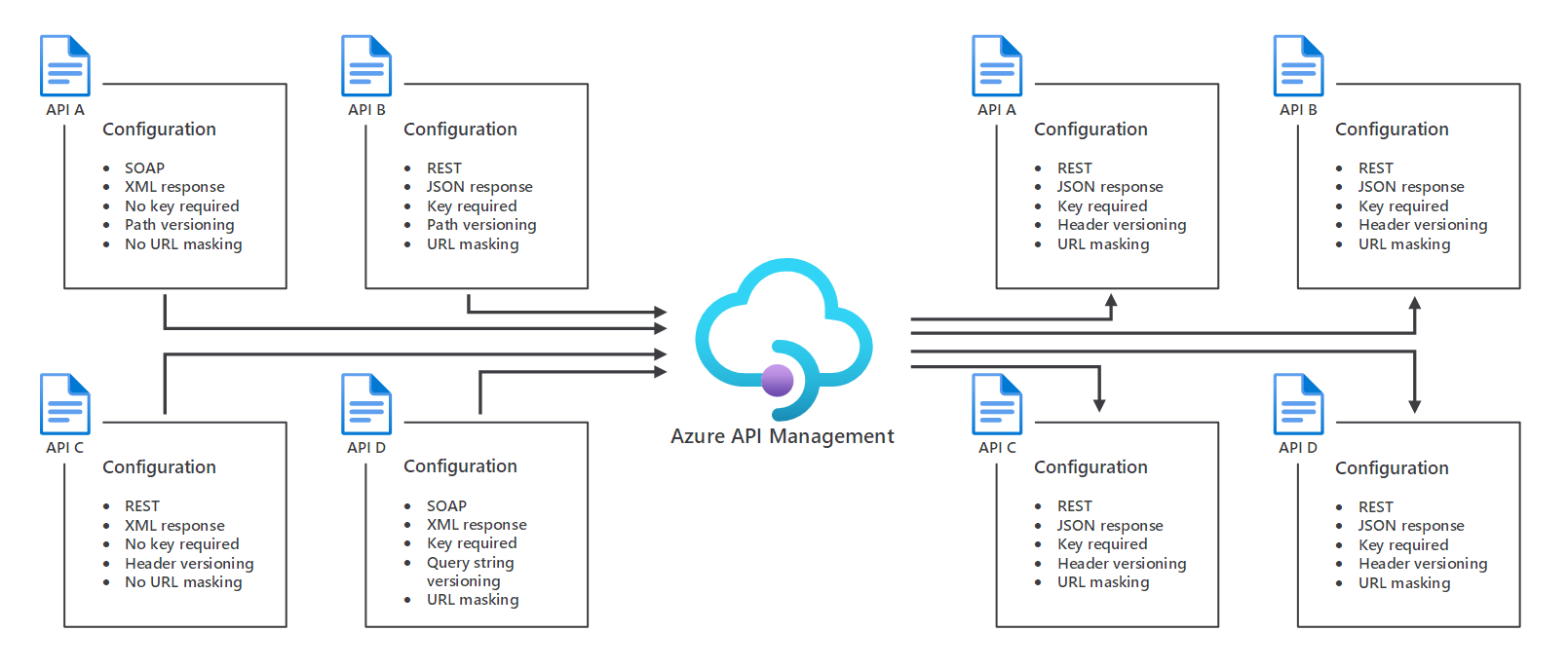
When to use Azure API Management
Now let's discuss some scenarios that illustrate when it's appropriate to use Azure API Management. Using the food delivery service as an example, let's investigate API lifecycle management with respect to standardizing APIs, centralizing API management and exposure, and enhancing API security. We can use the following criteria to help you decide whether Azure API Management is a suitable choice for managing and publishing your organization's inventory of APIs:
Decision criteria
| Criteria | Analysis |
|---|---|
| Number of APIs | The key consideration is the number of APIs that you manage. The more APIs you've deployed, the greater the need for deployment standardization and centralization of API control. |
| Rate of API changes | The next consideration is the rate at which your organization implements API revisions and versions. The faster you create API revisions and publish new API versions, the greater the need for a robust and flexible versioning control system. |
| API administration load | The last consideration is how much policy overhead you apply to your APIs. Policies such as usage quotas, call rate limits, request transformations, and request validation. The more configurations and options your APIs require, the greater the need for standardized and centralized policy implementations. |
Apply the criteria
Azure API Management is the correct choice for managing APIs through their lifecycles when you have a large API deployment that changes frequently and requires significant policy overhead. However, these criteria don't apply equally to all use cases. Let's consider how these criteria apply to the use cases for our scenario.
Should you use Azure API Management to standardize APIs?
By enabling management of multiple APIs from a single administrative interface, Azure API Management makes it easier to create consistency across multiple APIs. You can standardize many API features, including:
- Specifications. Standardizing API specs—such as using REST for all APIs and using a consistent naming scheme for JSON name-value pairs—reduces development time, decreases errors, and enables your organization to respond faster to customer suggestions and market forces.
- Documentation. Standardizing API documentation enables developers to get up to speed with an API quickly. It also reduces technical support queries and encourages developers to use more of your APIs.
- URLs. Standardizing the base URL for your APIs reduces consumer errors and gives your API deployments a more professional appearance.
- Analytics. Standardizing API analytics enables management teams and engineers to compare usage and performance across multiple APIs.
- Regulations. For APIs that must meet government or industry rules and regulations, standardization helps ensure compliance across all APIs.
In most cases, the need for standardization expands as:
- The number of APIs grows.
- The rate at which the APIs are revised increases.
- The API administration load gets larger.
This need is true of the food delivery platform scenario, which requires consistency across the APIs for the mobile app, the web app, and the partner restaurants.
Should you use Azure API Management to centralize API operations?
Azure API Management enhances the centralization of all API operations by bringing multiple APIs under a single administrative umbrella. Without an API management service, each API is on its own in terms of administration, deployment, and developer access. This decentralized model often results in duplicated efforts and increased overhead. Centralizing API operations can result in the following benefits:
- Administration. Apply administrative operations—such as policy creation, user management, and analytics—in a single location such as the administrative interface provided by Azure API Management. Centralizing admin tasks makes running these tasks simpler and more efficient.
- Deployment. Route all API requests through a single base URL, such as the endpoint created by the Azure API Management gateway. Deployment centralization makes it easier to enforce policies and apply transformations.
- Developer access. Place all developer resources—such as documentation, code samples, testing, and subscriptions—in a single location such as the developer portal in Azure API Management. Centralizing developer access makes it easier for developers to find and use your APIs.
The efficiencies that accrue from centralizing API operations tend to increase with the number of APIs and with the overall administrative load size you impose on your APIs. Having centralized APIs is a huge help when APIs are frequently updated because it enables a single versioning scheme for all products.
All these factors apply strongly to our food delivery platform scenario. For example, centralized consumer access through the developer portal makes it easier to sign up new developers, enhancing the monetization of the platform's APIs.
Should you use Azure API Management to secure access to your APIs?
Azure API Management was designed with API security in mind. So many organizations rely on APIs for the internal and external exchange of data between apps and devices. A haphazard or inconsistent approach to security is just asking for trouble. A proper API security strategy covers the following bases:
- Permissions. Control who can work with an API and what they can do with it. In Azure API Management, having all your API consumers as users and being able to organize those users into groups makes it easier and more efficient to apply permissions to control API access.
- Access. Only allow authorized users to submit requests. With Azure API Management, the developer portal supplies users with subscription keys, and you can restrict access to APIs by using multiple forms of authentication and JSON web tokens.
- Protection. Secure the API from malicious usage. Azure API Management enables you to throttle API access by using rate limits and usage quotas to help prevent consumer misuse (intentional or accidental) of the API.
- Compliance. Make sure your APIs satisfy all corporate or government security policies. Having all your APIs together in Azure API Management makes it easier to configure those APIs with security policies that achieve compliance.
The more APIs you manage, the greater the need for security. Having more APIs, means a greater attack surface and a greater risk of accidental data breaches or leaks. Also, the more often you revise your APIs, the greater the chance that a revision or new version can uncover a security flaw.
These security concerns are paramount in our food delivery scenario. Our platform generates and stores a great deal of sensitive data, including restaurant payments, customer names and addresses, and delivery vehicle locations.