Assistive technology
Some people with disabilities might use assistive technology (AT) to access technology or perform tasks. According to the Assistive Technology Industry Association (ATIA), "assistive technology is any item, piece of equipment, software program, or product that's used to increase, maintain, or improve the functional capabilities of people with disabilities."
Microsoft's Windows operating system has several built-in accessibility features designed to help with a wide range of needs and preferences. In Windows 11, the keyboard shortcut Windows + U opens accessibility settings that help to make it easier to interact with your display and device. For example:
Someone with low vision might use Magnifier to zoom in to enlarge text and images when viewing a web page, email, or a document.
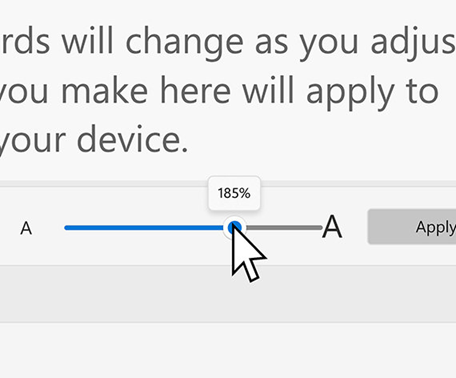
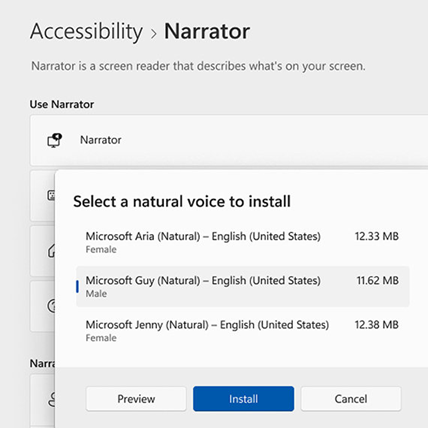
A person who is blind might choose to use Narrator, the Windows built-in screen reader.
Captions can help people who are deaf or hard of hearing consume audio and video content.
People with mobility disabilities can use Voice Access to control their device, author text, and interact with UI elements using only their voice.
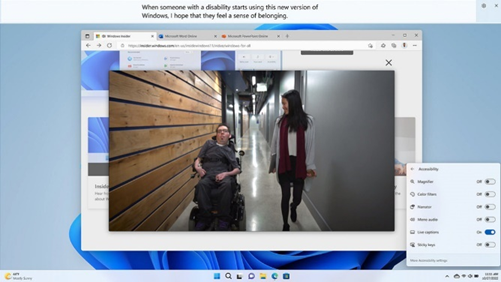
Focus minimizes distractions, making it easier for someone who is neurodiverse or has a mental health condition to schedule focus time and work breaks.