Machine learning and the data science lifecycle
Machine learning is part of the broader field of data science. It's essentially the process of creating knowledge from raw data.
Significant work is required to covert raw data to knowledge. For example, imagine you have a garden and you're trying to grow lettuce. You want to optimize your garden so that you can grow the most amount of lettuce in the least amount of time. You can collect a large amount of data that might influence how you set up the most successful environment to grow lettuce.
You can factor in sun exposure, temperature, moisture in the soil and air, the type of lettuce and seed source, exposure to fresh air, the size of the planter, and the quality and amount of soil. The list might be even longer because there might be some factors that affect growth that you aren't even be aware of, like noise level or the type of noise near your garden.
Data science lifecycle
An understanding of the data science lifecycle can guide you in your effort to create new knowledge from data sources.
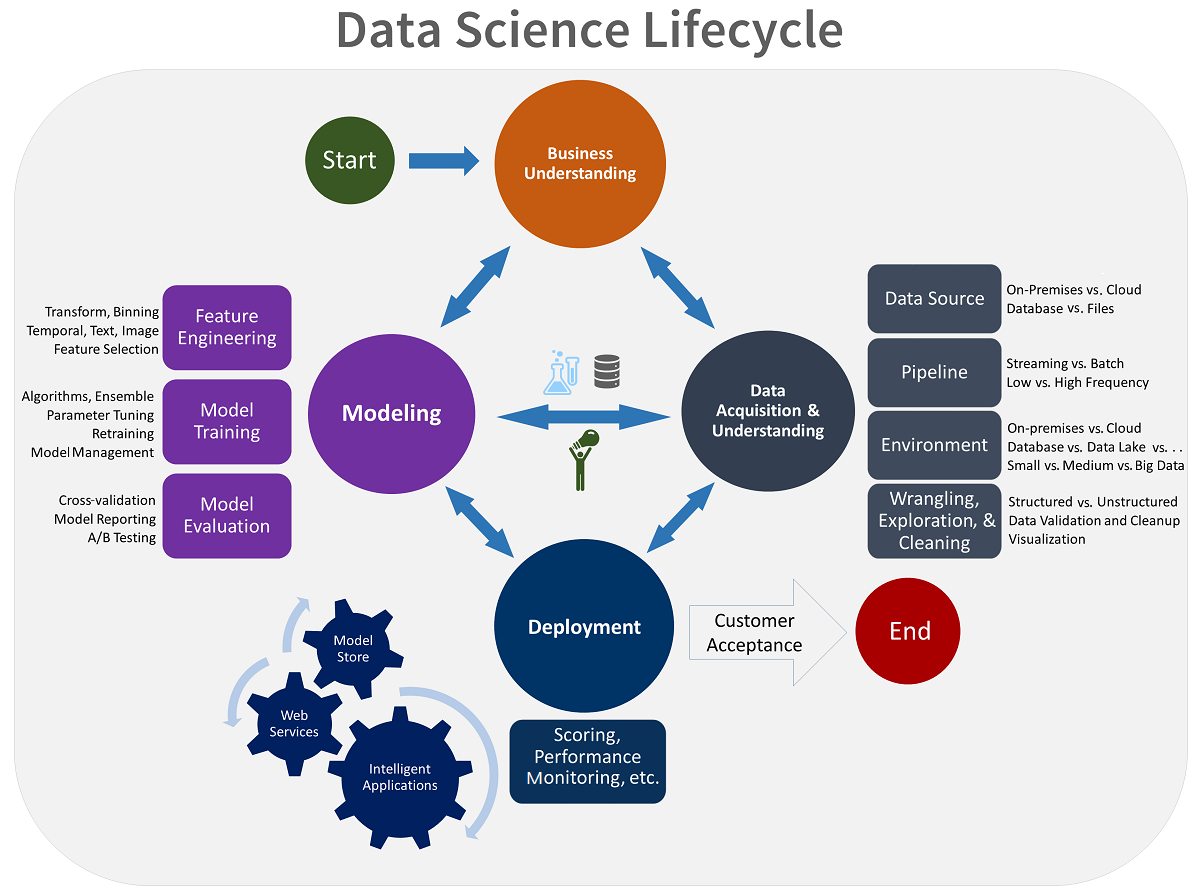
Here are the four steps of the data science lifecycle:
- Define a business goal by using subject matter expertise.
- Collect, clean, and manipulate your data.
- Choose a machine learning algorithm, and then train and test your model.
- Deploy your model, to be used with other applications.
Read on to look at each step in the data science lifecycle in more detail.