GitHub Copilot Large Language Models (LLMs)
GitHub Copilot is powered by Large Language Models (LLMs) to assist you in writing code seamlessly. In this unit, we focus on understanding the integration and impact of LLMs in GitHub Copilot. Let's review the following topics:
- What are LLMs?
- The role of LLMs in GitHub Copilot and prompting
- Fine-tuning LLMs
- LoRA fine-tuning
What are LLMs?
Large Language Models (LLMs) are artificial intelligence models designed and trained to understand, generate, and manipulate human language. These models are ingrained with the capability to handle a broad range of tasks involving text, thanks to the extensive amount of text data they're trained on. Here are some core aspects to understand about LLMs:
Volume of training data
LLMs are exposed to vast amounts of text from diverse sources. This exposure equips them with a broad understanding of language, context, and intricacies involved in various forms of communication.
Contextual understanding
They excel in generating contextually relevant and coherent text. Their ability to understand context allows them to provide meaningful contributions, be it completing sentences, paragraphs, or even generating whole documents that are contextually apt.
Machine learning and AI integration
LLMs are grounded in machine learning and artificial intelligence principles. They're neural networks with millions, or even billions, of parameters that are fine-tuned during the training process to understand and predict text effectively.
Versatility
These models aren't limited to a specific type of text or language. They can be tailored and fine-tuned to perform specialized tasks, making them highly versatile and applicable across various domains and languages.
Role of LLMs in GitHub Copilot and prompting
GitHub Copilot utilizes LLMs to provide context-aware code suggestions. The LLM considers not just the current file but also other open files and tabs in the IDE to generate accurate and relevant code completions. This dynamic approach ensures tailored suggestions, improving your productivity.
Fine-tuning LLMs
Fine-tuning is a critical process that allows us to tailor pretrained large language models (LLMs) for specific tasks or domains. It involves training the model on a smaller, task-specific dataset, known as the target dataset, while using the knowledge and parameters gained from a large pretrained dataset, referred to as the source model.
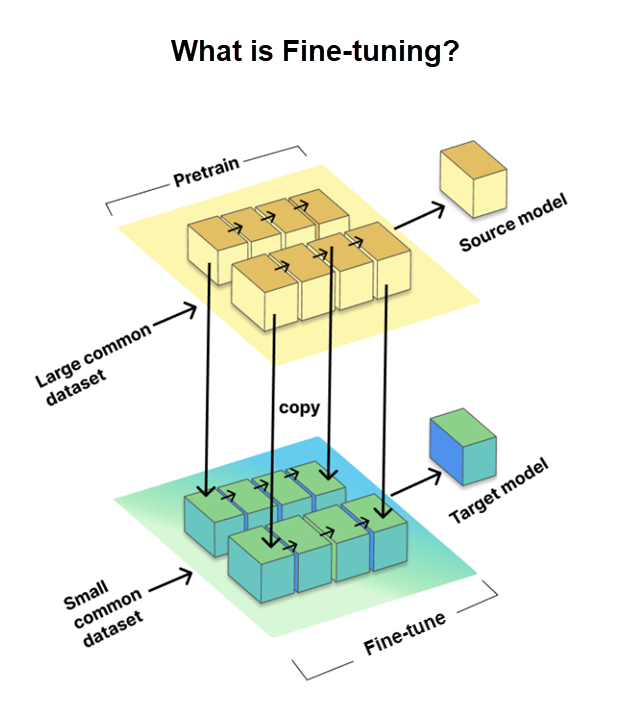
Fine-tuning is essential to adapt LLMs for specific tasks, enhancing their performance. However, GitHub took it a step further by using the LoRA fine tuning method, which we discuss next.
LoRA fine-tuning
Traditional full fine-tuning means to train all parts of a neural network, which can be slow and heavily reliant on resources. But LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation) fine-tuning is a clever alternative. It's used to make large pretrained language models (LLMs) work better for specific tasks without redoing all the training.
Here's how LoRA works:
- LoRA adds smaller trainable parts to each layer of the pretrained model, instead of changing everything.
- The original model remains the same, which saves time and resources.
What's great about LoRA:
- It beats other adaptation methods like adapters and prefix-tuning.
- It's like getting great results with fewer moving parts.
In simple terms, LoRA fine-tuning is about working smarter, not harder, to make LLMs better for your specific coding requirements when using Copilot.