How Azure Bot Service works
In this unit, you explore using Bot Framework Composer to help you design bots in an interactive, visual designer. You learn how to extend your bot with AI and language capabilities within Bot Framework Composer. You also gain a basic understanding of how to create a bot, extend bot capabilities, and publish a bot in the Azure Bot Service.
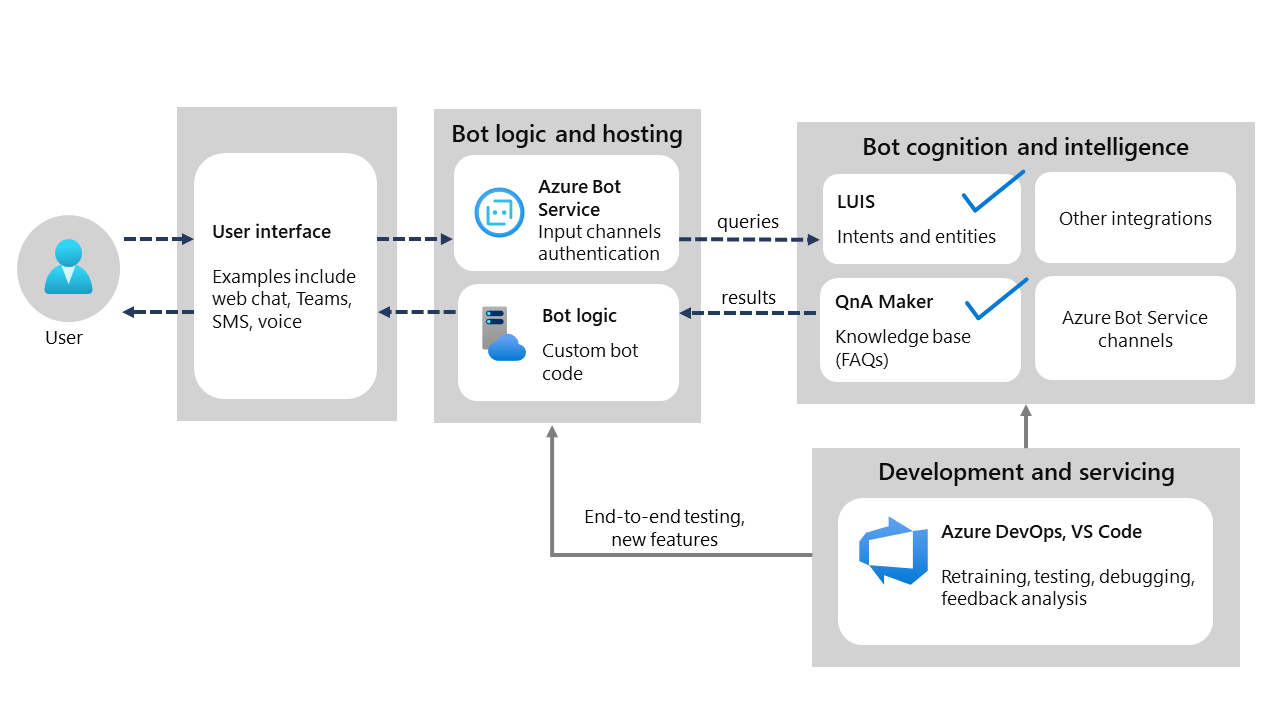
What is the architecture of a bot package?
Azure Bot Service and Bot Framework support the complete bot-creation process. The supported process includes design, building, testing, and publishing tasks.
Bot developers use Bot Framework Composer to create a bot package. This package contains the bot logic and details about bot integrations and connections, including input channels and authentication. The bot package also contains any custom bot code. The Azure Bot Service hosts the bot package. You can think of an Azure Bot as an Azure Web App with a few extra features that provides the primary endpoint for bot interaction. Through the Bot Service, users can interact with the bot. Meanwhile, it can manage incoming and outgoing REST interactions for external channels and other integrations.
Note
The bot package can also be serviced using the Bot Framework SDK through Visual Studio or Visual Studio Code.
Consider the type of bot you want to create
Before building your bot, you need to decide what kind of bot you're creating. As you decide, consider the following questions:
What is your bot used for? Determine what kind of bot you want to build. Planning helps define the functionalities you want to implement.
What problems does your bot intend to solve? Be clear about this answer. Solving problems for customers is a primary consideration when you're building bots. You should also consider things such as how to solve the user's problem better, easier, or faster than the alternative experiences.
Who uses your bot? If you're designing a bot, it's safe to assume that you're expecting users to use it. Different customers expect different user experiences. Knowing your audience helps determine how complex your bot design should be. Consider what languages to implement for the bot.
Tip
Ensuring a great user experience should be your number one priority when designing a bot.
Where is your bot used? You must decide which platforms your bot is going to run on. For example, a bot designed to run on a mobile device might require features such as sending Short Message Service (SMS) messages.
Important
The publishing experience varies from platform to platform.
Develop core bot functionality in Bot Framework Composer
You can use Composer to design, build, extend, and test a bot. Composer is a visual editing canvas for building bots. It's typically the starting point for the Azure Bot Service creation process.
You can use Composer's visual designer to intuitively develop the core functionality for your bot. You can use it to:
- Add natural language understanding capabilities to your bot with QnA Maker. You can use capabilities such as Language Understanding Intelligence Service (LUIS), QnA, or FAQ.
- Create text and speech variation responses for your Bot using language generation templates.
- Build bots in multiple languages.
- Test your bot directly inside Composer using embedded Web Chat.
- Publish bots to Azure App Service and Azure Functions.
- Integrate external services such as LUIS apps and QnA Maker knowledge bases.
Create dialogs and conversation flow
Dialogs control the conversations that a bot has with its users. Dialogs contain language-generation response templates that define bot responses and instructions for how a bot performs tasks. For example, making dinner reservations at a restaurant or creating an Outlook calendar item.
Many dialogs are linear, with a simple question and response sequence. But some dialogs also include advanced conversation logic. This logic might include branching, looping, and context-based dynamic and adaptive dialogs. These types of dialogs typically use external data, maintain stateful conversation data, and make necessary interruptions in the conversation.
Include external flows with skills and other bots
You can create more complex conversation flows by importing Composer skills, NuGet packages, and even other Azure Bot Service bots into your bot. You can create a nested series of bots to create a more modular and reusable set of bot functionality. You can combine these smaller, modular components in multiple combinations to provide a set of capabilities for different parent bots. For example, you might have a bot that handles conversation flow around managing calendar entries, with inputs and responses such as, "when's my next meeting?" or "Do you need a meeting room?" By packaging the bot as a skill, you can easily integrate the skill (and the associated calendar conversation-handling capability) into any other bot you create.
Use cards, images, and buttons to enhance conversation
You can use several visual and interactive methods to enhance conversation for your bot's users. Use cards to create rich text, image, and button-based content to provide a more interactive experience than plain text. Composer offers several card types, including thumbnail, sign-in, audio, and video.
Extend language understanding and intelligence with LUIS and QnA Maker
LUIS provides natural language processing with a complete intent and entity management system. You can integrate previously created LUIS apps or create new apps within Composer to add robust natural-language understanding capabilities to your bot.
QnA Maker is a cloud-based service. Use it to extract Question and Answer pairs from existing FAQ-style documents and websites. You then can import that information into a knowledge base that knowledge experts can curate manually. You can integrate your bot with a QnA knowledge base. This integration allows you to find the most appropriate answer for any given natural language input.
Test your bot with Web Chat
You can test your bot's functionality directly in Composer with Web Chat. Web Chat runs your bot in a local bot runtime, which means you can test your bot locally on your development machine without publishing it to Azure. Web Chat has complete debugging, transcript recording, and bot-state inspection capabilities for testing all aspects of bot capabilities.
Add middleware and extend bot functionality with the Bot Framework SDK
To edit bot source code and extend bot functionality, you can use Visual Studio, Visual Studio Code, or the supported IDE of your choice with the Bot Framework SDK. Package and publish bots as NuGet packages. Import these packages into Composer for easy integration. You can move seamlessly between Composer and the Bot Framework SDK throughout the bot-development lifecycle. This mobility ensures you're always using the most effective tool for any development task.
Publish your bot to Azure
The Azure Bot Service hosts bot functionality in Azure. Publish bots directly from the Composer interface, creating an end-to-end development experience within Composer.
Azure Bot Service hosts a bot in an Azure Web App resource. This resource contains the code, logic, and basic HTTP REST endpoints for connectivity to external resources. Azure Bot Service also provides ready-made Bot Service channels. Bot Service Channels provide an adapter layer that adapts bot interaction to another chat service protocol, such as Facebook, Slack, Teams, telephony, and others.
When you publish from Composer, the publishing process can also create or import dependent Azure resources. These resources include LUIS, QnA Maker, Azure Cosmos DB, Application Insights, and Blob Storage.