Extend Microsoft 365 Copilot
Microsoft 365 Copilot is an AI-powered productivity tool that keeps users in the flow of their work across Microsoft 365 applications like Outlook, Teams, and Word, grounding with Microsoft Graph data. It offers knowledge, such as emails, chats, and documents that users have permission to access, and skills, such as understanding, summarizing, predicting, recalling, translating, and generating content.
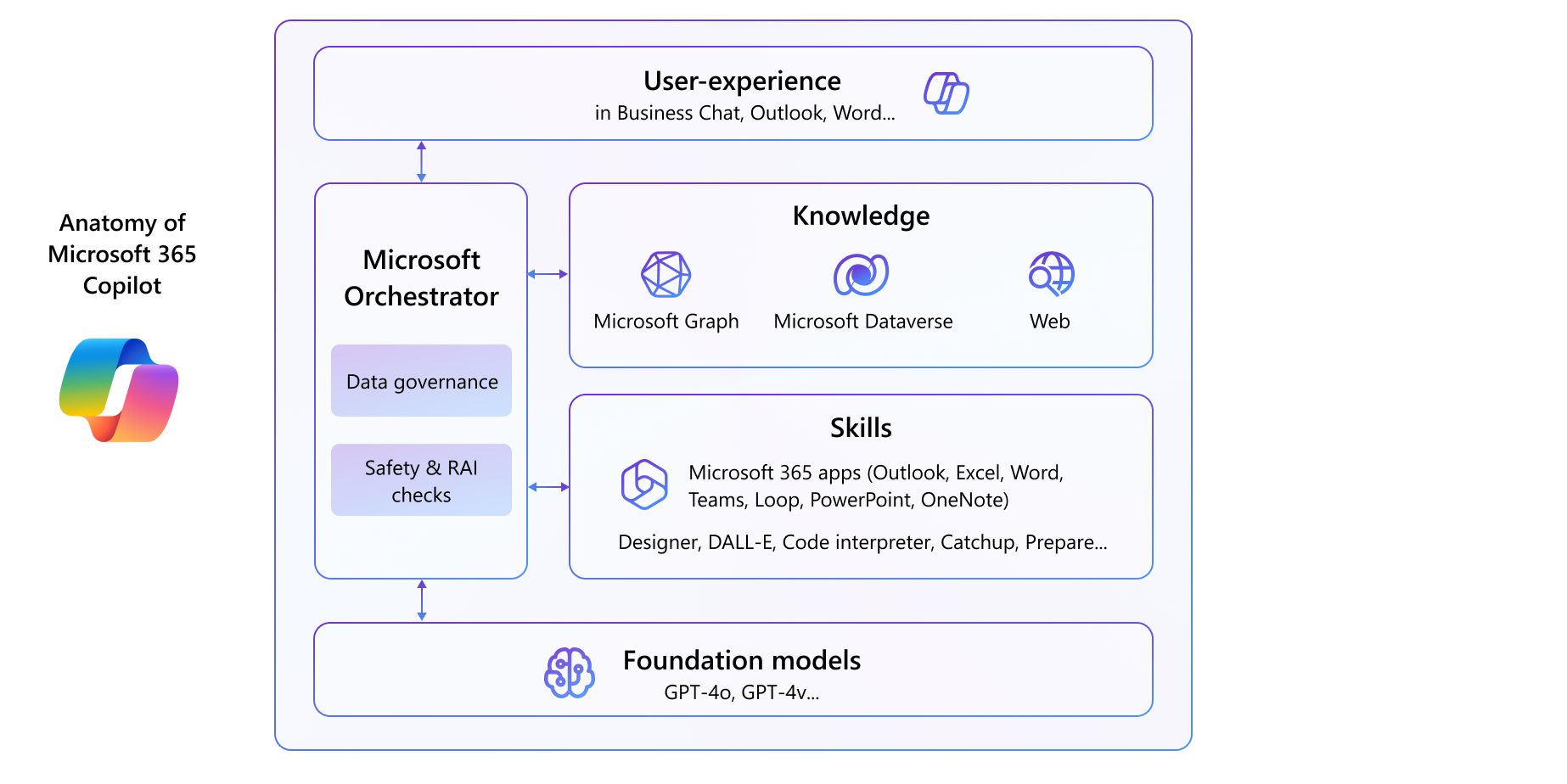
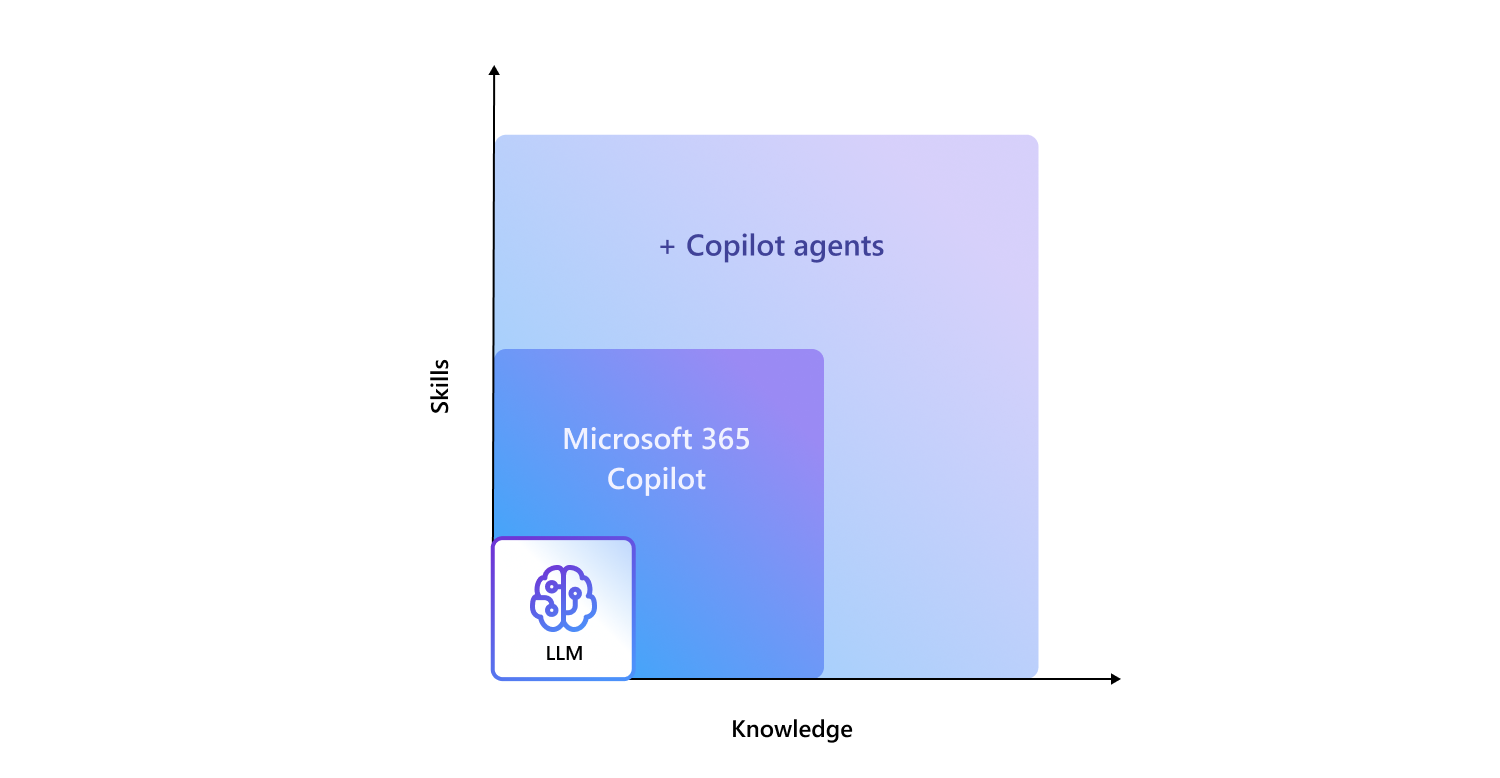
Copilot extensibility is the ability to customize and extend Microsoft 365 Copilot with more knowledge and skills. Developers can extend Microsoft 365 Copilot to build Copilot agents to bring custom knowledge, skills, and process automation into Microsoft 365 Copilot, tailoring it to suit the unique needs of their customers.
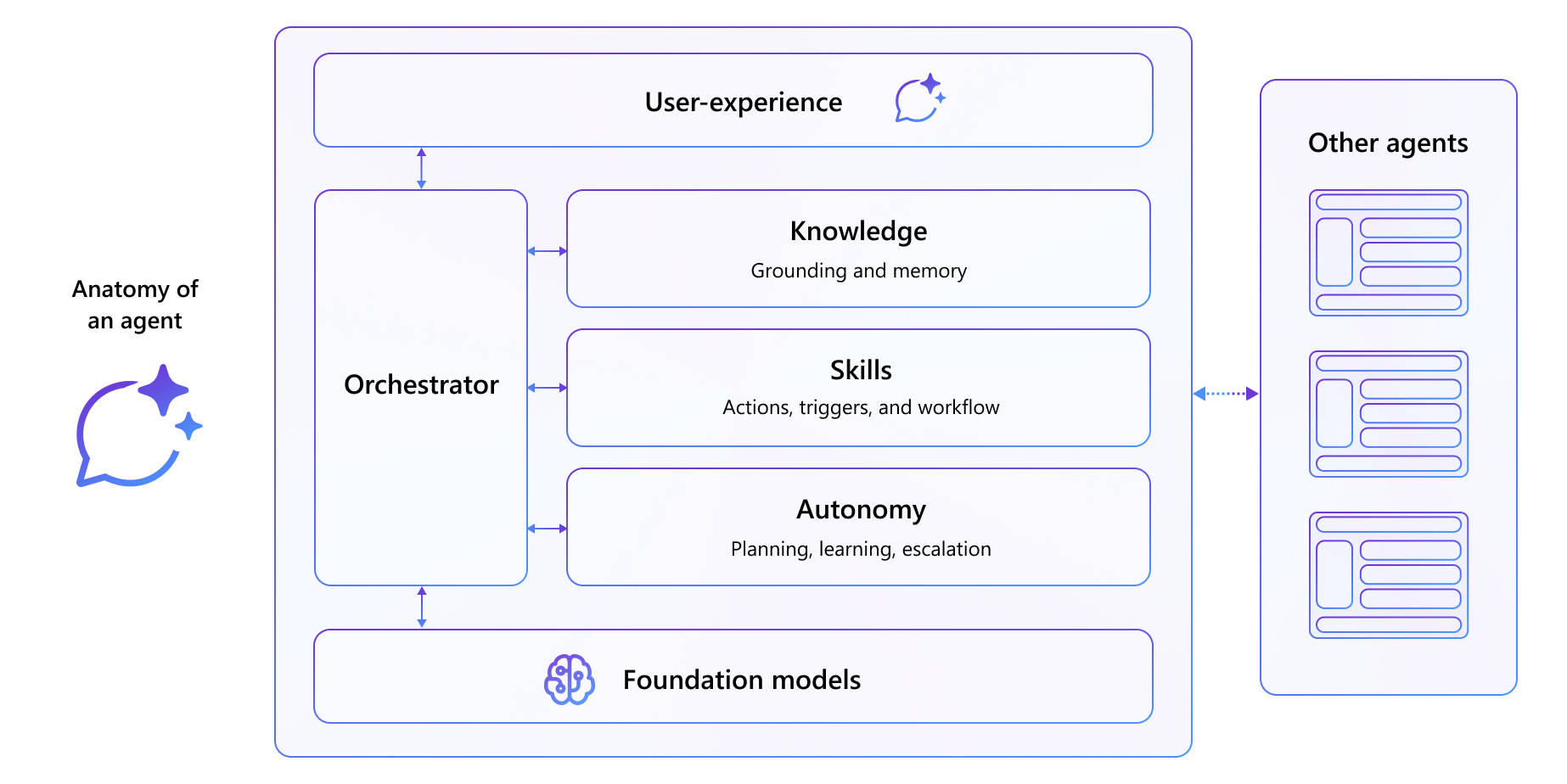
Copilot agents are fundamentally composed of Custom Knowledge (through instructions and grounding data), Custom Skills (including Actions, Triggers, and Workflows), and Autonomy (including planning, learning, and escalation).
Additionally, IT administrators can configure appropriate Copilot connectors in the Microsoft 365 admin center and the Power Platform admin center to expand knowledge available to all users in their tenant. These connectors respect the data access limitations from the knowledge source itself.
Note
This training unit introduces you to Copilot extensibility. Additional training is available that examines extensibility in greater detail.
What are agents?
In essence, agents are a scoped version of Copilot. They're designed to automate and execute specific business processes on your behalf. Each agent is an expert in one or two specific tasks, such as:
- Retrieving information
- Summarizing data
- Taking actions, such as sending emails or updating records
Agents can be customized to meet specific business needs, such as:
- Human Resources agent
- Analytics agent
- Project management agent
- Legal agent
- Image creation agent
The following list provides some practical examples of what you can develop for your organization:
- Project management agent for engineering team. Take, for example, an engineering team that relies on project management software. You can build an agent that enables users to monitor open tickets. For instance, a user can request information on all issues assigned to them, and your agent can seamlessly retrieve and present this data from your API.
- Product inventory agent for E-commerce. If your business operates in the realm of commerce, you can build an internal inventory agent by connecting it to your product database. For example, a user can ask Copilot to verify the availability of specific items, streamlining your internal processes.
- Image creation agent for marketing campaign. If you need images for your marketing, you can create an agent that helps develop marketing assets tailored to your campaign.

Types of agents
Copilot agents can be built using either a declarative or custom engine approach. While the difference might not be noticeable to end users, the development methods are distinct. This design gives developers the flexibility to choose how they want to build them.
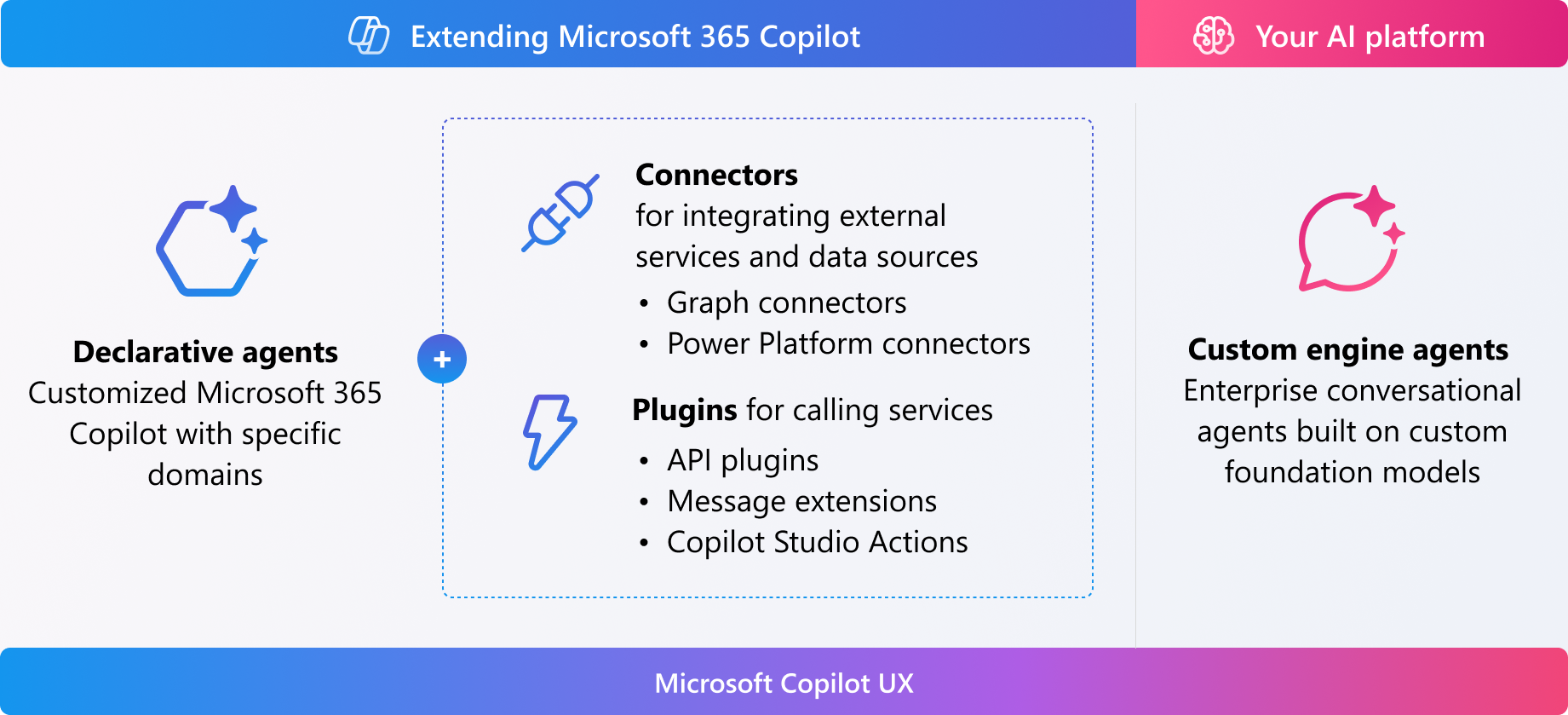
- Declarative agents. These agents are essentially a collection of custom knowledge (through instructions and grounding data), and custom skills (including Actions, Triggers, and Workflows). They're hosted on top of Copilot orchestrator and foundation models to create a rich conversational experience. These agents can be integrated with Microsoft 365. They can also utilize Copilot connectors for advanced functionality. They can also include other features like API plugins and app functionalities for Teams and Microsoft 365. Connectors and plugins are introduced later in this unit.
- Custom engine agents. These agents are developed using custom foundation models and orchestrators. They can be tailored to specific enterprise needs with your own stack. Custom engine agents can be built with various tools, including Copilot Studio, Teams AI library, and Azure AI. Custom engine agents currently work as standalone, Teams apps, and, in the future, as immersive Copilot agent experiences. Custom engine agents and Copilot Studio custom agents share a similar characteristic—they don't use the Microsoft Copilot foundation model or orchestration. If you need more advanced customization around orchestration, or if your users don't use Microsoft 365 Copilot, consider the custom agent path. You can build it through several alternatives, such as the Teams AI library or Azure OpenAI for custom engine agents, or Copilot Studio for building custom agents.
To find out which agents work the best for you, learn the differences at Your agent options for Microsoft 365.
Types of extensibility options
As you just learned, declarative agents comprise a collection of custom knowledge and custom skills. You can seamlessly integrate them within Microsoft 365 using Copilot connectors to call standard REST APIs to integrate with other applications or add your own functionality.
Declarative agents have:
- Familiar user interface. Declarative agents both look like Microsoft Copilot and work like Microsoft Copilot.
- Domain-specific knowledge applied for specific tasks. For example, travel planner or nutrition assistant.
- Ability to integrate with plugins and connectors. Declarative agents can call specialized services and access domain expertise
Additional reading. For more information, see Declarative agents.
Copilot connectors
Copilot connectors allow developers and IT administrators to apply custom knowledge and to build custom skills and to Microsoft Copilot’s out-of-box features through Copilot agents. There are two types of connectors:
- Microsoft Graph connectors. Graph connectors enable bringing additional information, including external data sources, to the Microsoft Graph. This process makes the information discoverable across various Microsoft 365 experiences, including Microsoft 365 Copilot. This integration allows Copilot to access and utilize a broader range of organizational knowledge. With Graph connectors, you can:
- Make the most of your external data. Connectors can give Copilot the ability to access and summarize your diverse datasets from different sources, enabling more comprehensive insights.
- Use Copilot as a research aid. Connectors can enable Copilot to find, summarize, and perform questions and answers (Q&A) natively by using the dataset of your choice.
- Surface the intelligence of Copilot in Microsoft Search, ContextIQ, and more. Connectors enable you to enhance the ways your users are already searching for answers.
- Power Platform connectors. Power Platform connectors are essential components that enable Power Platform applications, such as Power Automate, Power Apps, and Logic Apps, to interact with external services and data sources. They also enhance the capabilities of Microsoft 365 Copilot by enabling it to:
- Integrate with a wide range of external services and data sources.
- Perform custom actions.
- Access a broader range of data types.
Two of the main differences between Graph connectors and Power Platform connectors are connectivity and licensing.
- Connectivity. With Graph connectors, the connection to data-providing services is synchronous. Data is replicated data into Microsoft 365 for use in Copilot and other scenarios. Unlike Microsoft Graph connectors, Power Platform connectors are real-time data retrieval with read/write actions. For example, you can create a connector that allows your users to track an issue in real-time, and let them create actions, such as creating a ticket for a tracker.
- Licensing. For Microsoft Graph connectors, any valid Microsoft 365 Copilot, Microsoft 365, or Office 365 license allows you to view data from connectors in your search results. However, you need sufficient index quota to ingest content from those connectors. For Power Platform connectors, the licensing requirements can vary depending on the specific connectors and the actions you want to perform. Some connectors might require premium licenses, which aren't included in the standard Microsoft 365 licenses.
Additional reading. For more information, see Graph connectors overview and Connect and extend with Copilot Studio.
Plugins
Plugins are available as actions for declarative agents to interact with other systems to read or write information in near real-time. These actions include:
- Access real-time information. For example, finding the latest news coverage on a product launch.
- Retrieve relational data. For example, reporting on service tickets assigned to a given team member.
- Perform actions across apps. For example, creating a new task in your organization's work tracking system.
While the terms "actions" and "plugins" are sometimes used interchangeably, they're technically different. An action refers to a single API call from a plugin (for example, "Close ticket #1234"), whereas a plugin encompasses a collection of functions (for example, close, create, resolve, and so on).
In general, actions are the functionality that provides skills to Copilot within Declarative agents. For example, developers can:
- Use Copilot Studio to build Actions from Power Platform connectors.
- Create conversational, prompt, or flow connectors using the Copilot Studio design canvas.
- Use Teams Toolkit, or any technology stack that supports standard REST APIs, to build actions as API Plugins.
There are a few different ways to create plugins, including:
- API plugins. You can make an API into a Copilot plugin with API plugins.
- Teams Message extensions. You can use Teams Message extensions as standalone plugins.
- Copilot Studio Actions. You can create Copilot Studio Actions if you prefer no-code/low-code.
Important
API plugins are only supported as actions within declarative agents. They aren't enabled in Microsoft 365 Copilot.
Copilot agent in-app experiences
With actions, you can activate or enable Copilot agents that work in-context of Microsoft 365 Copilot. For example, Copilot agents can handle highly variable situations in real time, using judgment to plan their steps and perform specialized tasks required to complete the job. These agents can collaborate with multiple users and other agents to accomplish tasks that span disconnected systems, long time horizons, and organizational boundaries. Actions can also be used to provide skills to Copilot agents that work in immersive experiences, such as declarative agents.
In-context experience. For example, Business Chat (also known as BizChat) allows users to mention the agent and interact with it within the chat conversation with Microsoft 365 Copilot. To build in-context experiences, you can use plugins and declarative agents. In-context experiences bring additional information to the chat experience with Microsoft 365 Copilot, allowing it to reason over and provide responses in the context of the conversation. These experiences also enable Microsoft 365 Copilot to interact with external systems.
Note
Business Chat is the full featured and secure chat experience available to Microsoft 365 Copilot. It’s available on the web through the Microsoft 365 App, Teams, and Outlook.
Immersive experience. This experience allows users to chat directly with the agent, providing an embedded experience. To build an immersive experience, you use declarative agents. When a user activates a Copilot agent with an immersive experience, the conversation is a 1:1 interaction with the agent, tailored to its capabilities and scope.
