Configure business continuity and disaster recovery
Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server provides features to ensure business continuity and enable disaster recovery. In this unit, you learn how to configure high availability and work with backups.
Zone-redundant high availability
Let's look at how to set up zone-redundant high availability (HA), which involves replicating your flexible server instance to a standby server hosted in another availability zone.
Enable zone-redundant high availability
You can only enable zone-redundant HA during server creation. In the Compute + storage settings, under High availability, select Enable high availability.
Important
Zone-redundant high availability is only supported for the General Purpose and Business Critical pricing tiers.
You can enable same-zone HA even after server creation on the High availability settings page by selecting Enable high availability.
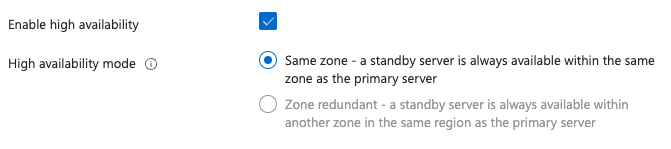
To enable zone-redundant HA after creation, or to move from same-zone to zone-redundant HA, you need to migrate to a new flexible server configured with zone-redundant HA during creation.
Force failover from primary to standby
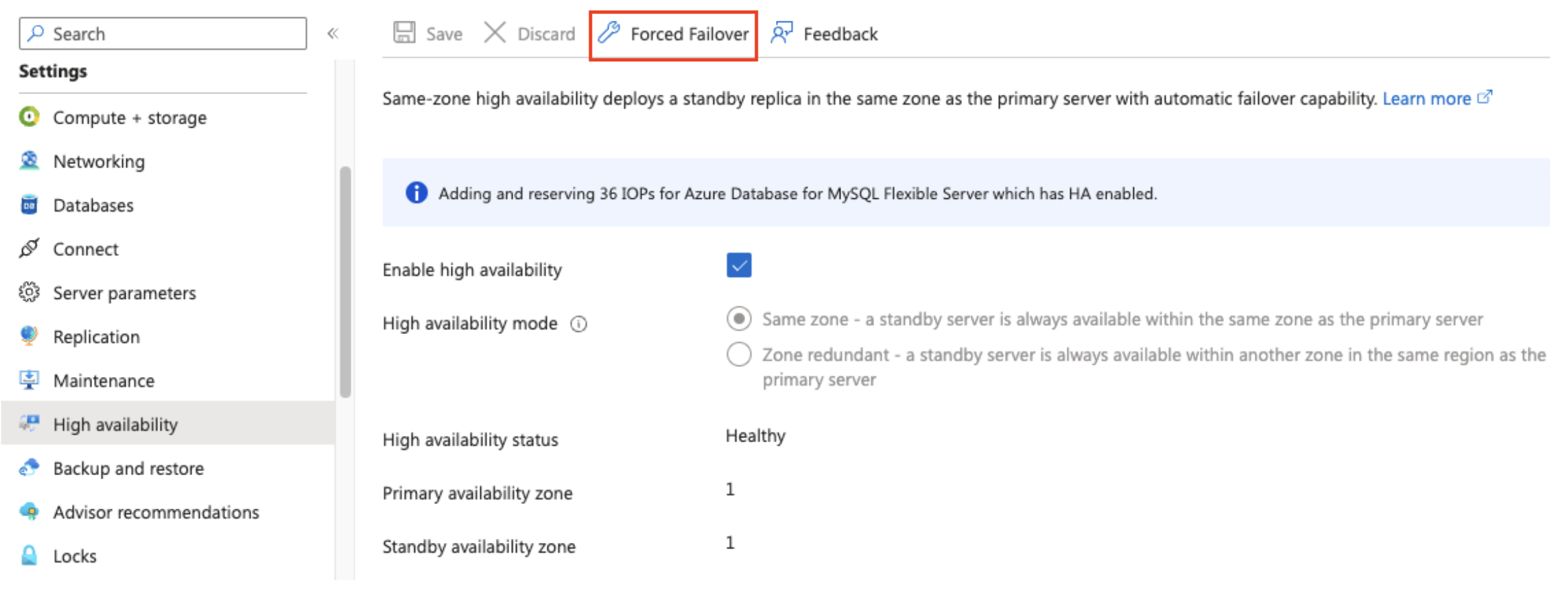
Azure Database for MySQL enables manual failover from the primary server to the standby replica. You can use this to test a disaster recovery failover scenario. You can force a failover in the Azure portal.
On the page associated with your MySQL flexible server, under Settings, select High Availability.
To initiate the manual failover procedure, select Forced Failover.
In the popup box informing you of the expected failover time depending on the current workload on the primary and the recency of the last checkpoint, read the message, and then select OK.
A notification indicates that the failover is in progress. Then, another notification indicates that the failover to the standby server succeeded.
Backups and recovery
Configure backup
You can select backup storage redundancy and retention periods during server creation. There are three levels of storage redundancy:
Locally redundant. Multiple backup copies are stored in the same availability zone (AZ). Available for same-zone HA servers, and servers without HA.
Zone-redundant. Multiple backup copies are stored in both the server's AZ and another AZ in the same region. Available for zone-redundant HA servers.
Geo-redundant. Multiple backup copies are stored in both the server's region and its geo-paired region. Available for all servers in paired regions. For the full list of supported regions, see the Azure regions section in the article [What is Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server?](/azure/mysql/flexible-server/overview" /l "azure-regions).
You can only enable or disable geo-redundancy at creation time for zone-redundant HA servers. For servers without HA, you can move from locally redundant to geo-redundant backup storage after creation by changing the backup storage setting under Compute + Storage. To move an HA server's backups from locally redundant or zone-redundant to geo-redundant, either restore a backup to a new server with geo-redundancy or create a new server with geo-redundant backups and perform a data migration.
Back up data on demand
You can create a managed database backup at any time by performing the following steps.
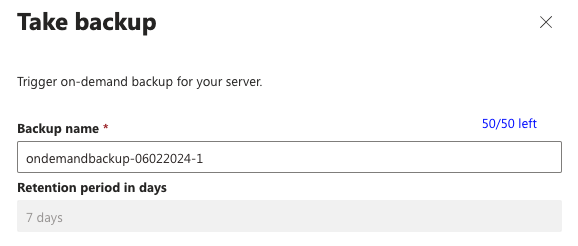
In the Azure portal, on the page associated with your MySQL flexible server, under Settings, select Backup and restore, and then select Backup now.
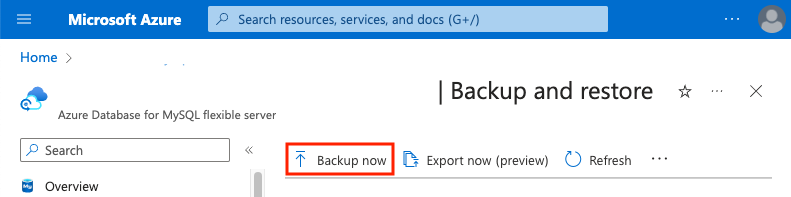
In the Take backup dialog box, pick a backup name. The backup uses your retention period.
Export data on demand
You can export the database to external storage at any time by performing the following steps.
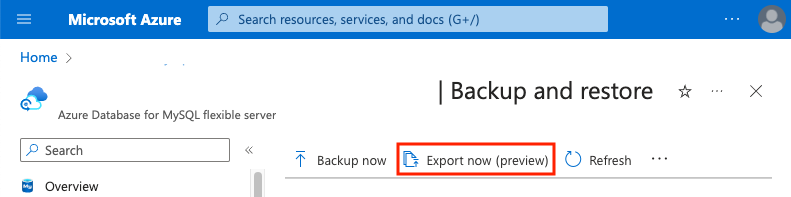
In the Azure portal, on the page associated with your MySQL flexible server, under Settings, select Backup and restore, and then select Export now.
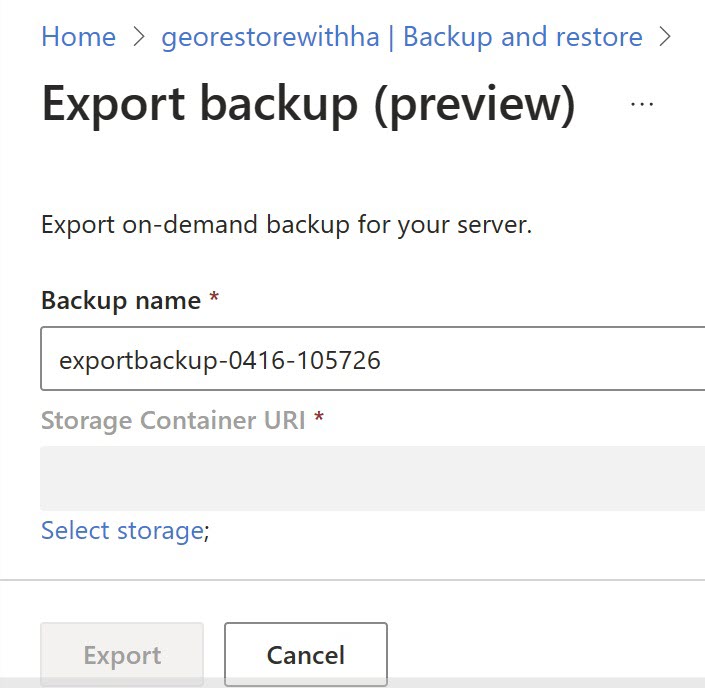
On the Export backup page, use the default name or specify your own, and then select Select storage.
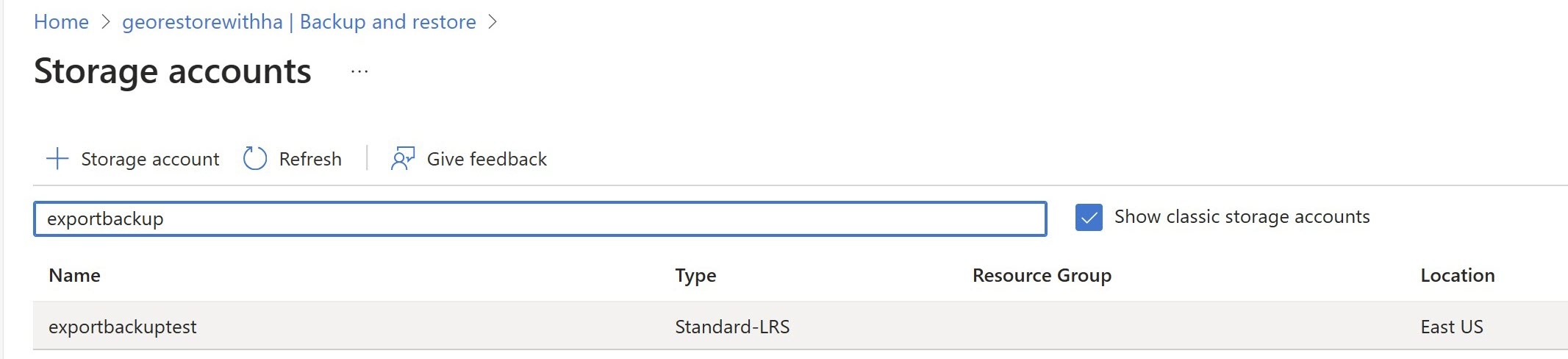
On the Storage accounts page, select the storage account to store the export.
On the Containers page, choose the storage container for the export data, and then select Select.
Lastly, back in the Export backup window, select Export.
Recover a backup
To restore your database from a point-in-time backup, perform the following steps.
In the Azure portal, on the page associated with your flexible server, under Settings, select Backup and restore.
Locate and select the backup you want to restore, and then select Fast restore.
Note
If you want, you can change the new flexible server's compute and backup settings before restoring the backup to a new server.
To begin restoring the backup, select Review + create.