Azure Key Vault authentication
Authentication with Key Vault works in conjunction with Microsoft Entra ID, which is responsible for authenticating the identity of any given security principal.
A security principal is an object that represents a user, group, service, or application that's requesting access to Azure resources. Azure assigns a unique object ID to every security principal.
- A user security principal identifies an individual who has a profile in Microsoft Entra ID.
- A group security principal identifies a set of users created in Microsoft Entra ID. Any roles or permissions assigned to the group are granted to all of the users within the group.
- A service principal is a type of security principal that identifies an application or service, which is to say, a piece of code rather than a user or group. A service principal's object ID acts like its username; the service principal's client secret acts like its password.
For applications, there are two ways to obtain a service principal:
- Recommended: enable a system-assigned managed identity for the application. With managed identity, Azure internally manages the application's service principal and automatically authenticates the application with other Azure services. Managed identity is available for applications deployed to a variety of services.
- If you cannot use managed identity, you instead register the application with your Microsoft Entra tenant, as described on Quickstart: Register an application with the Azure identity platform. Registration also creates a second application object that identifies the app across all tenants.
Configure the Key Vault firewall
By default, Key Vault allows access to resources through public IP addresses. For greater security, you can also restrict access to specific IP ranges, service endpoints, virtual networks, or private endpoints.
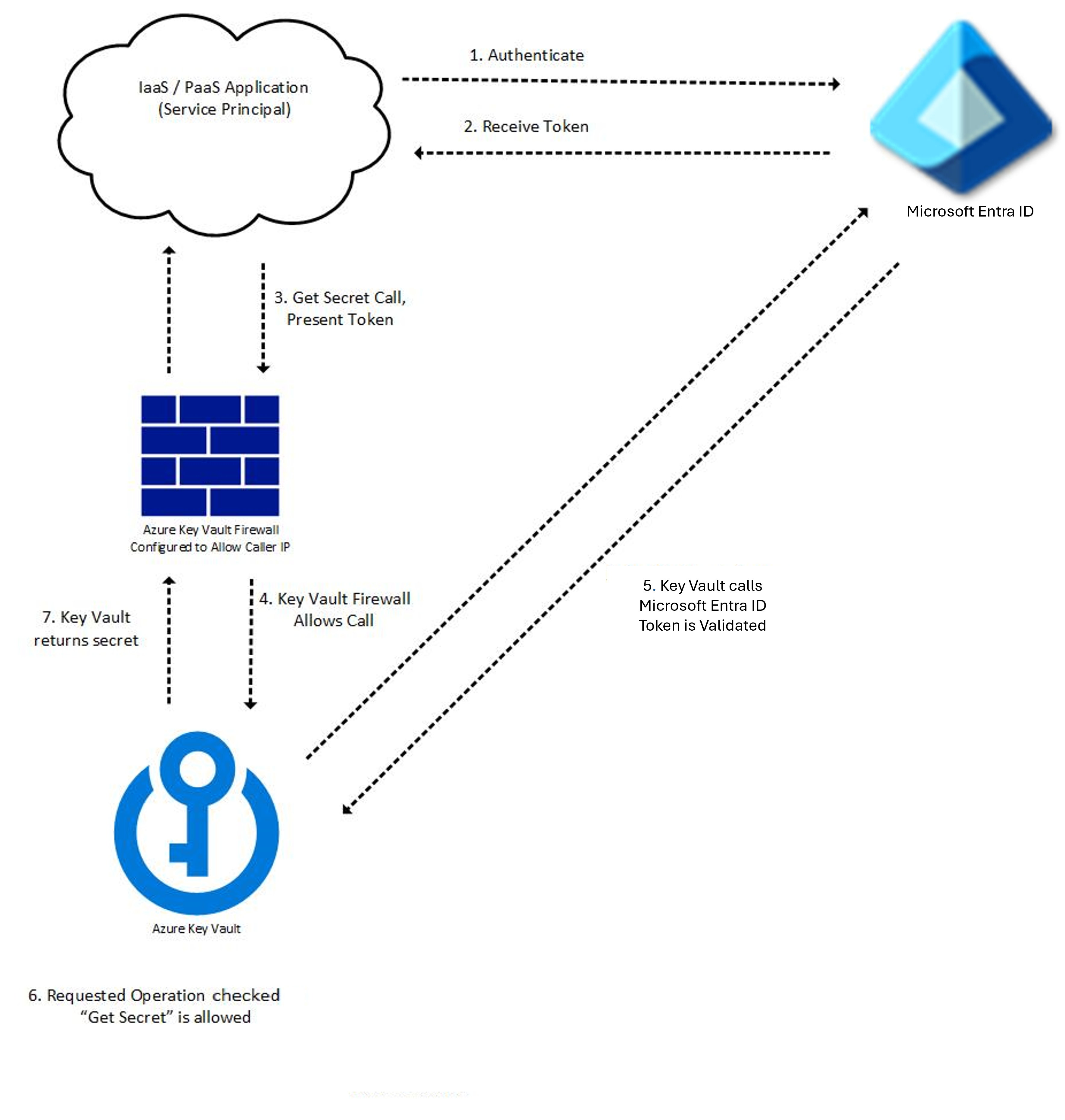
The Key Vault request operation flow with authentication
Key Vault authentication occurs as part of every request operation on Key Vault. Once token is retrieved, it can be reused for subsequent calls. Authentication flow example:
A token requests to authenticate with Microsoft Entra ID, for example:
- An Azure resource such as a virtual machine or App Service application with a managed identity contacts the REST endpoint to get an access token.
- A user logs into the Azure portal using a username and password.
If authentication with Microsoft Entra ID is successful, the security principal is granted an OAuth token.
A call to the Key Vault REST API through the Key Vault's endpoint (URI).
Key Vault Firewall checks the following criteria. If any criterion is met, the call is allowed. Otherwise the call is blocked and a forbidden response is returned.
- The firewall is disabled and the public endpoint of Key Vault is reachable from the public internet.
- The caller is a Key Vault Trusted Service, allowing it to bypass the firewall.
- The caller is listed in the firewall by IP address, virtual network, or service endpoint.
- The caller can reach Key Vault over a configured private link connection.
If the firewall allows the call, Key Vault calls Microsoft Entra ID to validate the security principal’s access token.
Key Vault checks if the security principal has the necessary permission for requested operation. If not, Key Vault returns a forbidden response.
Key Vault carries out the requested operation and returns the result.
Note
Key Vault SDK clients for secrets, certificates, and keys make an additional call to Key Vault without access token, which results in 401 response to retrieve tenant information.
Authentication to Key Vault in application code
Key Vault SDK is using Azure Identity client library, which allows seamless authentication to Key Vault across environments with same code
Azure Identity client libraries
| .NET | Python | Java | JavaScript |
|---|---|---|---|
| Azure Identity SDK .NET | Azure Identity SDK Python | Azure Identity SDK Java | Azure Identity SDK JavaScript |