GitHub Copilot for the Command Line
GitHub Copilot isn't just a tool for writing code in your favorite IDE; it’s also a powerful assistant that can help streamline your command-line workflows. By integrating with the GitHub CLI, Copilot can provide explanations for unfamiliar commands, suggest commands based on your needs, and even execute them on your behalf. Whether you're new to the command line or a seasoned user, Copilot can enhance your productivity by offering intelligent suggestions and simplifying complex tasks.
This unit covers:
- Guiding you through the common GitHub Copilot CLI commands,
- Exploring configuration options enabling you to make the most of GitHub Copilot directly from your terminal.
Common commands
Once you have Copilot set up in the CLI, here are some frequently used commands for interacting with it:
Getting command explanations:
If you're unsure about what a specific command does, you can ask Copilot to explain it. For instance:
gh copilot explain "sudo apt-get"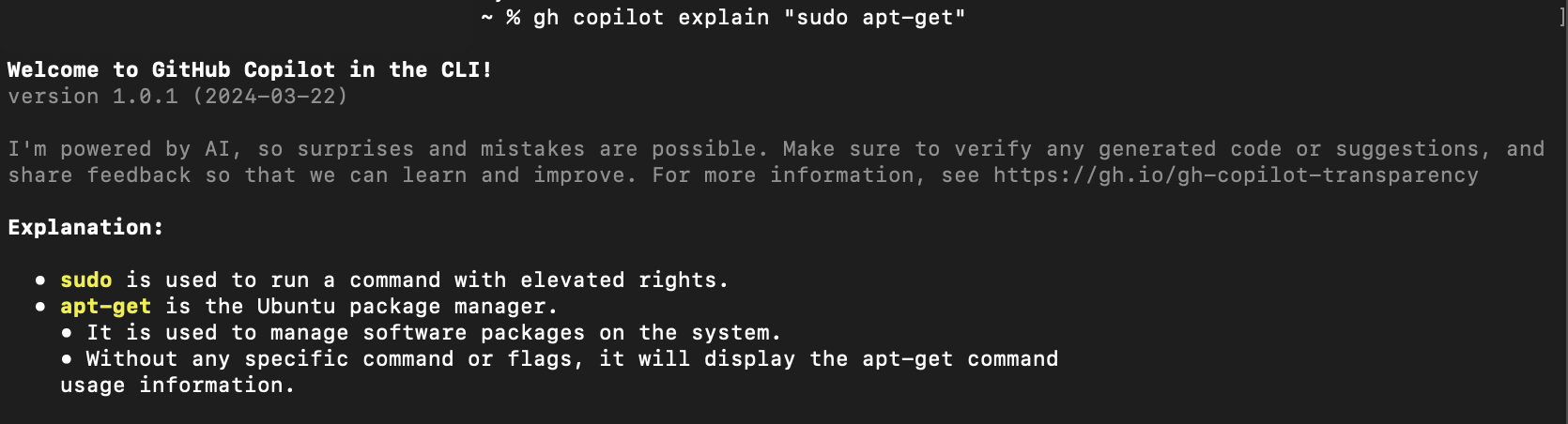
This command provides you with a detailed explanation of the provided command.
Getting command suggestions:
Need help with constructing a command? You can ask Copilot to suggest a command based on what you want to accomplish:
gh copilot suggest "Undo the last commit"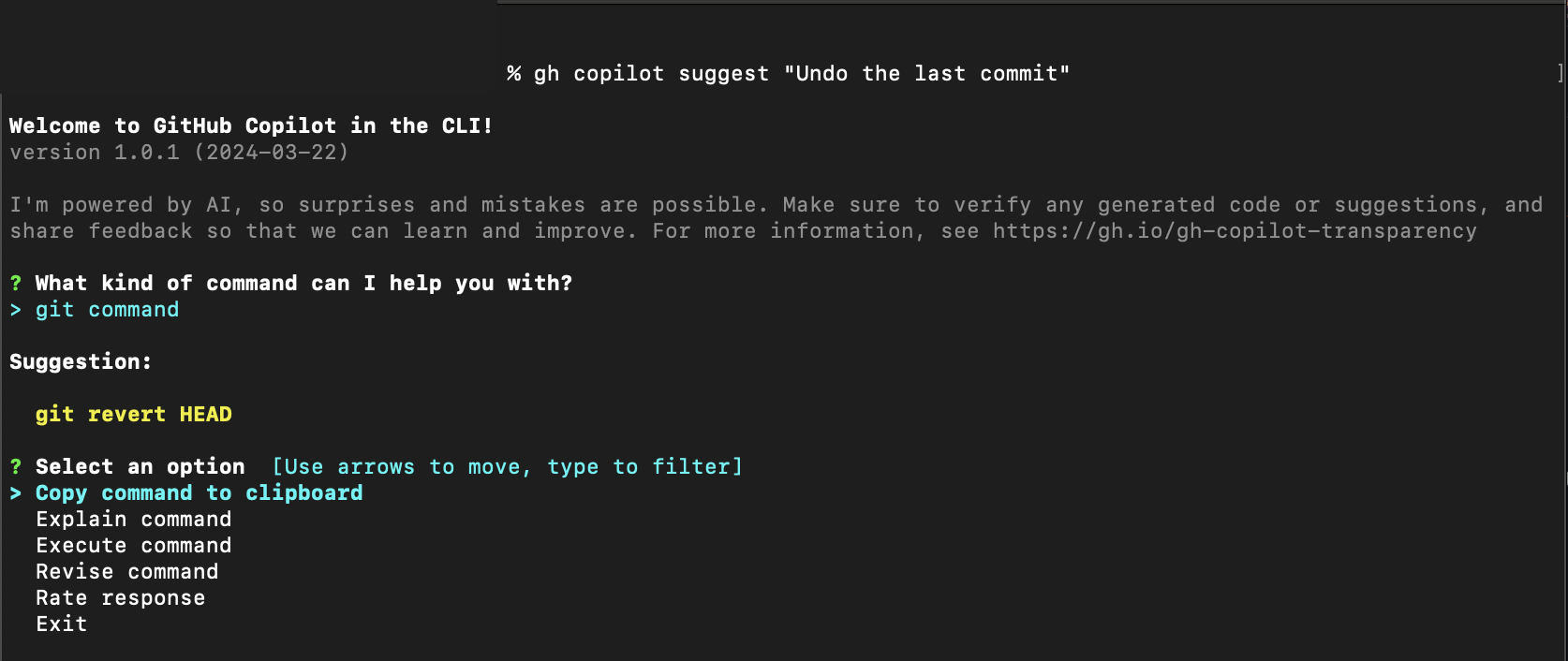
Copilot starts an interactive session to clarify your request and suggest the best command.
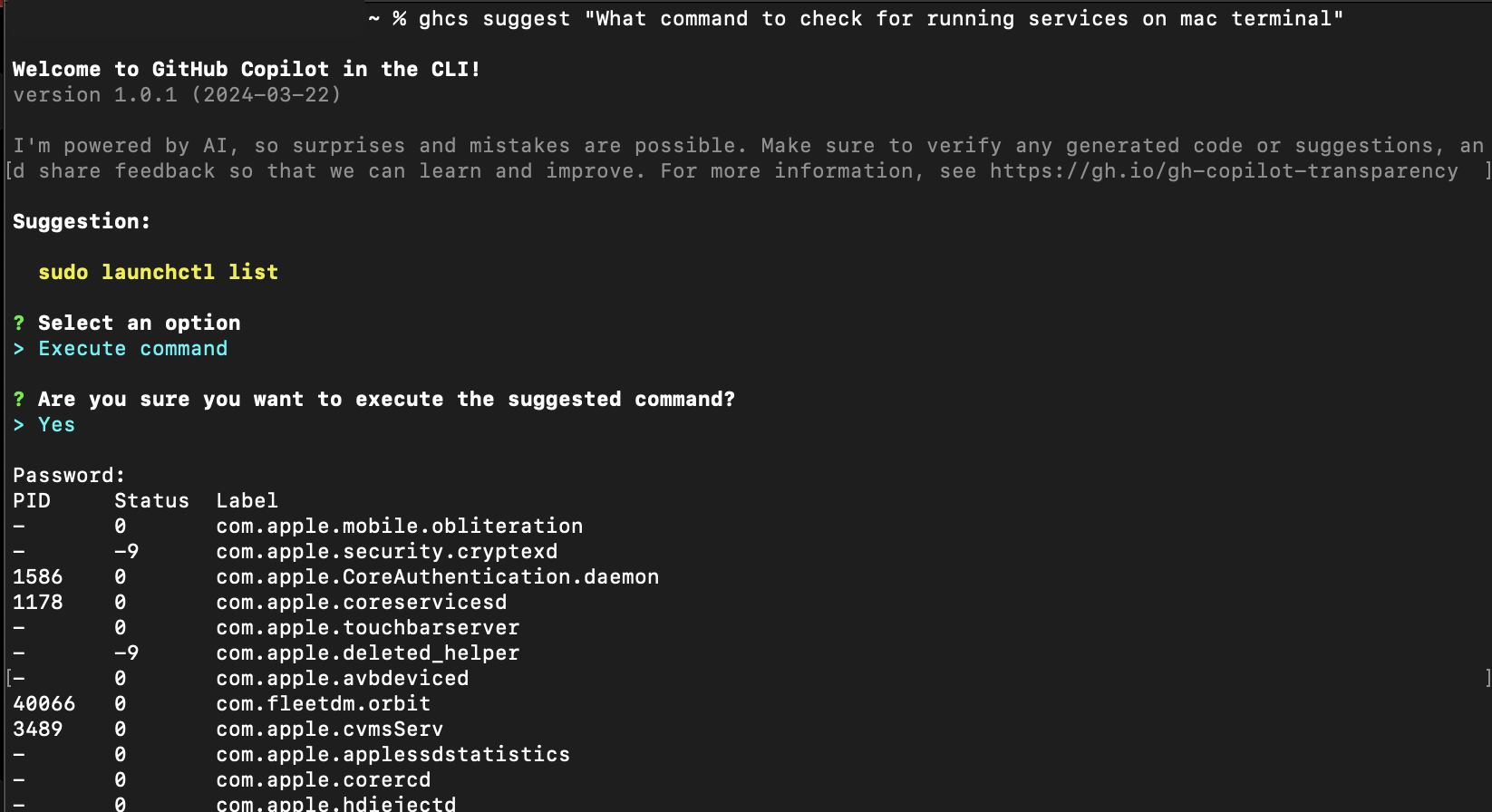
Executing suggested commands: After receiving a suggestion, you can choose the
Execute commandoption. This copies the command to your clipboard. You can also allow Copilot to execute commands on your behalf only if you configure theghcsalias, you.Using the alias:
ghcs suggest "What command to see running docker containers"Revise suggested command: To give GitHub Copilot CLI to rework or revise a command to make it better or more suited to your expectations, use the "Revise command" option along with your feedback.
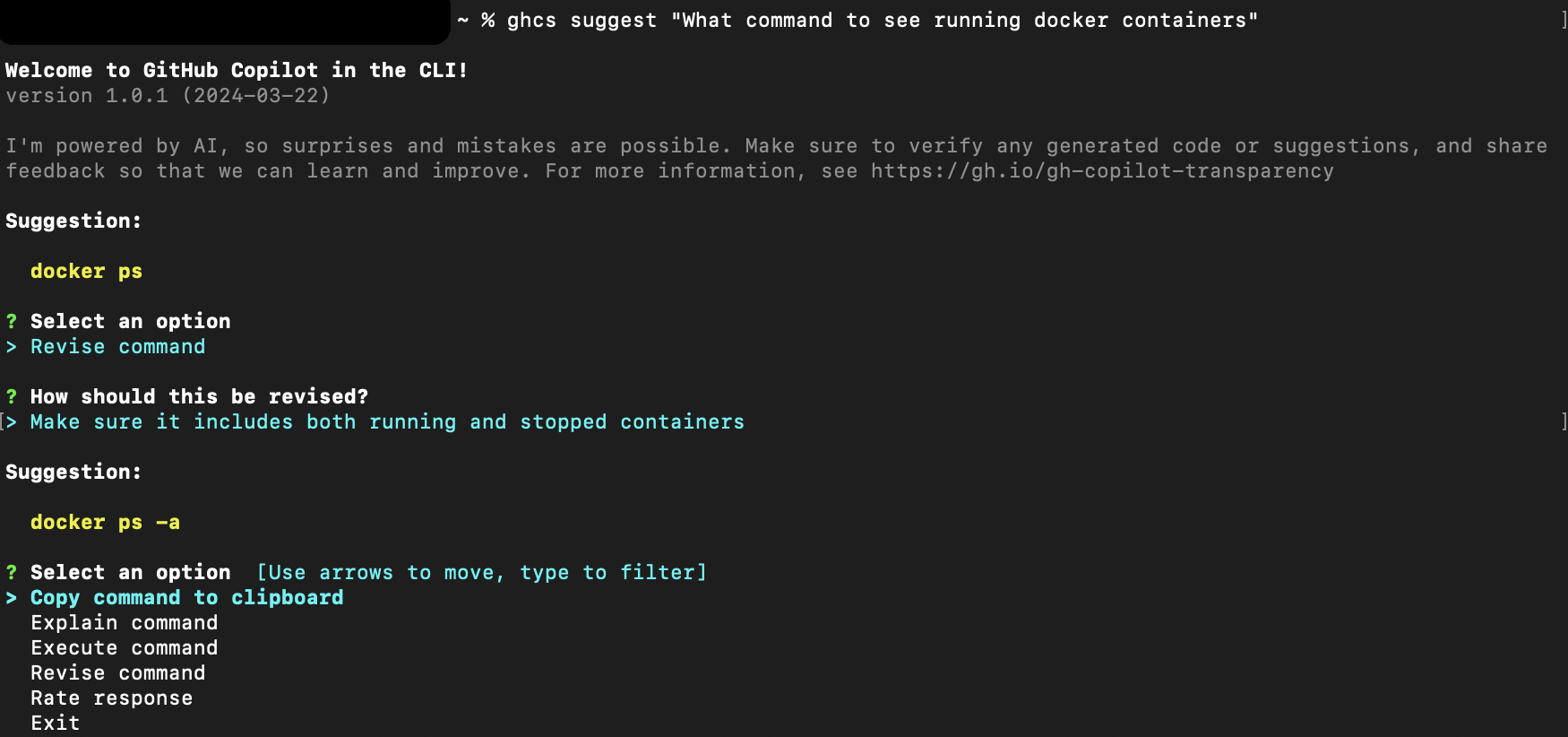
Configuration options
To make the most out of Copilot in the CLI, you may want to configure certain settings:
Alias Configuration: If you want Copilot to execute commands on your behalf directly, you need to set up the
ghcsalias. Using an alias allows you to bypass copying and pasting commands manually, and instead Copilot does it for you.To configure the
ghcsalias, run the following commands:For bash:
echo 'eval "$(gh copilot alias -- bash)"' >> ~/.bashrcFor PowerShell:
$GH_COPILOT_PROFILE = Join-Path -Path $(Split-Path -Path $PROFILE -Parent) -ChildPath "gh-copilot.ps1" gh copilot alias -- pwsh | Out-File ( New-Item -Path $GH_COPILOT_PROFILE -Force ) echo ". `"$GH_COPILOT_PROFILE`"" >> $PROFILEFor Mac terminal or Zsh:
echo 'eval "$(gh copilot alias -- zsh)"' >> ~/.zshrcFeedback mechanism: Copilot encourages user feedback to improve its suggestions. You can rate the quality of a suggestion by selecting the
Rate responseoption after Copilot provides you with a command.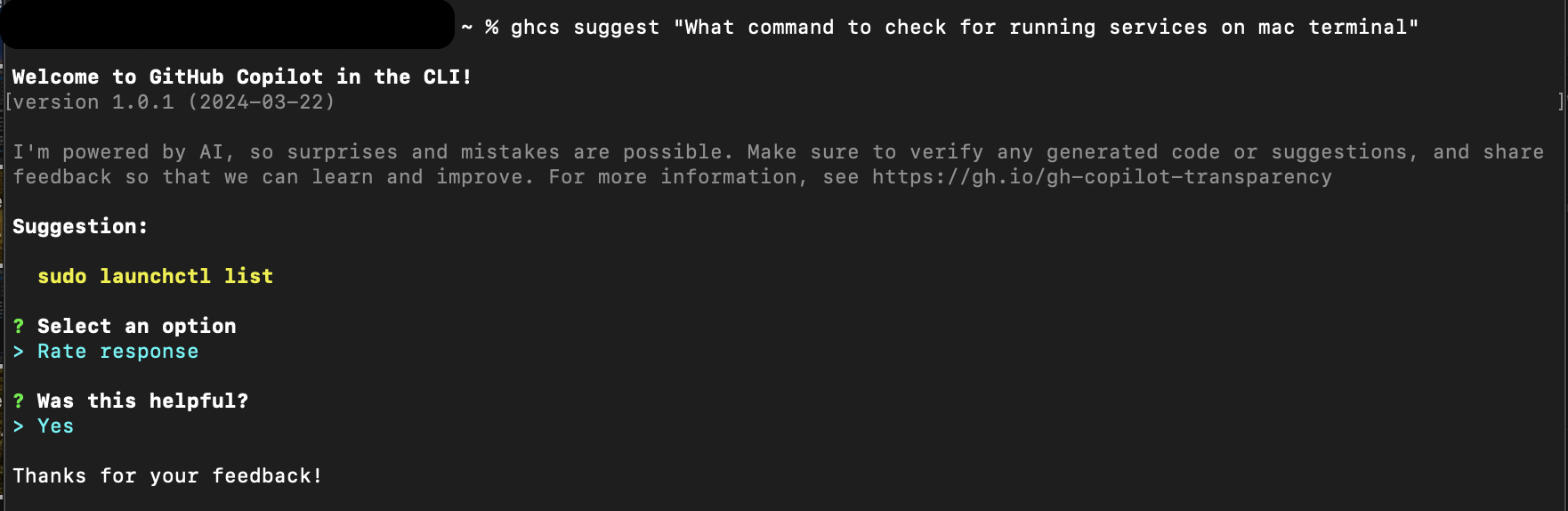
Organizational settings: If you're using Copilot within an organization your access to certain features may be governed by your organization's policies. Administrators can enable or disable Copilot's capabilities within the CLI.
For further customization and detailed configuration so you can optimize Copilot's functionality for your specific needs, refer to the GitHub documentation.
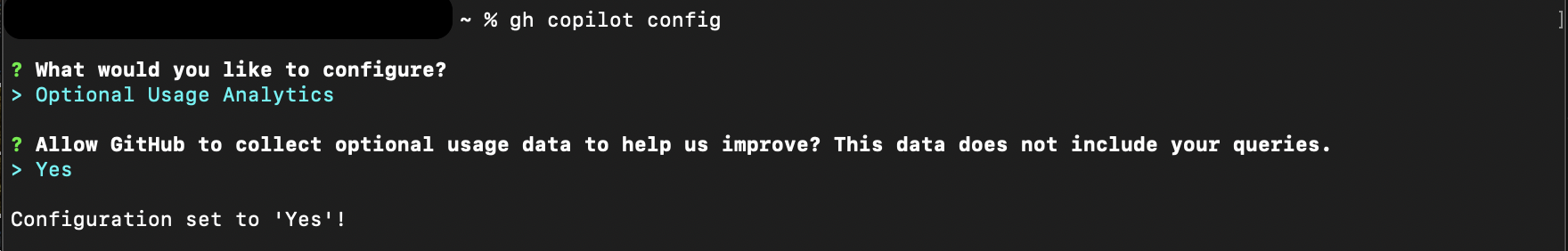
Data handling: GitHub Copilot CLI doesn't retain your prompts, but it keeps your usage analytics. You can configure whether you want GitHub Copilot to keep and use your usage data to improve the product. Enter the command
gh copilot config, select "Optional Usage Analytics", then select "No" if you want to opt out.