GitHub Enterprise features
In this unit, you learn the difference between the two types of GitHub Enterprise features: upkeep and automation. As an administrator, you're responsible for knowing how and when to use them to make development easier.
Let's say your organization forms a major partnership with a contractor who helps implement a new feature. As an administrator, you want to integrate each contractor employee with the internal team and help all collaborators cut down on repetitive tasks as they rapidly expand the code base. To accomplish these goals, you want to build a secure knowledge base by creating limited-access sites on GitHub Pages. You also need to keep track of the number of GitHub Actions minutes that collaborators use. Limited-access GitHub pages are an upkeep feature, and GitHub Actions minutes enable automation.
GitHub Enterprise is the GitHub product that provides the most assistance and features to developers. In addition to its unique benefits, GitHub Enterprise also has all the features included at the GitHub Team pricing level.
Developer workflow basics
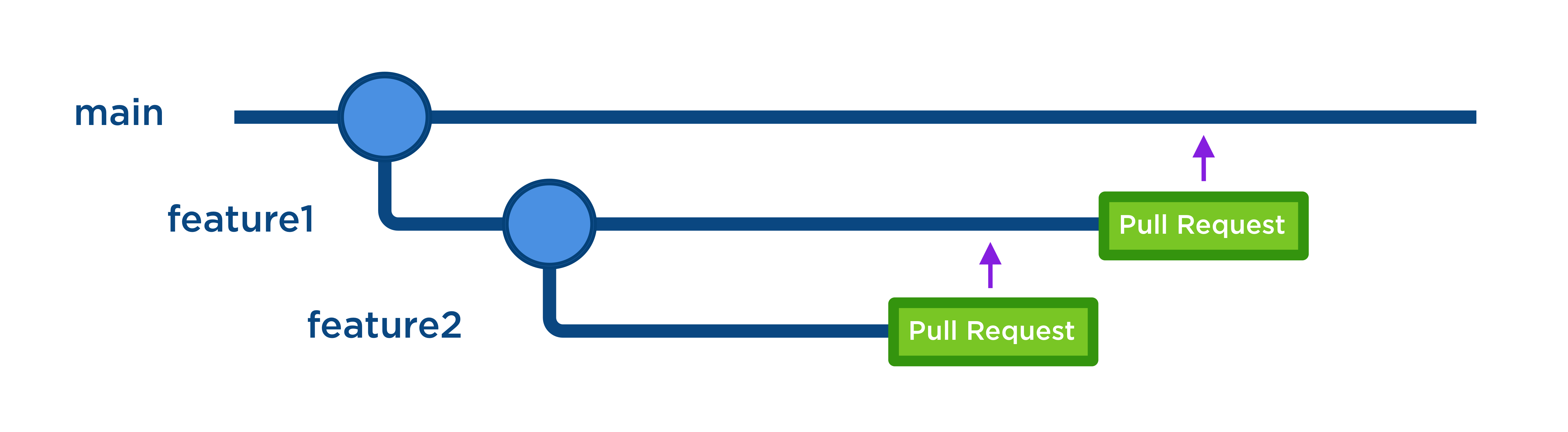
Before we go further, you should understand the standard developer workflows that form the basis of GitHub collaboration. This knowledge helps you make sense of how GitHub Enterprise features facilitate those workflows. A workflow that we discuss in this unit is distinct from script workflows that we discuss in unit 4.
- When you create a repository, it has a default or main branch, which is the base branch for new pull requests and code commits.
- You create new branches from the default branch of your repository, usually to isolate the development of a feature. Authenticated users who have privileges in the repository can merge the changes after review of a pull request.
- As an administrator, you protect certain branches against deletion or force pushes to those branches. You can designate code owners who must review pull requests on those branches.
- Authenticated users without privileges in a public repository that wish to work with the repository's code base can fork the repository, creating an independent copy of the code base for outside use.
- Before they commit changes, release new versions, and at other regular intervals, collaborators often run scripts on GitHub to complete common tasks, like scanning code for security issues. You can also automate these scripts.
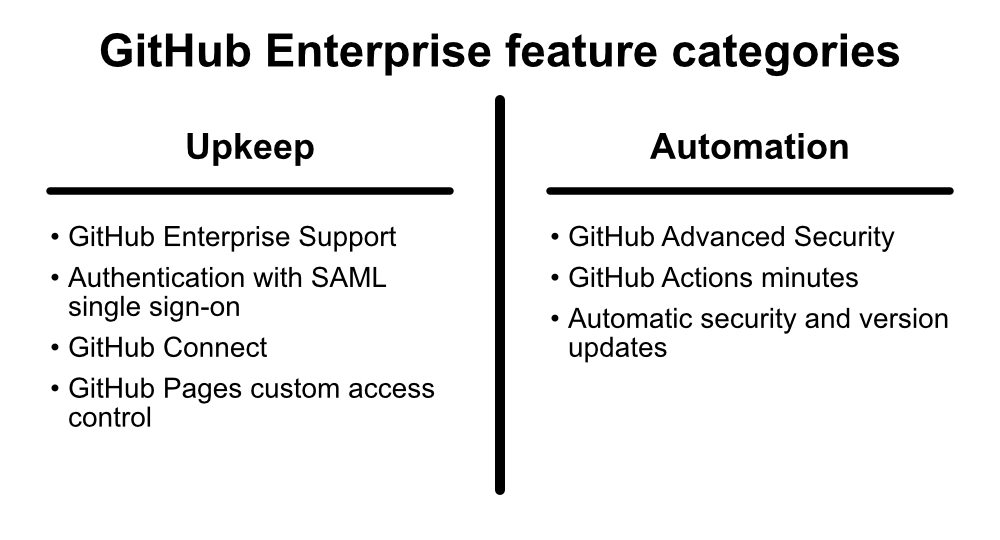
Upkeep features
One of your primary roles as an administrator for a GitHub organization is to help minimize the friction users feel when interacting with GitHub. Friction refers to problems like difficulty signing in, finding files in the code base, and sharing project knowledge within the right circles.
If you enable your collaborators to manage a limited number of authentication credentials and portals, build a knowledge base without worrying about breaking non-disclosure agreements, and feel safe against threat actors, then they can get down to the business of the real work--coding and deployment. Upkeep features help achieve these tasks, and they include:
- GitHub Enterprise Support - The most in-depth level of support GitHub provides.
- Authentication with Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) single sign-on and access provisioning with SAML or SCIM - Makes it easier for users to authenticate and for administrators to ensure everyone has the appropriate level of access.
- GitHub Connect - Shares data between a GitHub Enterprise Server instance and the GitHub Enterprise Cloud, enabling more redundancy.
- Access control for GitHub Pages sites - Allows you to limit the sharing of your organization's documentation.
Some features are available to organizations running an instance of GitHub Enterprise Server on their own local server, but more features are available to organizations using GitHub Enterprise Cloud.
How can you enable upkeep features?
You need to prepare to use upkeep features. Start with authentication using SAML single sign-on.
- Connect your identity provider to your GitHub organization.
- Access the settings for your organization.
- Review the existing security configurations for that organization.
- If you want to unify all the Enterprise organizations under SAML single sign-on, select Require SAML authentication and provide the requested technical information (sign on URL, optional issuer, and public certificate).
Then, secure the knowledge base for any of your private repositories that exist on the GitHub Enterprise Cloud.
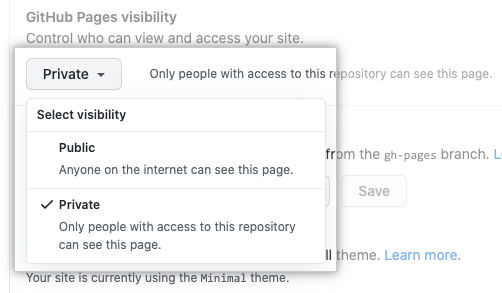
- Navigate to your site's repository and access its settings.
- Change GitHub Pages visibility to Private.
- Verify your privacy by checking that no URLs appear under GitHub Pages.
Finally, if you're running an instance of GitHub Enterprise Server and also using the GitHub Enterprise Cloud, use GitHub Connect to enable unified search and contributions between the two platforms.
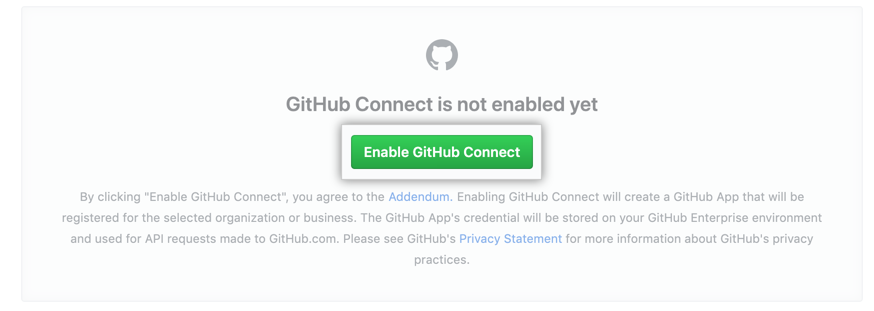
- Sign in to GitHub Enterprise Server and GitHub.com.
- In Enterprise Server, access Enterprise settings and select "Enable GitHub Connect."
- Choose the organizations you want to connect from the list.
GitHub Support can assist you with managing users' accounts, security threats, and abuse of social features. You learn more about these use cases in the next unit.
Automation features
While upkeep features make using GitHub easier for your organization, automation features make collaborating on creative work easier and safer. Automation features decrease the need for manual intervention in common programming tasks. For example, programmers have a strong demand for automated processes that increase the security of the code bases for their projects. As an administrator, you can enable and track the use of several built-in GitHub processes that serve this purpose.
Automation features include:
- GitHub Advanced Security (GHAS) - A specialized add-on to GitHub Enterprise that scans code and other resources for errors, security vulnerabilities, and potential sensitive data.
- GitHub Actions minutes - Expand the kinds of actions you can automate in response to common GitHub events.
- Automatic security and version updates.
Like with upkeep, certain automation features are limited to organizations using GitHub Enterprise Cloud.
What are your automation responsibilities as an administrator?
During new feature development, collaborators across your organization can take advantage of GitHub Actions scripts, Advanced Security scanning (if purchased), and automatic updates to dependencies. Because GitHub provides these features to a specific number of seats within a given runtime, you're responsible for keeping track of the rate at which your coworkers are using these services.
You can track your GitHub Enterprise organization's use of GitHub Advanced Security scanning by checking in the settings for Your enterprises.
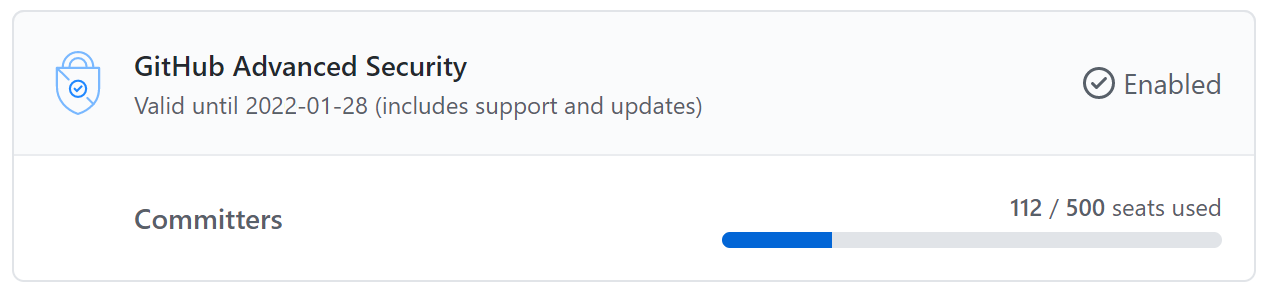
- Select an Enterprise organization in Your enterprises and access Settings.
- Check the number of seats your Enterprise organization is using. If you're near to or exceeding the limit your organization purchased, discuss with organizational stakeholders.
- Select "GitHub Advanced Security" in Billing in the left sidebar to learn more details about Advanced Security use, like whether an Enterprise organization has many committers using GHAS only in that organization.
It's even easier to track the use of GitHub Actions by your users. Your Enterprise account allows 50,000 minutes of GitHub Actions runtime per month and 50 GB of Actions storage. Check in the settings for Your enterprises to learn how much of that allotment your organizations have that month.
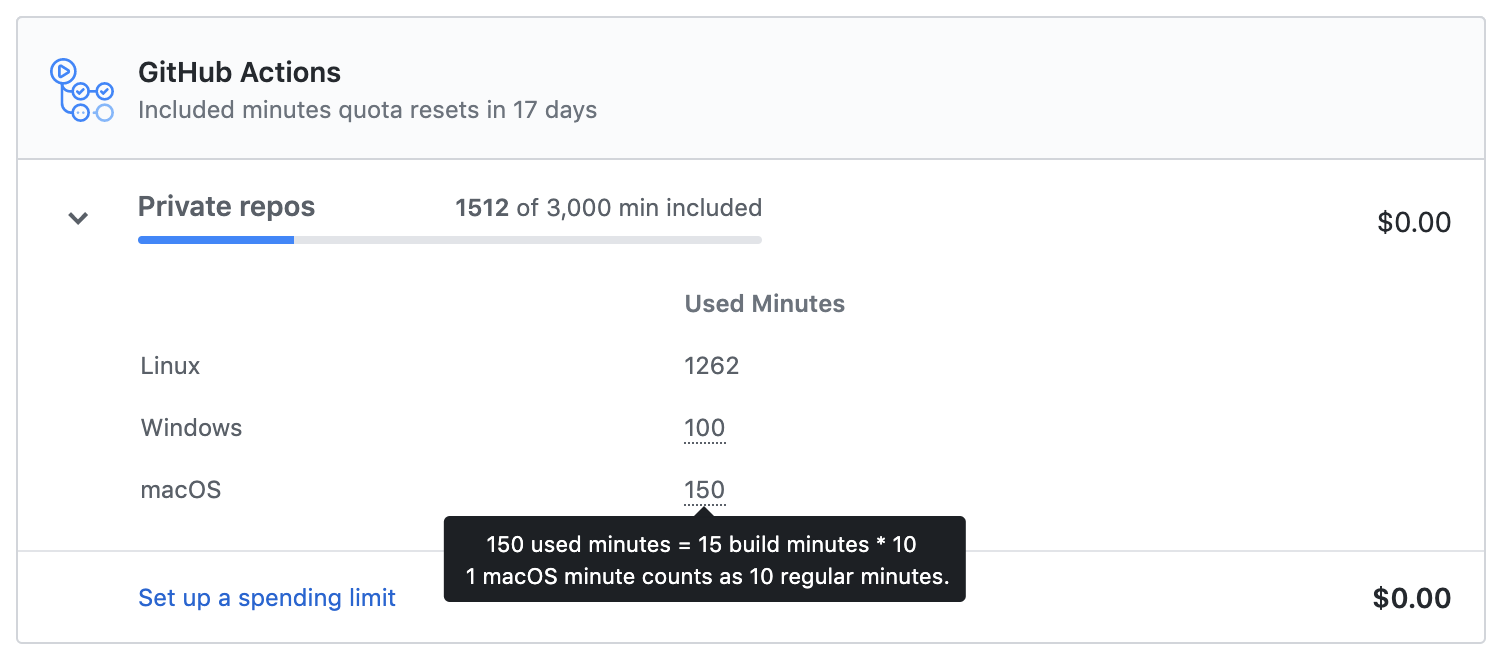
- Select an Enterprise organization in Your enterprises and access Settings.
- Select GitHub Actions in Billing to see how many minutes or how much storage your organizations uses. If you're near to or exceeding the limit, discuss with organizational stakeholders.
- Keep your collaborators' operating systems in mind; Windows runners use minutes at twice the rate of Linux runners, and macOS runners use minutes at 10 times the rate of Linux runners.
Identify organization strengths with activity statistics
You can track more statistics than just feature use. If you're a user within a GitHub Enterprise Cloud organization, you can learn about the overall health of your organization. The beta feature organization activity insights and the feature organization dependency insights, give you a wealth of data. As an administrator, leaders of your GitHub Enterprise Cloud organization might expect you to track these insights.
Organization activity insights display issue and pull request activity, top programming languages used, and other data about where collaborators spend their time. This knowledge is useful when deciding where to direct collaborators to serve as extra resources for a complex feature deployment. Or, whether more training might expand a team's language capabilities.
Access your organization's activity insights by choosing an Enterprise Cloud organization in Your organizations. Then, select Insights. You can view the past week, month, or year's data for up to three organizations at once.
Organization dependency insights are available when you enable the Dependency Graph. The insights display information about vulnerabilities, licenses, and other data about open source projects integrated into or related to your organization's projects. These insights can help identify if too many of your dependencies have outstanding security advisories, prompting a discussion about how to better secure your code base.
Access your organization's dependency insights by choosing an Enterprise Cloud organization in Your organizations. Then, select Insights and select the Dependencies tab. You can view all dependency insights, Open security advisories, or explore more granular data.
Help use tools as an administrator
In addition to managing the built-in features that GitHub provides to Enterprise organizations, administrators can help choose and implement tools built by independent developers.
In this context, a tool is usually an extension (sometimes called an integration) or an action that helps improve a user or team's interaction with the GitHub workflow. An extension might connect GitHub with a full-featured editor like Visual Studio Code, allowing easier pull request management. Or, with a project management tool like Jira Cloud, making it possible to quickly respond to Jira tracking tickets.
What are your tooling responsibilities as an administrator?
You can install integrations in your personal account or in organizations that you own. You can also install GitHub Apps from a third-party in a specific repository where you have admin permissions or that your organization owns. These permissions mean that, as an administrator, you're in a position to approve or deny adding integrations or tools to the GitHub workflow.
Third-party tools usually require permissions at the repository level, and these permissions might change. If a tool's developer changes its permissions, and the permissions are for a repository only, then you can review and accept the new permissions.
The best way to find trustworthy tools for your Enterprise organization, and to construct workflows from trustworthy tools, is to take advantage of the GitHub Marketplace's categorization system. Using this system, you can find tools that receive independent security verification.
Although anyone can publish an action in the GitHub Marketplace, publishers must complete a verification process in order to be listed under the Verified Creator category in the Marketplace. This process includes establishing a line of communication between GitHub and the publisher, demonstrating that the publisher meets basic security requirements, and verifying the publisher's domain. (However, GitHub doesn't analyze apps and actions on the GitHub Marketplace.)

The verified creator badge, which appears as a check mark next to the publisher's name in a listing on the GitHub Marketplace, signifies verification status.
- For GitHub Apps, the badge means that GitHub verified the publisher's domain and email address, and the publisher requires two-factor authentication for their organization.
- For GitHub Actions, the badge means that GitHub is in active partnership with the organization.
Tools that focus on continuous integration and continuous delivery
Your team probably places a high priority on building a CI/CD pipeline--a series of automated workflows that help DevOps teams cut down on manual tasks:
- Continuous integration (CI) automatically builds, tests, and integrates code changes within a shared repository.
- Then, continuous delivery (CD) automatically delivers code changes to production-ready environments for approval.
- Or, continuous deployment (CD) automatically deploys code changes to customers directly.
Your administrative duties are likely to extend to approving, implementing, and maintaining tools that focus entirely on improving this pipeline. With that in mind, GitHub Enterprise organizations that make the most of their GitHub Actions minutes and automatic security and version updates choose tools that meet these criteria:
- Tools should use open standards, because these tools are easiest to teach.
- Tools should use dynamic variables, so you can define variables externally and effect major improvements with minor changes.
- Tools should be portable and flexible, to adapt easily to a change in cloud architecture.