Customer Insights architecture
Customer Insights - Data makes gaining detailed customer insights a reality for organizations of all sizes. It automates the orchestration of customer data and empowers employees to connect and engage with customers in the moment. Organizations can obtain a truly complete view of each customer across channels from:
Campaign responses
Website visits
In-store visits and purchases
Online purchases
Loyalty redemptions
Customer service encounters
Social interactions
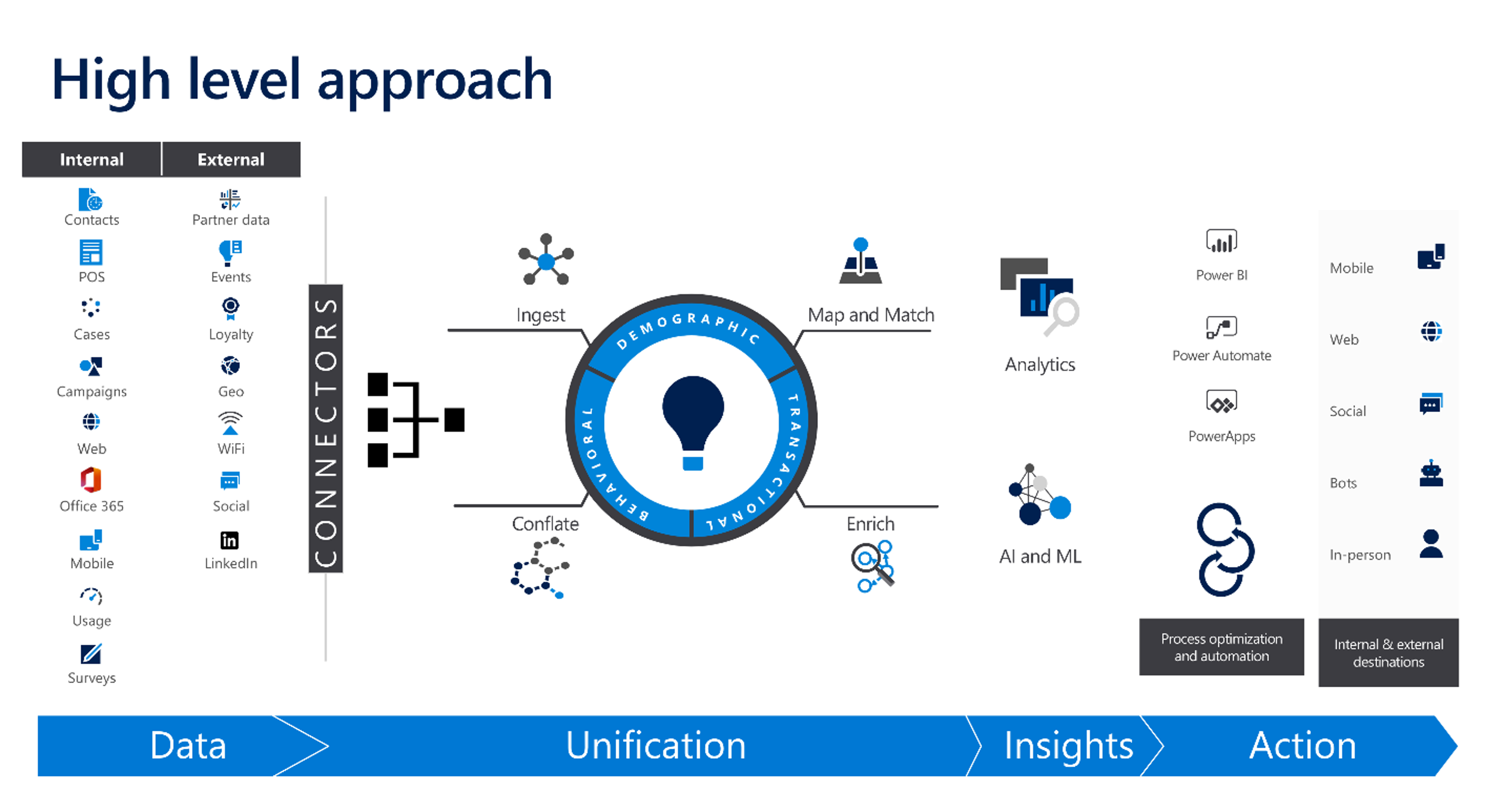
How does it do it? Let's examine the architecture behind Customer Insights - Data. At a high level, there are four steps:
Data - Data is the different siloed data across your organization. This could be internal data such as a CRM or ERP system, or it could be external data coming from places such as social media. Customer Insights - Data provides multiple options for connecting and ingesting data.
Unification - Unification is the process of taking the customer data that you ingested and consolidating it into a singular unified customer view. Customer Insights - Data includes multiple tools for mapping customer data and enriching data for other data sources.
Insights - Using the built-in or external tools you can analyze your data so you can better group customers, identify trends, and more.
Action - Also sometimes referred to as activation, this is where you start to use the information you gathered in Customer Insights - Data inside other applications. This is how most of your users interact with Customer Insights data. They don't actually spend time in the application.
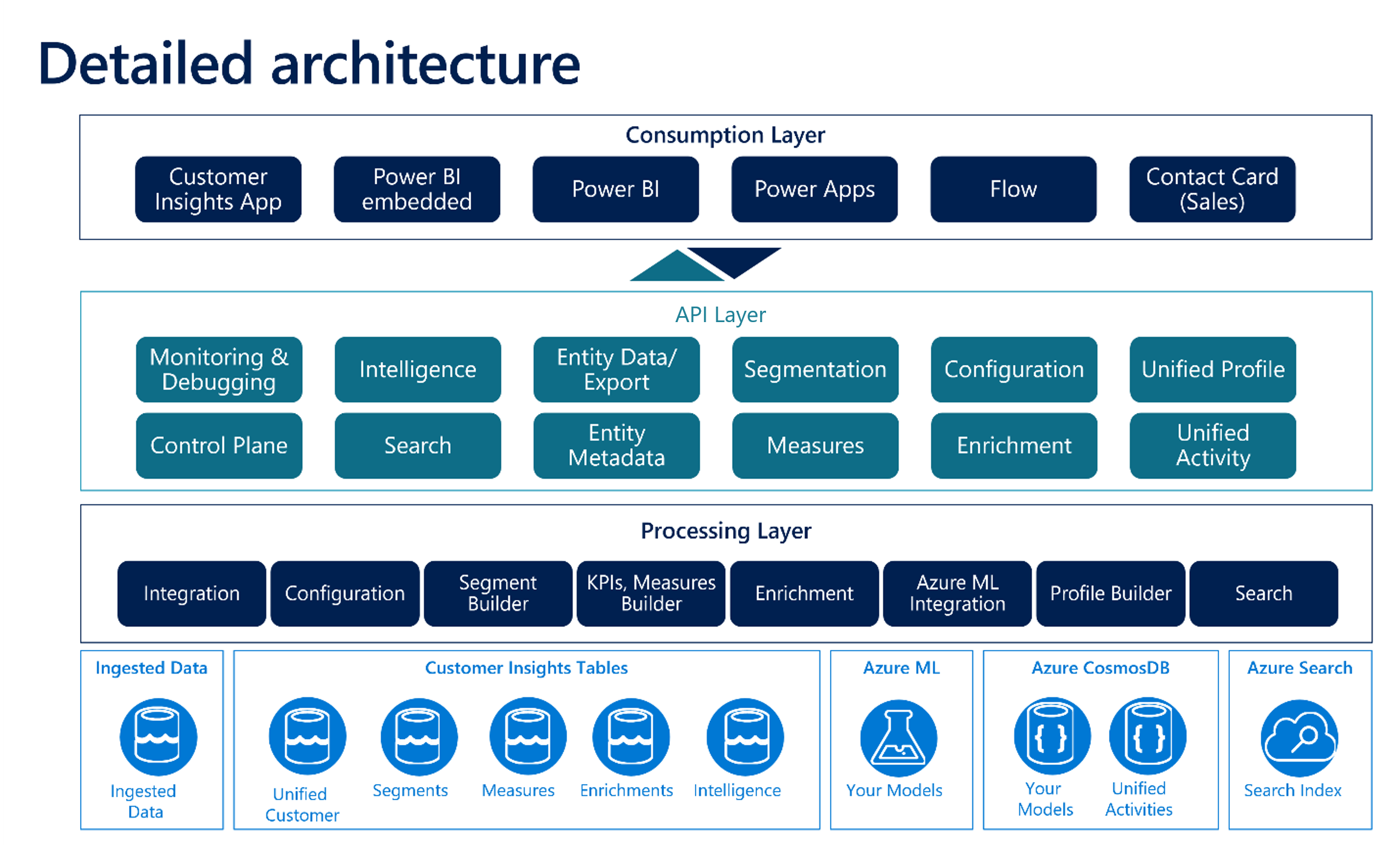
Let's break it down a little further. In the following image, you can see that there are three layers:
Processing - Refers
API
Consumption
Processing layer
The processing layer represents the various data lakes and services that are being used to deliver the solution. Some examples of items in the processing layer include:
Your Data: The data you bring you is stored in the data lake. You can also bring in your own data lake if your data is in the Common Data Model
Customer Insights Tables: Customer Insights tables are CDM compatible tables created by the system on your behalf. These can be exported and power other scenarios Like Power Automate, Power Apps, etc.
For AI Insights: Azure Machine Learning models can be linked to Customer Insights to allow you to train and score your Tables in Customer Insights.
In App processing: In-application processing includes the out-of-the-box functionality that is available in Customer Insights - Data to help analyze your data. This includes items such as the segment builder, and measures builder.
API layer
As mentioned previously, the important thing to remember about Customer Insights - Data is that most of your users aren't going to use the application directly. They're going to use the data that is being processed in the application in other applications. This might include custom applications.
To assist with this, Customer Insights -Data is powered by a full set of Public APIs (application programming interfaces) which expose "all" the features of the underlying platform. These APIs can be used programmatically to update the unified customer profiles, call measures, create segments, and more.
Consumption layer
The consumption layer represents how the data in Customer Insights is used and how it's available to users. There are various connectors available that allow you to use Customer Insights data in other applications.
For example:
You might create a custom Power App that connects to your Unified Customer Profile, to build a custom application that your employees can use.
You might use the data in Customer Insights- Data to power different Power BI reports.
Segments created in Customer Insights can be exported into other applications for use such as LinkedIn, Google Adds and more.