Explore the language models in the model catalog
Selecting a language model for your generative AI app is important as it affects how well your app works. When you develop a generative AI app with Azure AI Foundry, you build a chat application that can use language models for several purposes:
- To understand the user question.
- To search for relevant context.
- To generate an answer to the user question.
Within the Azure AI Foundry portal, you can browse available language models in the model catalog. Let's explore the model catalog and the types of language models available through Azure AI.
Explore the model catalog
In the Azure AI Foundry portal, you can navigate to the model catalog to explore all available language models. Additionally, you can import any model from the Hugging Face open-source library into the model catalog.
Tip
Hugging Face is an open-source community making models available to the public. You can find all models in their catalog. Additionally, you can explore the documentation to learn more about how individual models work, like BERT.
The Azure AI Foundry model catalog integrates with models from Hugging Face and other sources. Through the model catalog, you can explore, fine-tune, and deploy models.
Important
Model availability differs per location, also referred to as region. Your location is specified on the AI hub level. When you create a new AI Hub, you can use the Location helper to specify the model you want to deploy to get a list of locations you can deploy it in. You can also explore the model summary table and region availability to learn more.
Explore language models
Foundation or language models available in the model catalog are already pretrained. You can deploy a language model to an endpoint or fine-tune a model to make it perform better in a specialized task or on domain-specific knowledge.
Your selected model depends on your use case and deployment preferences. First of all, you need to think about the task you want the model to perform. For example:
- Text classification
- Token classification
- Question answering
- Summarization
- Translation
Some language models that are commonly used for various tasks are:
| Model | Description |
|---|---|
| BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) | Focused on encoding information by using context from before and after a token (bidirectional). Commonly used when you want to fine-tune a model to perform a specific task like text classification and question answering. |
| GPT (Generative Pretrained Transformer) | Trained to create coherent and contextually relevant text, and is most commonly used for tasks like text generation and chat completions. |
| LLaMA (Large Language Model Meta AI) | A family of models created by Meta. When training LLaMA models, the focus has been on providing more training data than increasing the complexity of the models. You can use LLaMA models for text generation and chat completions. |
| Phi-3-mini (3.8B parameters variation of phi models) | A lightweight, state-of-the-art model optimized for resource-constrained environments and local inference (like on a phone), supporting long-context prompts up to 128-K tokens. It's developed with a focus on safety, alignment, and reinforcement learning from human feedback. |
After selecting a task and filtering the available models that are suitable for your objective, you can review the model summary in the Azure AI Foundry to take some other considerations into account:
- Model capabilities: Evaluate the capabilities of the language model and how well they align with your task. For example, a model like BERT is better at understanding short texts.
- Pretraining data: Consider the dataset used for pretraining the language model. For example, GPT-2 is trained on unfiltered content from the internet that can result in biases.
- Limitations and biases: Be aware of any limitations or biases that might be present in the language model.
- Language support: Explore which models offer the specific language support or multilingual capabilities that you need for your use case.
Tip
Though the Azure AI Foundry provides you with descriptions for each language model in the model catalog, you can also find more information about each model through the respective model card. The model cards are referenced in the overview of each model and hosted on the website of Hugging Face
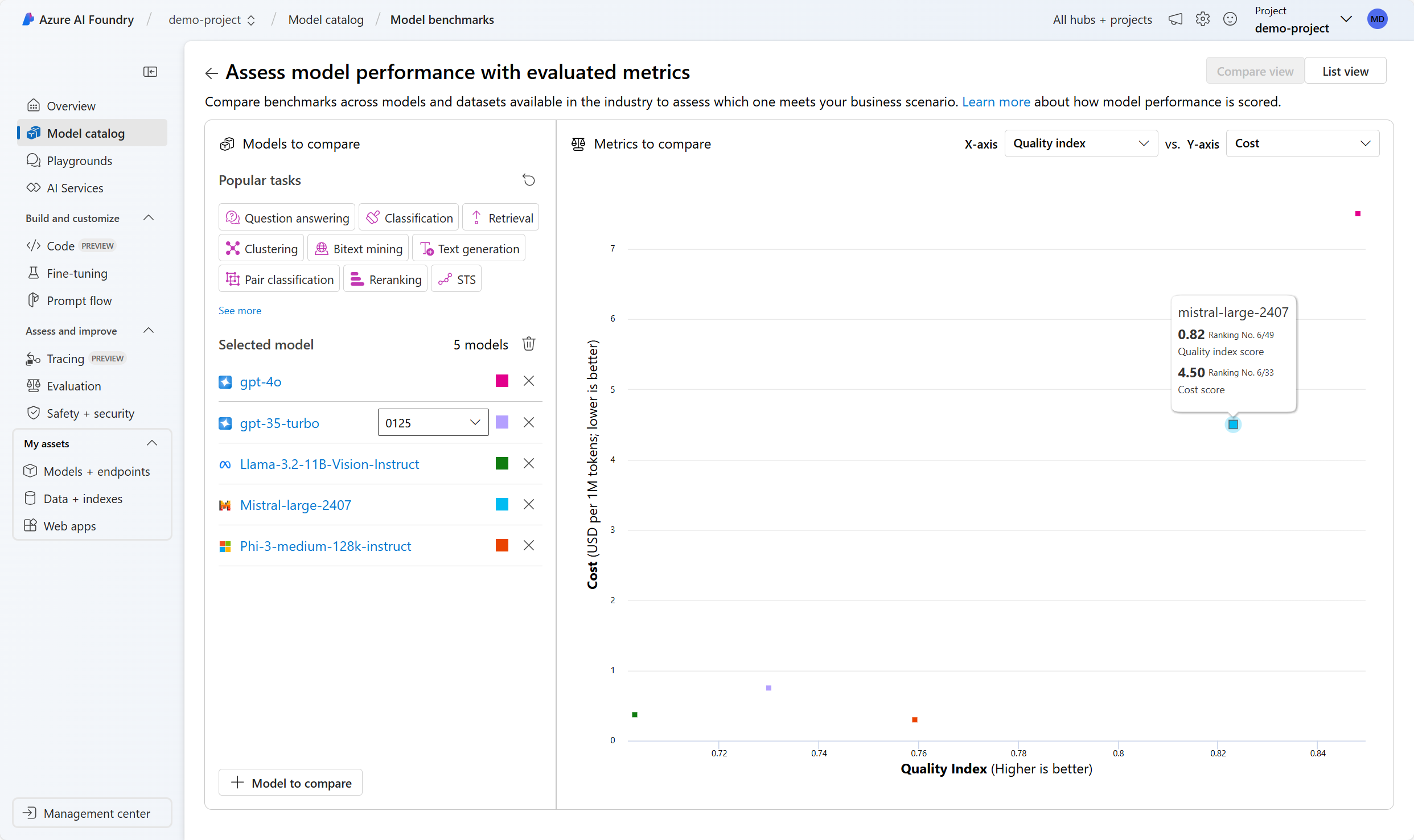
Compare benchmarks across models
When you're exploring language models, you can also compare the available model benchmarks to assess the quality of the models before you deploy and integrate a model. Benchmarks are like report cards for language models. Benchmarks help you understand how well a model performs by comparing it to other models using specific tests or tasks. The model benchmarks in the Azure AI Foundry portal provide a curated list of the best performing models for a given task, based on benchmarking metrics.
Some commonly used metrics to assess the performance of language models are:
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Accuracy | Accuracy scores are available at the dataset and the model levels. At the dataset level, the score is the average value of an accuracy metric computed over all examples in the dataset. The accuracy metric used is exact-match in all cases except for the HumanEval dataset that uses a pass@1 metric. Exact match simply compares model generated text with the correct answer according to the dataset, reporting one if the generated text matches the answer exactly and zero otherwise. Pass@1 measures the proportion of model solutions that pass a set of unit tests in a code generation task. At the model level, the accuracy score is the average of the dataset-level accuracies for each model. |
| Coherence | Coherence evaluates how well the language model can produce output that flows smoothly, reads naturally, and resembles human-like language. |
| Fluency | Fluency evaluates the language proficiency of a generative AI's predicted answer. It assesses how well the generated text adheres to grammatical rules, syntactic structures, and appropriate usage of vocabulary, resulting in linguistically correct and natural-sounding responses. |
| GPTSimilarity | GPTSimilarity is a measure that quantifies the similarity between a ground truth sentence (or document) and the prediction sentence generated by an AI model. It's calculated by first computing sentence-level embeddings using the embeddings API for both the ground truth and the model's prediction. These embeddings represent high-dimensional vector representations of the sentences, capturing their semantic meaning and context. |
| Groundedness | Groundedness measures how well the language model's generated answers align with information from the input source. |
| Relevance | Relevance measures the extent to which the language model's generated responses are pertinent and directly related to the given questions. |
Note
When you develop and evaluate applications that use language models, it's important to use metrics to measure the model's and application's performance. The same metrics used for benchmarks, which compare different models, can also be used to evaluate an individual model's performance during development. These metrics help you understand how well your model is doing and identify areas for improvement.
Selecting the model that fits your needs, can be an iterative process. Next, you learn how to deploy a model so you can test it and experiment with how to optimize the model for your use case.