Explore foundation models in the model catalog
The Transformer architecture has allowed us to train models for Natural Language Processing (NLP) in a more efficient way. Instead of processing each token in a sentence or sequence, attention allows a model to process tokens in parallel in various ways.
To train a model using the Transformer architecture, you need to use a large amount of text data as input. Different models have been trained, which mostly differ by the data they've been trained on, or by how they implement attention within their architectures. Since the models are trained on large datasets, and the models themselves are large in size, they're often referred to as Large Language Models (LLMs).
Many LLMs are open-source and publicly available through communities like Hugging Face. Azure also offers the most commonly used LLMs as foundation models in the Azure Machine Learning model catalog. Foundation models are pretrained on large texts and can be fine-tuned for specific tasks with a relatively small dataset.
Explore the model catalog
In the Azure Machine Learning studio, you can navigate to the model catalog to explore all available foundation models. Additionally, you can import any model from the Hugging Face open-source library into the model catalog.
Tip
Hugging Face is an open-source community making models available to the public. You can find all models in their catalog. Additionally, you can explore the documentation to learn more about how individual models work, like BERT.
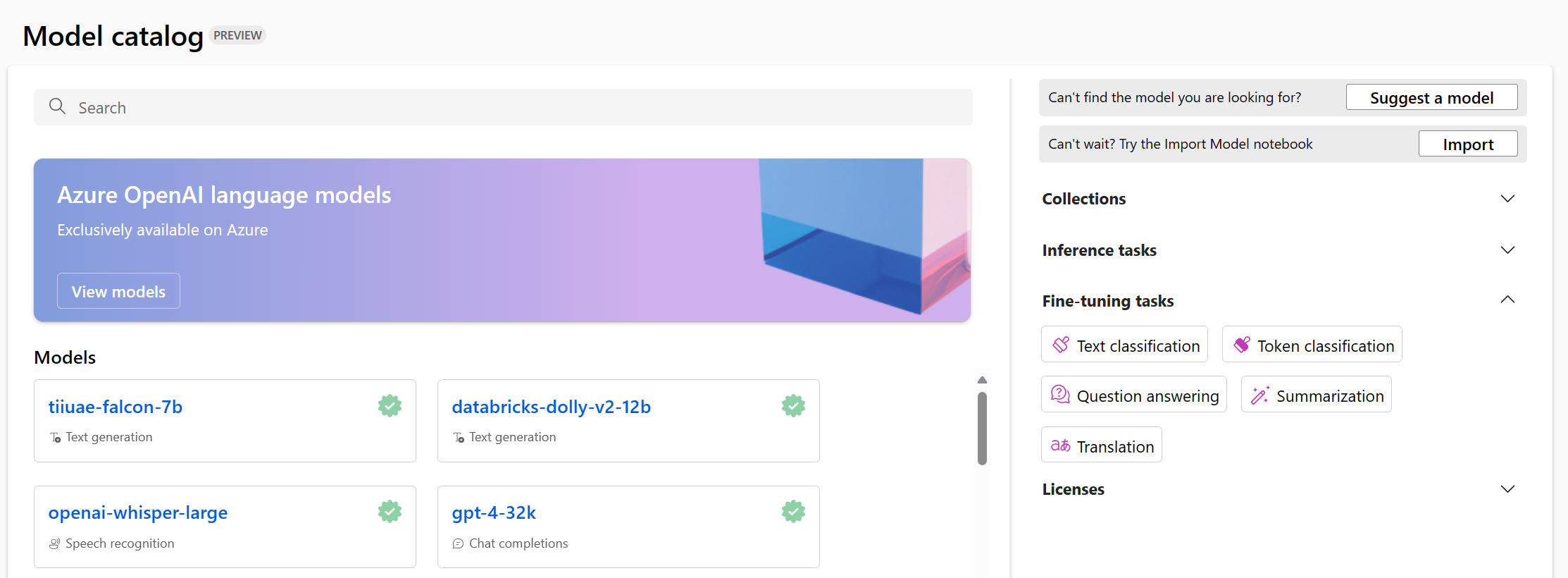
The Azure Machine Learning model catalog integrates with models from Hugging Face and other sources. The Azure Machine Learning model catalog makes it easier to explore, test, fine-tune, and deploy models.
Explore foundation models
When you select a model from the Azure Machine Learning catalog, you can experiment with it to explore whether it meets your requirements. A foundation model is already pretrained and you can deploy a foundation model to an endpoint without any extra training. If you want the model to be specialized in a task, or perform better on domain-specific knowledge, you can also choose to fine-tune a foundation model.
Foundation models can be used for various tasks, including:
- Text classification
- Token classification
- Question answering
- Summarization
- Translation
To choose the foundation model that best fits your needs, you can easily test out different models in the model catalog. You can also review the data the models are trained on and possible biases and risks a model may have.
Some foundation models that are commonly used are:
| Model | Description |
|---|---|
| BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) | Focused on encoding information by using context from before and after a token (bidirectional). Commonly used when you want to fine-tune a model to perform a specific task like text classification and question answering. |
| GPT (Generative Pretrained Transformer) | Trained to create coherent and contextually relevant text, and is most commonly used for tasks like text generation and chat completions. |
| LLaMA (Large Language Model Meta AI) | A family of models created by Meta. When training LLaMA models, the focus has been on providing more training data than increasing the complexity of the models. You can use LLaMA models for text generation and chat completions. |
| T5 (Text-to-Text Transfer Transformer) | An encoder-decoder model that uses a text-to-text approach. By focusing on converting text-to-text, these types of models are ideal for translation. |