Explore notebooks
Notebooks provide an interactive environment in which you can combine text and graphics in Markdown format with cells containing code that you run interactively in the notebook session.
As a data scientist, you may be most familiar with writing and executing code in notebooks. Microsoft Fabric offers a familiar notebook experience, powered by Apache Spark.
In Microsoft Fabric, data scientists, business users, and analysts all work on the same platform, enhancing data sharing and collaboration at scale.
Use of notebooks in data science
Notebooks are a common tool for data scientists as they allow combining code, explanatory text, and multimedia resources in a single document. This creates a narrative that can drive exploration by facilitating the sharing of codes, and quick prototyping.
Notebooks also allow data scientists to rapidly experiment and share insights through quick environment creation.
Notebooks in Microsoft Fabric
You can get started with notebooks in Microsoft Fabric with zero setup effort. You can either create a new notebook or import an existing notebook. You can also select multiple notebooks and import them in a batch.
Microsoft Fabric notebooks currently support four Apache Spark languages:
- PySpark (Python)
- Spark (Scala)
- Spark SQL
- SparkR
Create a notebook
To create a new notebook, select New option in the Home in your Fabric enabled workspace.
The screenshot below walks you through the main notebook components in Fabric.
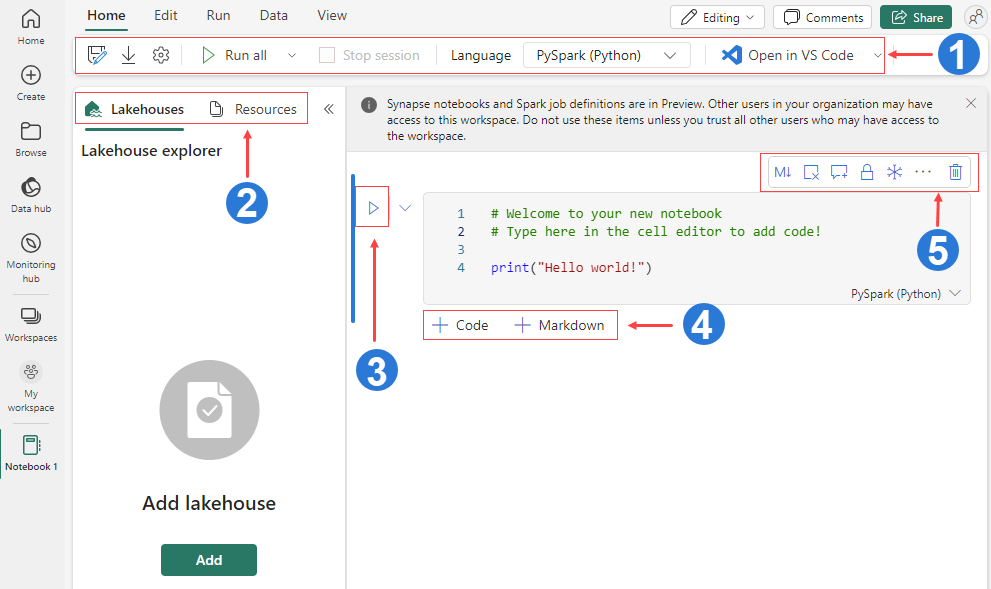
The menu bar in a Microsoft Fabric notebook offers various features. It allows you to save and export your notebook, manage cells, terminate the session, schedule the execution of your notebook, launch Data Wrangler, adjust the layout, among others. To access all these features, simply switch between the Home, Edit, Run, Data, and View tabs.
On the Lakehouses tab, you can add a new or existing lakehouse from the lakehouse explorer. The Resources tab provides a Unix-like storage for small files like code, datasets, and images, accessible directly from the notebook.
Run the current cell. Alternatively, you can press Ctrl+Enter, or press Alt+Enter to run the current cell and insert a new cell.
Add a new code or markdown cell. This option is also available from the menu by selecting Edit -> Add code cell.
It provides various options for managing a specific cell, such as repositioning the cell within the notebook, converting it to a markdown or code cell, clearing the output, adding comments, and more.
Note
If you’re unable to find the notebook option, it could be because either the tenant or the workspace hasn’t been enabled for Fabric. To learn how to enable Fabric, see Enable Microsoft Fabric for your organization.
Work with data in notebooks
Drag and drop allows you to easily import data from the Lakehouse explorer. It supports various file types like text files, tables, images, etc. You can drop the data into an existing or new cell, and the notebook generates a code snippet to preview the data.
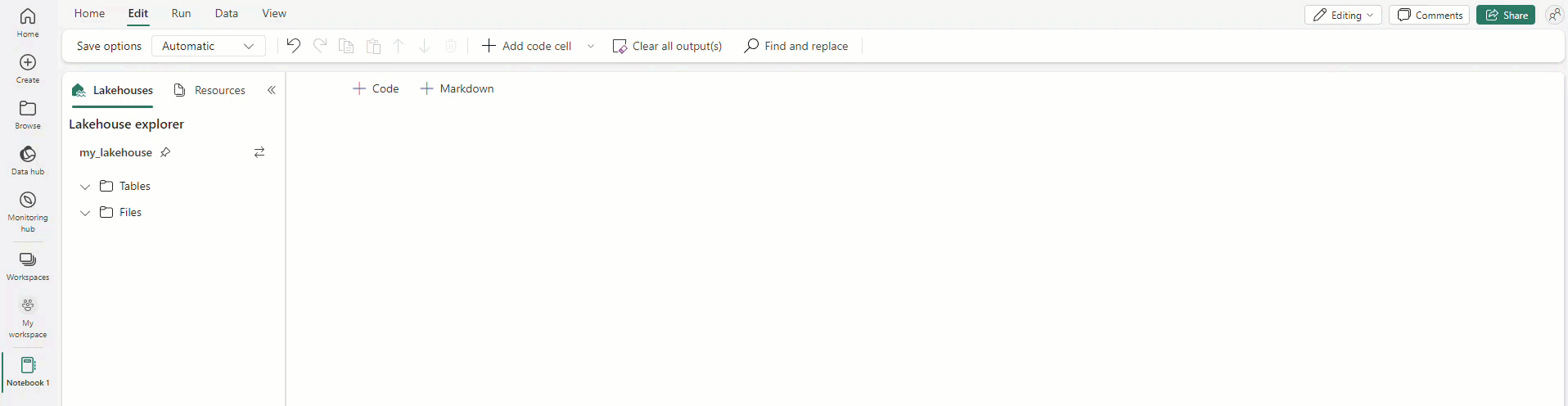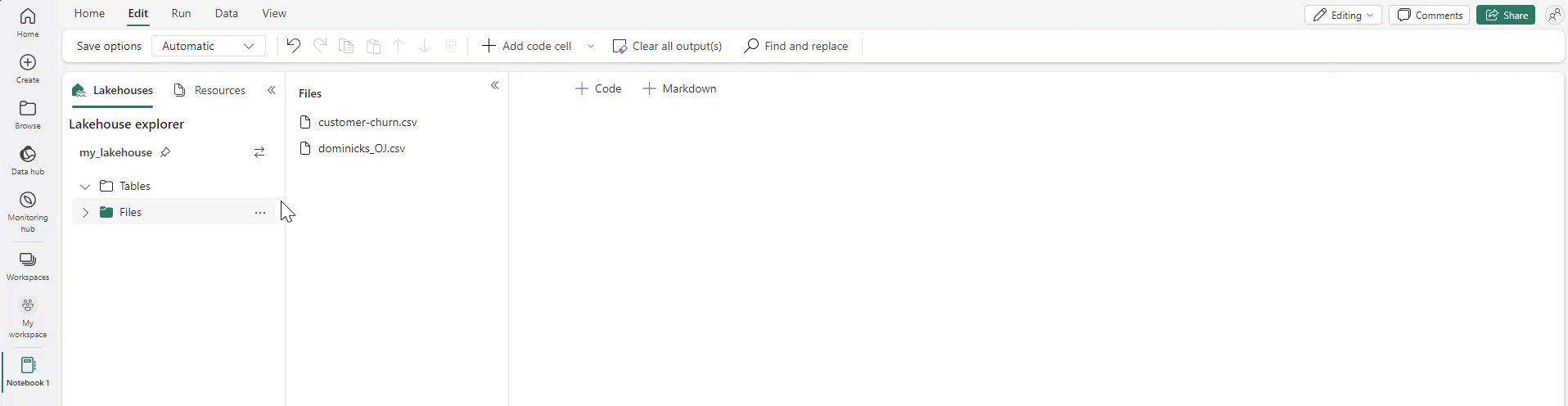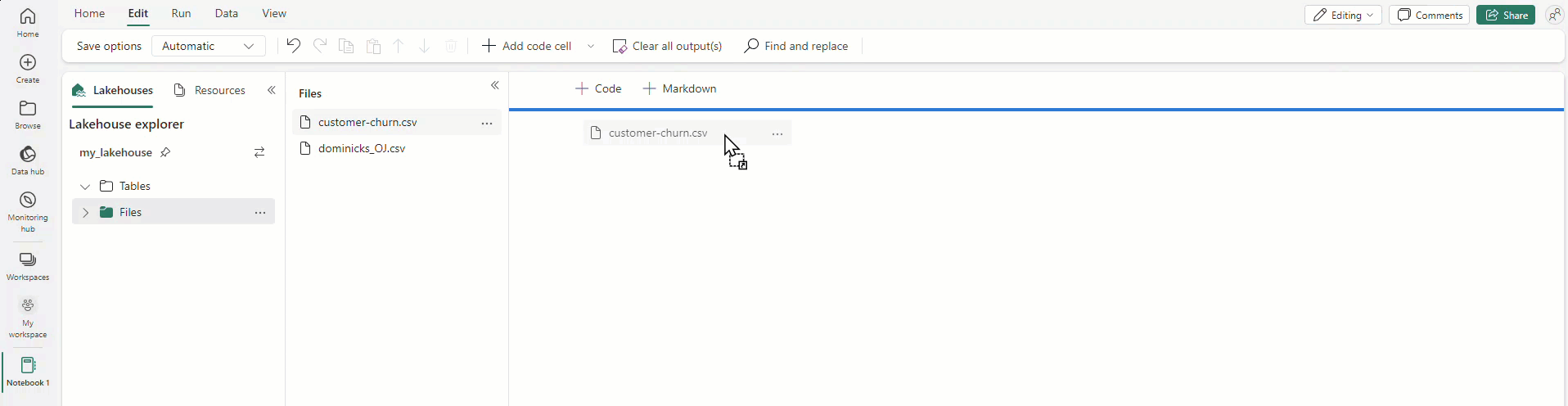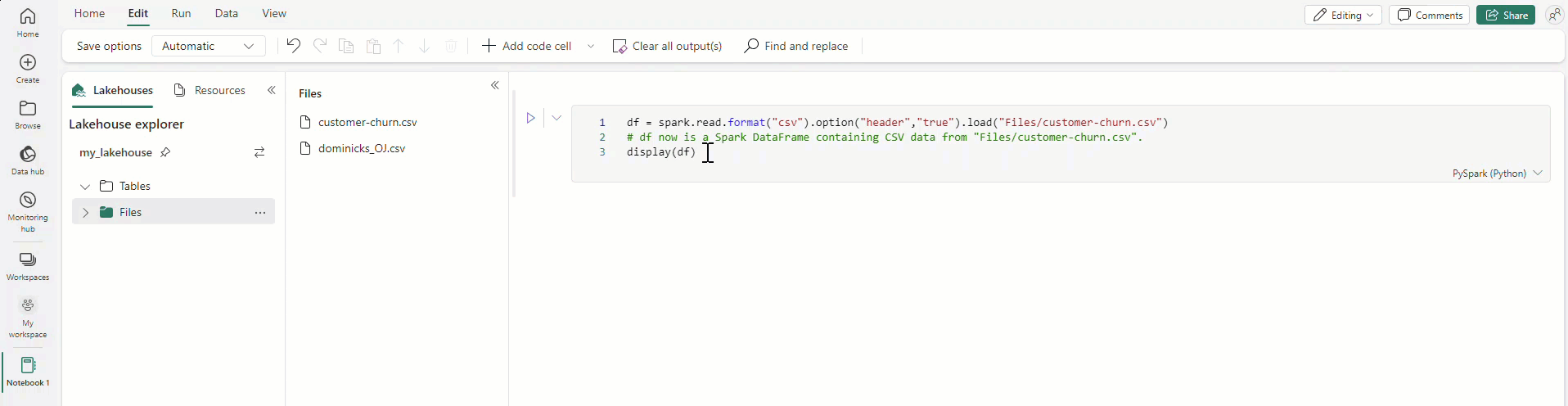
Also, you can easily insert images into a markdown cell by dragging and dropping them from your browser or local computer.
Write code in notebooks
The IntelliSense enhances code writing and error identification with features like syntax highlighting, error marking, and automatic code completions. As you type, it predicts what you’re trying to write and offers suggestions. This not only speeds up coding but also helps avoid typos and learn API calls.
Keep track of your variables in notebooks
It’s not uncommon when working in a notebook to have hundreds of variables, each playing a crucial role in your data analysis or model development. Keeping track of all these variables can be a challenging task. This is where the built-in variables explorer in Microsoft Fabric notebook comes into play.
As you execute code cells in your PySpark (Python) notebook in Microsoft Fabric, the variables you define are automatically tracked and listed in the variables explorer. This allows you to see the state of your variables at any point in your coding process.
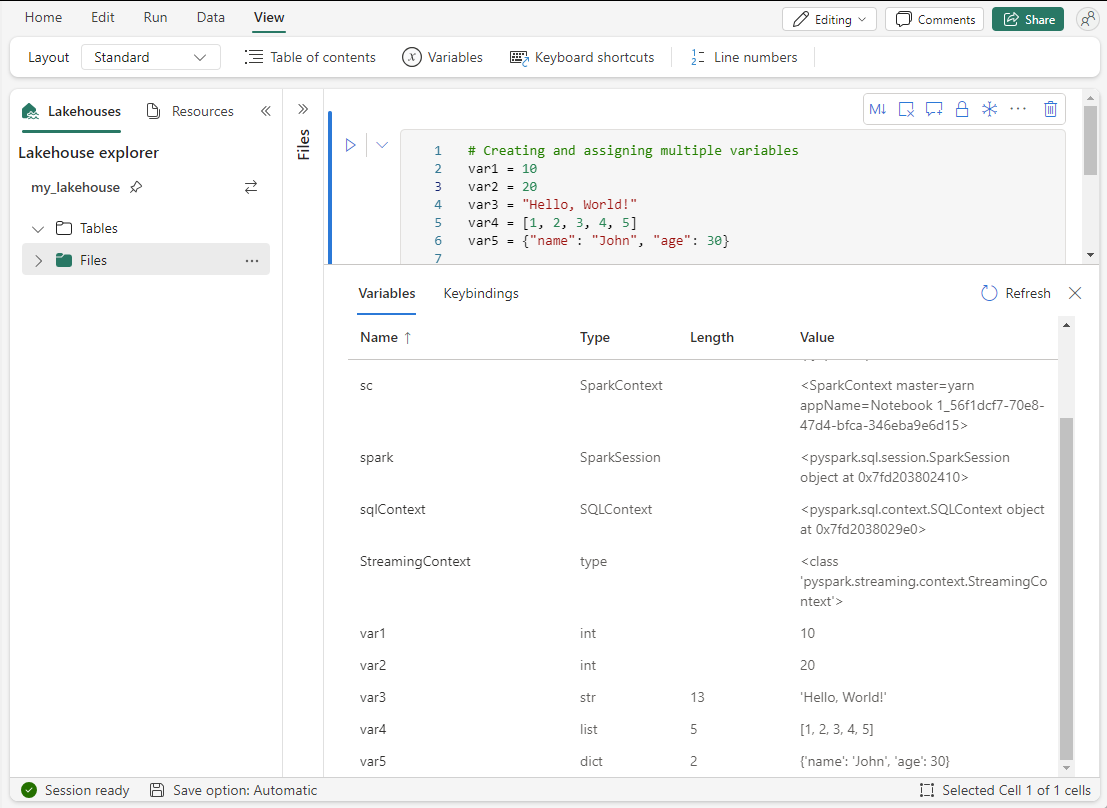
For each variable, the explorer shows its name, type, length, and value. This gives you a quick overview of your data without needing to print or log these details manually.
Manage libraries and dependencies
In Microsoft Fabric, you can manage libraries and dependencies in two ways: through workspace settings or in-line within a notebook.
Workspace settings
Libraries installed at the workspace level can be used by all notebooks and Spark jobs within that workspace, and are accessible across different sessions. So, if you need to create a common environment for all sessions in a workspace, it's best to use workspace-level libraries.
From the left navigation pane, select Workspaces. This displays a list of your workspaces. Select the workspace you want to work with.
Select Workspace settings for your current workspace, and then select Data Engineering/Science.
Select Library management to install both Python feed and custom libraries.
In-line installation
The %pip command in Microsoft Fabric works the same as pip command in many data science notebooks. Use %pip commands to directly install feed libraries into your notebook.
Note
Any libraries installed with the %pip command are only available for the current session. Also, running a %pip command will restart the Python interpreter, which means any variables defined before running the command will be lost.
The %pip install command is used to install the latest versions of these libraries. The import statement is then used to import these libraries into the current Python environment.
%pip install seaborn
%pip install sklearn
import seaborn as sns
from sklearn import datasets
Tip
It's a good practice to put all the commands for adding, deleting, or updating Python packages at the beginning of your notebook.
Collaborate in notebooks
Sharing and collaborating on notebooks allow for collective problem-solving, and efficiency in data science projects. Microsoft Fabric notebooks offer a powerful feature where multiple users can simultaneously edit the same document. This functionality is useful in scenarios such as pair programming, remote troubleshooting, and knowledge sharing.
In our scenario, imagine you and your colleague are working on a project using Microsoft Fabric notebooks. You're stuck on a piece of code and ask your colleague for help. Your colleague opens the same notebook and you see their profile appear. As your colleague reviews and edits the code, you can see their cursor movements, selections, and changes in real-time. This immediate feedback helps you identify and understand the solution quickly.
This real-time collaboration feature of Microsoft Fabric notebooks not only helps you solve your coding problem but also provides an excellent opportunity for learning from your more experienced colleague.
To learn more about all the features available Microsoft Fabric notebooks, see Develop, execute, and manage Microsoft Fabric notebooks.