Explore access management
Access management for cloud resources is a critical function for any organization that's using the cloud. Role-based access control (RBAC) helps you manage who has access to Azure resources, what they can do with those resources, and what areas they have access to. RBAC is an authorization system built on Azure Resource Manager that provides fine-grained access management of Azure resources.
The way you control access to resources using RBAC is to create role assignments. This is a key concept to understand – it’s how permissions are enforced. A role assignment consists of three elements: security principal, role definition, and scope.
Security principal: A security principal is an object that represents a user, group, service principal, or managed identity that's requesting access to Azure resources.
- User: An individual who has a profile in Microsoft Entra ID.
- Group: A set of users created in Microsoft Entra ID.
- Service principal: A security identity used by applications or services to access specific Azure resources. You can think of it as a user identity (username and password or certificate) for an application.
- Managed identity: An identity in Microsoft Entra ID that's automatically managed by Azure. You typically use managed identities when developing cloud applications to manage the credentials for authenticating to Azure services. For example, you can assign a managed identity to an Azure Virtual Machine to allow software running within that virtual machine access to other Azure resources.
Role definition: A role definition is a collection of permissions. It's sometimes called a role. A role definition lists the operations that can be performed, such as read, write, and delete. Roles can be high-level, like owner, or specific, like virtual machine reader. Azure includes several built-in roles that you can use. The following lists four fundamental built-in roles. The first three apply to all resource types.
Owner: Has full access to all resources including the right to delegate access to others.
Contributor: Can create and manage all types of Azure resources but can’t grant access to others.
Reader: Can view existing Azure resources.
User Access Administrator: Lets you manage user access to Azure resources.
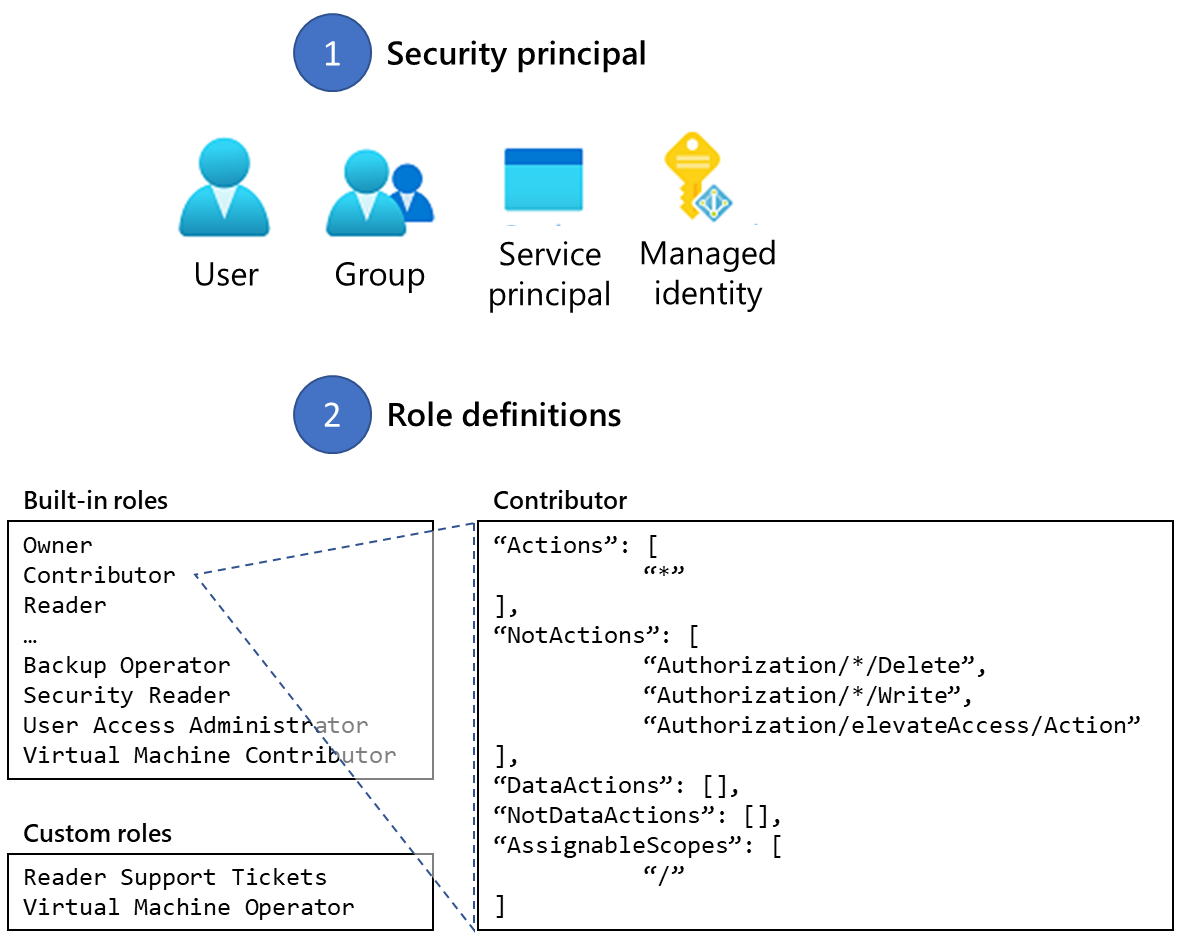
The rest of the built-in roles allow management of specific Azure resources. For example, the Virtual Machine Contributor role allows a user to create and manage virtual machines. If the built-in roles don't meet the specific needs of your organization, you can create your own custom roles for Azure resources.
Scope: Scope is the set of resources that the access applies to. When you assign a role, you can further limit the actions allowed by defining a scope. In Azure, you can specify a scope at multiple levels: management group, subscription, resource group, or resource. Scopes are structured in a parent-child relationship.