Describe Conditional Access
Conditional Access is a feature of Microsoft Entra ID that provides an extra layer of security before allowing authenticated users to access data or other assets. Conditional Access is implemented through policies that are created and managed in Microsoft Entra ID. A Conditional Access policy analyses signals including user, location, device, application, and risk to automate decisions for authorizing access to resources (apps and data).
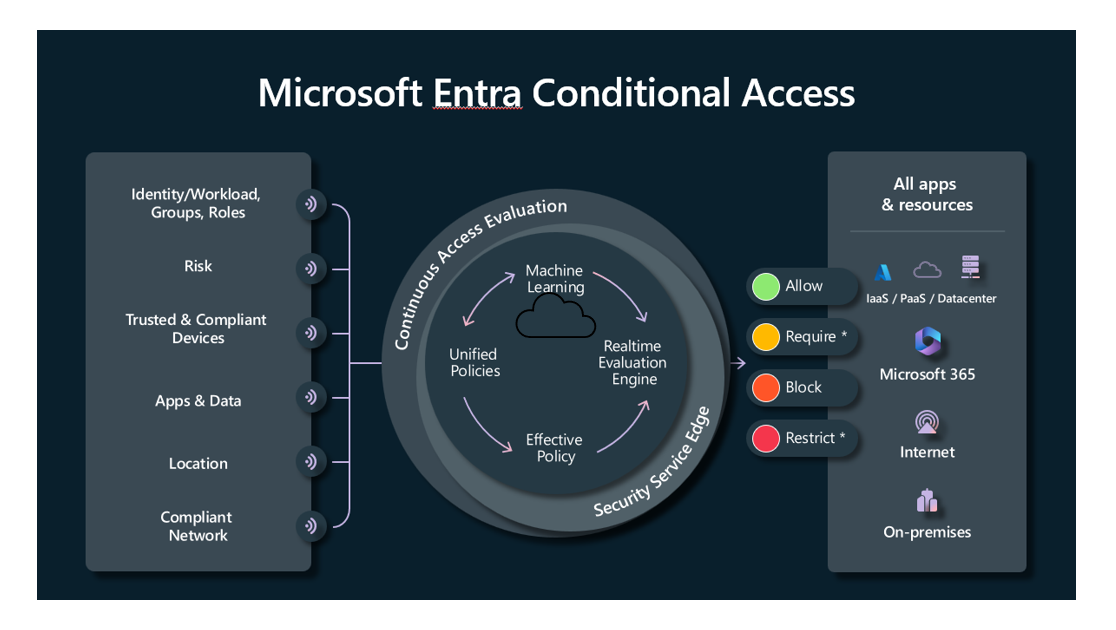
Conditional Access policies at their simplest are if-then statements. For example, a Conditional Access policy might state that if a user belongs to a certain group, then they're required to provide multifactor authentication to sign in to an application.
Important
Conditional Access policies are enforced after first-factor authentication is completed. Conditional Access isn't intended to be an organization's first line of defense for scenarios like denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, but it can use signals from these events to determine access.
Conditional access policy components
A conditional access policy in Microsoft Entra ID consists of two components, assignments and access controls.
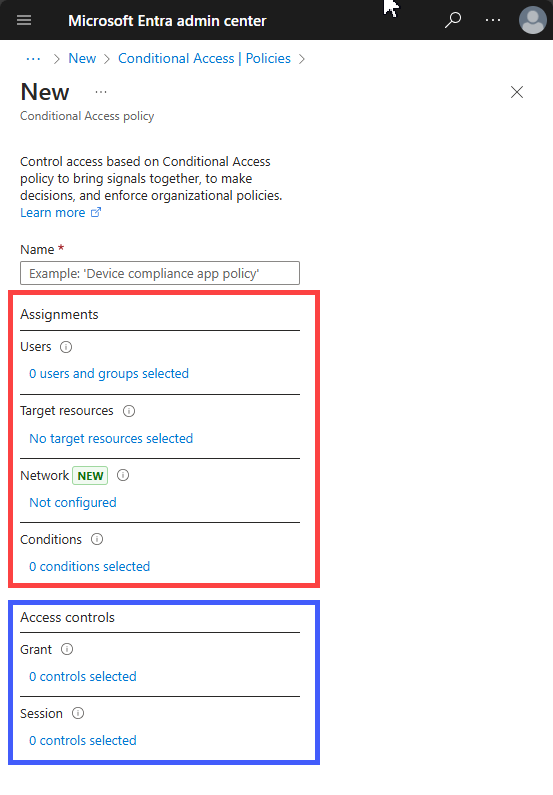
Assignments
When creating a conditional access policy, admins can determine which signals to use through assignments. The assignments portion of the policy controls the who, what, where, and when of the Conditional Access policy. All assignments are logically ANDed. If you have more than one assignment configured, all assignments must be satisfied to trigger a policy. Some of the assignments include:
- Users assign who the policy will include or exclude. This assignment can include all users in the directory, specific users and groups, directory roles, external guests, and workload identities.
- Target resources include applications or services, user actions, Global Secure Access (preview), or authentication context.
- Cloud apps - Administrators can choose from the list of applications or services that include built-in Microsoft applications, including Microsoft Cloud applications, Office 365, the Windows Azure Service Management API, Microsoft Admin portals, and any Microsoft Entra registered applications.
- User actions - Administrators can choose to define policy not based on a cloud application but on a user action like Register security information or Register or join devices, allowing Conditional Access to enforce controls around those actions.
- Global Secure Access (preview) - Administrators can use conditional Access policies to secure the traffic that passes through the Global Secure Access service. This is done by defining traffic profiles in Global Secure Access. Conditional Access policies can then be assigned to the Global Secure Access traffic profile.
- Authentication context - Authentication context can be used to further secure data and actions in applications. For example, users that have access to specific content in a SharePoint site may be required to access that content via a managed device or agree to specific terms of use.
- Network allows you to control user access based on the user's network or physical location. You can include any network or location, locations marked as trusted networks or trusted IP address ranges, or named locations. You can also identify compliant networks that are made up of users and devices that comply with your organization's security policies.
- Conditions define where and when the policy will apply. Multiple conditions can be combined to create fine-grained and specific Conditional Access policies. Some of the conditions include:
- Sign-in risk and user risk. Integration with Microsoft Entra ID Protection allows Conditional Access policies to identify suspicious actions related to user accounts in the directory and trigger a policy. Sign-in risk is the probability that a given sign-in, or authentication request, isn't authorized by the identity owner. User risk is the probability that a given identity or account is compromised.
- Insider risk. Administrators with access to Microsoft Purview adaptive protection can incorporate risk signals from Microsoft Purview into Conditional Access policy decisions. Insider risk takes into account your data governance, data security, and risk and compliance configurations from Microsoft Purview.
- Devices platform. Device platform, which is characterized by the operating system that runs on a device can be used when enforcing Conditional Access policies.
- Client apps. Client apps, the software the user is employing to access the cloud app, including browsers, mobile apps, desktop clients, can also be used in access policy decision.
- Filters for devices. Organizations can enforce policies based on device properties, by using the filters for devices option. As an example, this option may be used to target policies to specific devices like privileged access workstations.
In essence, the assignments portion controls the who, what, and where of the Conditional Access policy.
Access controls
When the Conditional Access policy has been applied, an informed decision is reached on whether to block access, grant access, grant access with extra verification, or apply a session control to enable a limited experience. The decision is referred to as the access controls portion of the Conditional Access policy and defines how a policy is enforced. Common decisions are:
- Block access
- Grant access. Administrators can grant access without any additional control, or they can choose to enforce one or more controls when granting access. Examples of controls used to grant access include requiring users to perform multifactor authentication, requiring specific authentication methods to access a resource, requiring devices to meet specific compliance policy requirements, require a password change, and more. For a complete list, refer to Grant controls in Conditional Access policy.
- Session. Within a Conditional Access policy, an administrator can make use of session controls to enable limited experiences within specific cloud applications. As an example, Conditional Access App Control uses signals from Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps to block the download, cut, copy, and print capabilities for sensitive documents, or to require labeling of sensitive files. Other session controls include sign-in frequency and application enforced restrictions that, for selected applications, use the device information to provide users with a limited or full experience, depending on the device state. For a complete list, refer Session controls in Conditional Access policy.
In summary, the assignments portion controls the who, what, and where of the Conditional Access policy while the access controls portion controls how a policy is enforced.