Examine the IoT Hub built-in endpoint
By default, messages are routed to the built-in service-facing endpoint (messages/events) which is compatible with Event Hubs. This endpoint is currently only exposed using the AMQP protocol on port 5671 and AMQP over WebSockets on port 443. An Azure IoT hub exposes the following properties to enable you to control the built-in endpoint.
Property
Description
Partition count
Set this property at creation to define the number of partitions for device-to-cloud event ingestion.
Retention time
This property specifies how long in days messages are retained by Azure IoT Hub. The default is one day, but it can be increased to seven days.
Azure IoT Hub allows data retention in the built-in endpoint for a maximum of seven days. You can set the retention time during creation of your Azure IoT Hub. Data retention time in Azure IoT Hub depends on your Azure IoT hub tier and unit type. In terms of size, the built-in Event Hubs endpoint can retain messages of the maximum message size up to at least 24 hours of quota. For example, for 1 S1 unit Azure IoT Hub provides enough storage to retain at least 400 thousand messages of 4k size each. If your devices are sending smaller messages, they may be retained for longer (up to seven days) depending on how much storage is consumed. We guarantee to retain the data for the specified retention time as a minimum.
Azure IoT Hub also enables you to manage consumer groups on the built-in device-to-cloud receive endpoint. You can have up to 20 consumer groups for each Azure IoT Hub.
If you're using message routing and the fallback route is enabled, all messages that don't match a query on any route go to the built-in endpoint. If you disable this fallback route, messages that don't match any query are dropped.
You can modify the retention time, either programmatically using the Azure IoT Hub resource provider REST APIs, or with the Azure portal.
Azure IoT Hub exposes the messages/events built-in endpoint for your back-end services to read the device-to-cloud messages received by your hub. This endpoint is Event Hubs-compatible, which enables you to use any of the mechanisms the Event Hubs service supports for reading messages.
Read from the Built-in endpoint
Some product integrations and Event Hubs SDKs are aware of Azure IoT Hub and let you use your Azure IoT hub service connection string to connect to the built-in endpoint.
When you use Event Hubs SDKs or product integrations that are unaware of Azure IoT Hub, you need an Event Hubs-compatible endpoint and Event Hubs-compatible name. You can retrieve these values from Azure IoT hub service in the Azure portal by opening the Built-in endpoints blade.
The Event Hub Details section contains the following values: Partitions, Event Hubs-compatible name, Event Hubs-compatible endpoint, Retention for, and Consumer Groups.
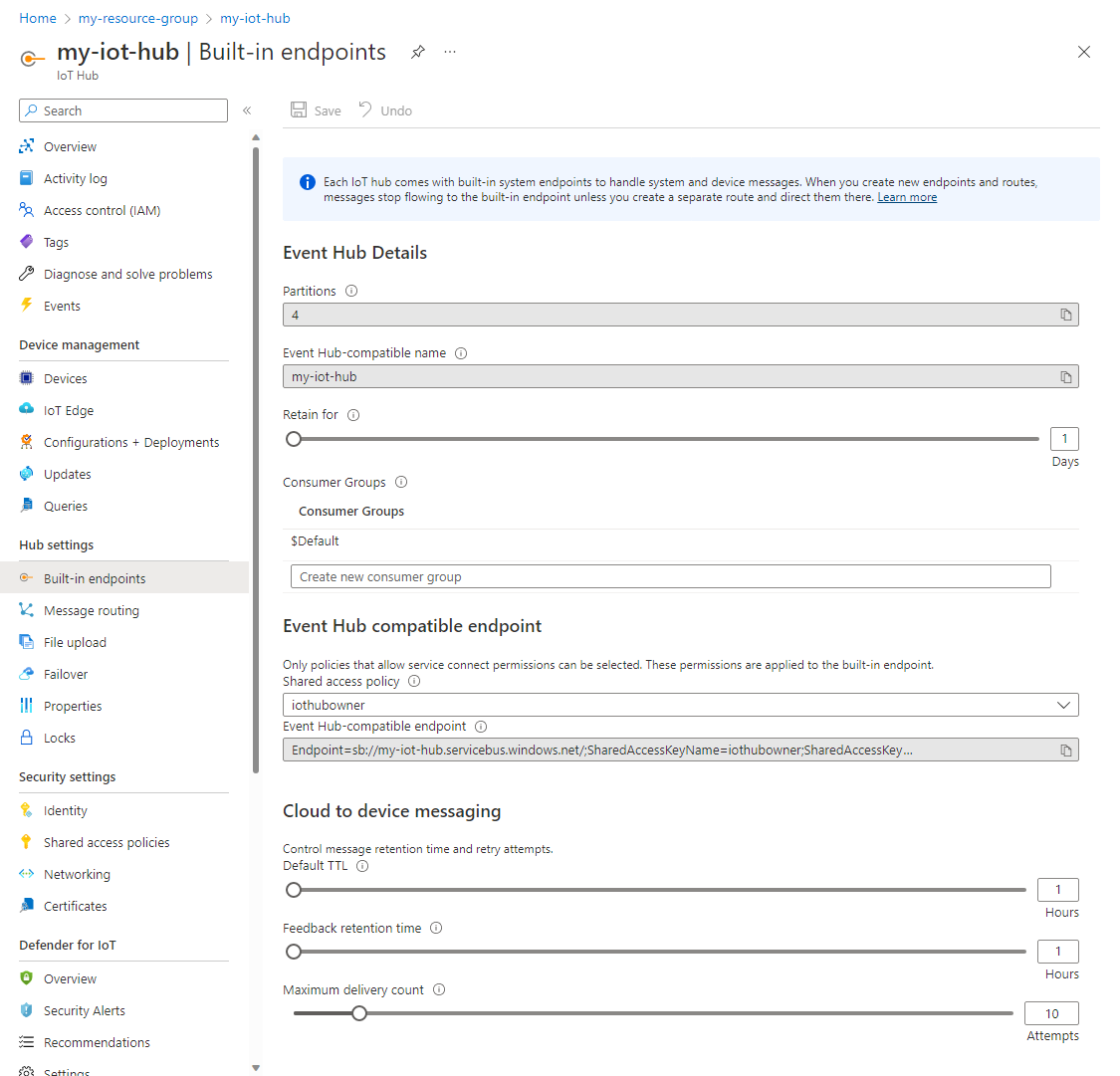
In the portal, the Event Hubs-compatible endpoint field contains a complete Event Hubs connection string that looks like: Endpoint=sb://abcd1234namespace.servicebus.windows.net/;SharedAccessKeyName=iothubowner;SharedAccessKey=keykeykeykeykeykey=;EntityPath=iothub-ehub-abcd-1234-123456. If the SDK you're using requires other values, then they would be:
Name
Value
Endpoint
sb://abcd1234namespace.servicebus.windows.net/
Hostname
abcd1234namespace.servicebus.windows.net
Namespace
abcd1234namespace
You can then use any shared access policy that has the ServiceConnect permissions to connect to the specified Event Hubs.
The SDKs you can use to connect to the built-in Event Hubs-compatible endpoint that Azure IoT Hub exposes include:
Language
SDK
Example
Notes
.NET
Uses Event Hubs-compatible information
Java
Uses Event Hubs-compatible information
Node.js
Uses Azure IoT Hub connection string
Python
Uses Azure IoT Hub connection string
The product integrations you can use with the built-in Event Hubs-compatible endpoint that Azure IoT Hub exposes include:
- Azure Functions
- Azure Stream Analytics
- Time Series Insights
- Apache Storm spout
- Apache Spark integration
- Azure Databricks