Exercise - Deploy a PHP and MySQL - Flexible Server app on Azure App Service
In this unit, you build and deploy a sample PHP app to Azure App Service, and integrate it with Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server on the back end.
STEP 1 - Create an Azure Database for MySQL flexible server
First, you provision a MySQL flexible server with public access connectivity, configure firewall rules to allow the app to access the server, and create a production database.
You use the Azure portal to walk through the MySQL flexible server creation experience.
Sign in to the Azure portal using the same account you used to activate the sandbox.
In the search box at the top of the page, enter MySQL, and then select Azure Database for MySQL flexible servers.
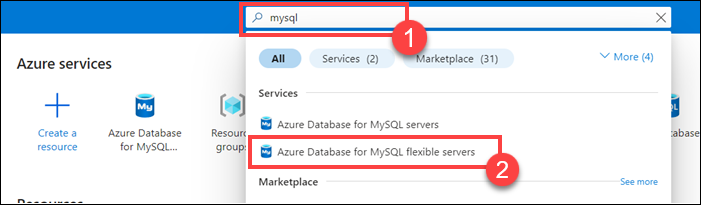
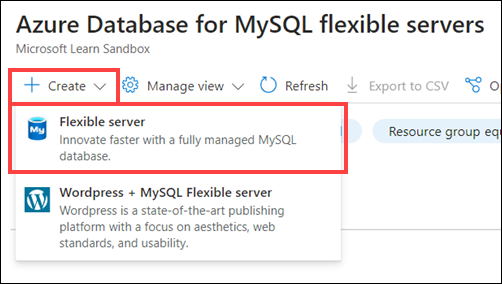
On the Azure Database for MySQL flexible servers page, select + Create, and then select Flexible server.
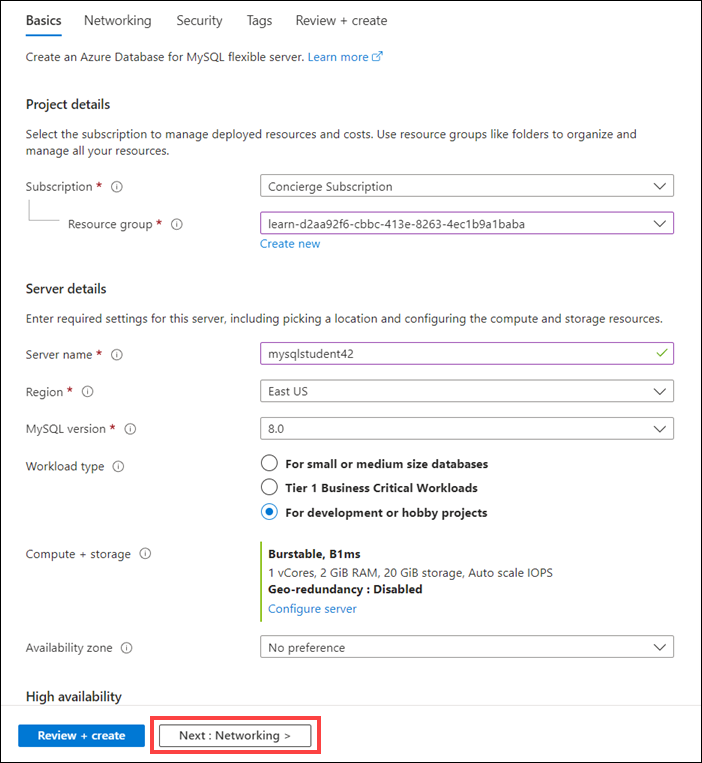
On the Flexible server page, on the Basics tab, enter the information in the following table.
Setting Suggested Value Subscription Concierge Subscription Resource group From the dropdown list, select the resource group starting with learn- Server name Enter a globally unique name that identifies your flexible server. MySQL version 8.0 Workload type Select For development or hobby projects Admin username Enter mysqladmin. Don't use azure_superuser, admin, administrator, root, guest, or public. Password Enter Passw0rd123. The password must contain between 8 and 128 characters and include characters from three categories: English uppercase letters, English lowercase letters, numbers (0 through 9), and nonalphanumeric characters (such as !, $, #, %). Keep the default values for all other settings.
On the Basics tab, under Compute + Storage, select Configure server.
On the Compute + Storage page, configure the following settings:
- Compute
- Select the Burstable compute tier.
- From the Compute size dropdown list, select Standard_B1s (1 vCore, 1 GiB memory, 400 max iops).
- Storage
- Verify that the Storage size (in GB) is set to 20.
- Select Pre-provisioned IOPS and leave the value is set to 360.
- Verify that the Storage Auto-growth check box is selected.
- High Availability
- Verify that the Enable High Availability check box isn't selected.
- Backups
- Verify that the Backup retention period (in days) is set to 7.
- Verify that the Recover from regional outage or disaster check box as not selected.
- Compute
Select Save, and then navigate to the Networking tab.
In the Networking tab, select Public access (allowed IP addresses) connectivity method, check Allow public access to this resource through the internet using a public IP address, and check Allow public access from any Azure service within Azure to this server as shown in the following screenshot.
Select Review + create to review your MySQL flexible server configuration.
Select Create to provision the server. Provisioning can take up to 10 minutes.
After the deployment is done, select Go to resource to view the Azure Database for MySQL flexible server's Overview page.
For the remainder of this exercise, you run the commands using the Azure Cloud Shell, which appears to the right of this window.
To create a new MySQL production database sampledb to use with the PHP app, run the following command:
az mysql flexible-server db create \
--resource-group <rgn>[Sandbox resource group name]</rgn> \
--server-name <your-mysql-server-name> \
--database-name sampledb
STEP 2 - Clone your app
For this exercise, you use a sample PHP app that displays and manages a product catalog. The app provides basic functionalities like viewing the products in the catalog, adding new products, updating existing item prices, and removing products.
You directly clone the coded app and learn how to deploy it on Azure App Service.
Note
To learn more about the app code, go ahead and explore the app in the GitHub repository!
To clone the sample app repository and change to the repository root, run the following commands:
git clone https://github.com/Azure-Samples/php-mysql-app-service.git cd php-mysql-app-serviceRun the following command to ensure that the default branch is
main.git branch -m main
STEP 3 - Create and configure an Azure App Service Web App
In Azure App Service (Web Apps, API Apps, or Mobile Apps), an app always runs in an App Service plan. An App Service plan defines a set of compute resources for a web app to run. In this step, you create an Azure App Service plan and an App Service web app within it, which will host the sample app.
To create an App Service plan in the Free pricing tier, run the following command:
az appservice plan create --name plan-learn \ --resource-group <rgn>[Sandbox resource group name]</rgn> \ --location centralus \ --sku FREE --is-linuxIf you want to deploy an app to Azure web app using deployment methods like FTP or Local Git, you need to configure a deployment user with username and password credentials. After you configure your deployment user, you can take advantage of it for all your Azure App Service deployments.
az webapp deployment user set \ --user-name <your-deployment-username> \ --password <your-deployment-password>To create an App Service web app with PHP 8.0 runtime and to configure the Local Git deployment option to deploy your app from a Git repository on your local computer, run the following command.
Note: Replace
<your-app-name>with a globally unique app name (valid characters are a-z, 0-9, and -).az webapp create \ --resource-group <rgn>[Sandbox resource group name]</rgn> \ --plan plan-learn \ --name <your-app-name> \ --runtime "PHP|8.0" \ --deployment-local-gitImportant
In the Azure CLI output, the URL of the Git remote is displayed in the
deploymentLocalGitUrlproperty, with the formathttps://<username>@<app-name>.scm.azurewebsites.net/<app-name>.git. Save this URL, as you'll need it later.The
config.phpfile in the sample PHP app retrieves the database connection information (server name, database name, server username and password) from environment variables using thegetenv()function. In App Service, to set environment variables as Application Settings (appsettings), run the following command:az webapp config appsettings set \ --name <your-app-name> \ --resource-group <rgn>[Sandbox resource group name]</rgn> \ --settings DB_HOST="<your-server-name>.mysql.database.azure.com" \ DB_DATABASE="sampledb" \ DB_USERNAME="<your-mysql-admin-username>" \ DB_PASSWORD="<your-mysql-admin-password>" \ MYSQL_SSL="true"This command above configures the MySQL flexible server database connection settings in the Web App.
STEP 4 - Deploy your app using Local Git
Now, you deploy the sample PHP app to Azure App Service using the Local Git deployment option.
Since you're deploying the main branch, you need to set the default deployment branch for your App Service app to main. To set the DEPLOYMENT_BRANCH under Application Settings, run the following command:
az webapp config appsettings set \ --name <your-app-name> \ --resource-group <rgn>[Sandbox resource group name]</rgn> \ --settings DEPLOYMENT_BRANCH='main'Verify that you are in the app repository's root directory.
To add an Azure remote to your local Git repository, run the following command.
Note: Replace
<deploymentLocalGitUrl>with the URL of the Git remote that you saved in the Create an App Service web app step.git remote add azure <deploymentLocalGitUrl>To deploy your app by performing a
git pushto the Azure remote, run the following command. When Git Credential Manager prompts you for credentials, enter the deployment credentials that you created in Configure a deployment user step.git push azure main
The deployment might take a few minutes to succeed.
STEP 5 - Test your app
Finally, test the app by browsing to https://<app-name>.azurewebsites.net, and then adding, viewing, updating, or deleting items from the product catalog.
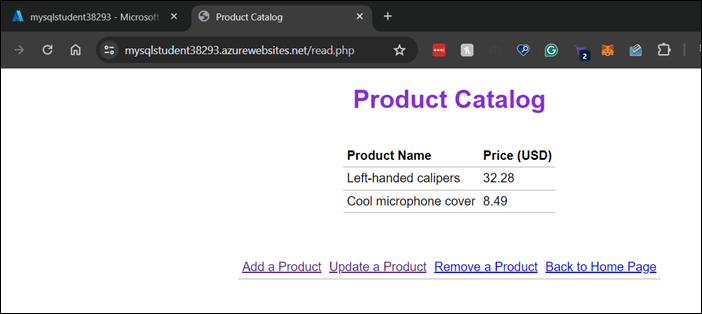
Congratulations! You have successfully deployed a sample PHP app to Azure App Service and integrated it with Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server on the back end.