Design for Azure blob backup and recovery
Azure Backup provides operational backup for Azure blobs, which is a local backup solution for Azure Blob Storage. In this backup method, your backup data is stored in your source Azure storage account rather than being transferred to an Azure Backup storage vault.
Things to know about Azure Blob Storage backup and recovery
Here are some of the prominent features available for backup and recovery of Azure Blob Storages.
Operational backup for Azure blobs provides you with a continuous backup solution. You don't need to schedule any backups.
All changes in an operational blob backup are retained for a specified period of time, and restorable from a selected point in time.
The soft delete feature lets you protect your data from accidental deletion or corruption. During the retention period, you can restore a soft-deleted blob object to its state at the time it was deleted. Soft delete is available for blobs and containers.
The retention period for deleted blobs or containers can be specified between 1 and 365 days. The default period is seven days.
The operational backup solution supports blob versioning. You can restore an earlier version of a blob, or recover your data after incorrect modification or deletion.
The point-in-time restore feature for block blobs lets you protect against accidental deletion or corruption. During the retention period, you can restore block blobs from the present state to a state at a previous time.
The resource lock feature prevents resources from being accidentally deleted or changed. You can set the resource lock to prohibit deletion or allow reading only.
Let's examine some of these features in more detail. As you review these options, consider which features can benefit the Tailwind Traders solution.
Things to consider when using soft delete and versioning
You can implement the soft delete feature to protect an individual blob, snapshot, container, or blob version from accidental deletes or overwrites. Soft delete maintains the deleted data in the system for your specified retention period. During the retention period, you can restore a soft-deleted object to its state at the time it was deleted.
The following diagram shows a high-level view of the soft delete feature for containers and blobs, and blob versions.
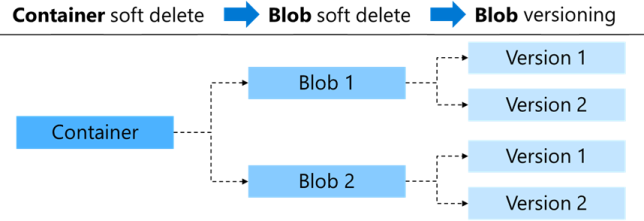
There are different options for implementing soft delete and blob versioning:
Implement blob soft delete to restore a specific deleted file, such as a blob, snapshot, or blob version.
Use container soft delete to restore a container and its contents.
Note
Container soft delete doesn't protect against the deletion of a storage account, but only against the deletion of containers in a storage account.
Add blob versioning to automatically maintain previous versions of a blob. You can restore an earlier version of a blob, or use the feature to recover your data. Blob versioning is useful when you have multiple authors editing the same files. Implement blob versioning to maintain or restore individual changes from each author.
Things to consider when using point-in-time restore
Like soft delete, point-in-time restore for block blobs also protects against accidental deletion or corruption. Create a management policy for the source storage account and specify your retention period. During the retention period, you can restore block blobs from the present state to a state at a previous time. Point-in-time restore lets you test scenarios that require reverting a data set to a known state before you run further tests.
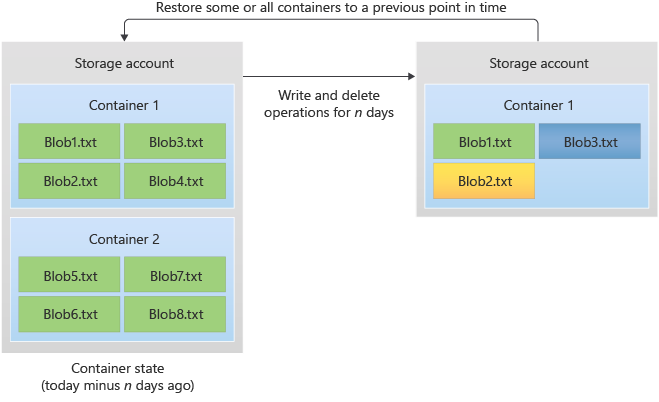
The following diagram shows how point-in-time restore works. One or more containers or blob ranges is restored to its previous state. The result of the process is to revert write and delete operations that occurred during the retention period.
Things to consider when using resource locks
You can protect your data and avoid accidental changes by using resource locks. This feature prevents resources from being accidentally deleted or changed. There are two lock levels: CanNotDelete and ReadOnly.
CanNotDelete permits authorized users to read and modify a resource, but they can't delete the resource without first removing the lock.
ReadOnly allows authorized users to read a resource, but they can't delete or change the resource. Applying this lock is like restricting all authorized users to the permissions granted by the Reader role in Azure RBAC.