Design for Azure Backup
Azure Backup uses Azure resources for short-term and long-term storage. Azure Backup minimizes or even eliminates the need for maintaining physical backup media. Some examples of backup media include tapes, hard drives, and DVDs.
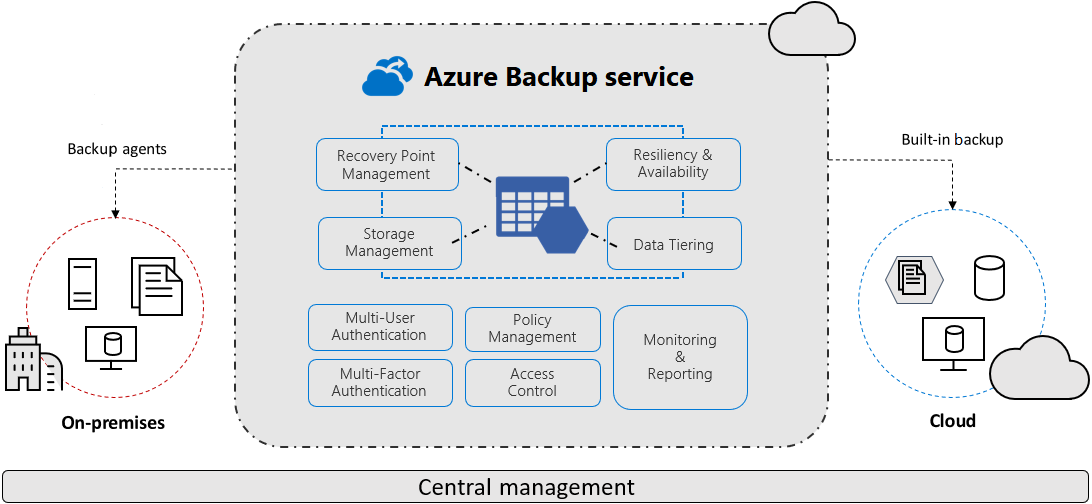
Things to know about Azure Backup
Azure Backup offers multiple components that you can download and deploy on the appropriate computer, server, or in the cloud. The component (or agent) that you deploy depends on what you want to protect. The following table summarizes the types of backup you can perform with Azure Backup.
| Backup type | Description |
|---|---|
| On-premises | Back up files, folders, and system state with the Microsoft Azure Recovery Services (MARS) agent. You can also use System Center Data Protection Manager (DPM) or the Microsoft Azure Backup Server (MABS) agent to protect on-premises virtual machines (both Hyper-V and VMware) and other on-premises workloads. |
| Azure Virtual Machines | Back up entire Windows or Linux virtual machines (by using backup extensions), or back up files, folders, and system state with the MARS agent. |
| Azure Files | Back up Azure file shares to a storage account. |
| SQL Server in Azure virtual machines | Back up SQL Server databases running on Azure virtual machines. |
| SAP HANA databases in Azure virtual machines | Back up SAP HANA databases running on Azure virtual machines. |
| Microsoft cloud | Azure Backup can replace your existing on-premises or off-site backup solution with a cloud-based solution that's reliable, secure, and cost-competitive. |
Azure Backup storage vaults
Azure Backup organizes your backup data in a storage entity called a vault. A storage vault stores backup copies, recovery points, and backup policies. There are two types of vaults: Azure Backup and Azure Recovery Services. The primary differences are the types of supported data sources and Azure products.
Azure Backup vault: Azure Backup vaults are used with Azure Backup only. Supported data sources include Azure Database for PostgreSQL servers, Azure blobs, and Azure disks.
Azure Recovery Services vault: Azure Recovery Services vaults can be used with Azure Backup or Azure Site Recovery. Supported data sources include Azure virtual machines, SQL, or SAP HANA in an Azure virtual machine, and Azure file shares. You can back up data to a Recovery Services vault from Azure Backup Server, Azure Backup Agent, and System Center Data Protection Manager.
Things to consider when using storage vaults
In your planning for Azure Backup and vault storage, consider the following points. Think about how you can use Azure Backup and storage vaults to support the Tailwind Traders BCDR requirements.
Consider vault organization. Think about how you want to organize your storage vaults. If all your workloads are managed from a single subscription and single resource, you can use a single vault. If your workloads are spread across subscriptions, you can create multiple vaults. Use separate vaults for Azure Backup and Azure Site Recovery.
Consider Azure Policy. For consistent policy settings across all your vaults, use Azure Policy to propagate your backup policy across multiple vaults. A backup policy is scoped to a vault.
Consider role-based protection. Protect your vaults by using Azure role-based access control (RBAC). You can secure your vaults and manage access with role-based access.
Consider redundancy. Specify how data in your vault is replicated for redundancy.
- Use locally redundant storage (LRS) to protect against failure in a datacenter. LRS replicates data to a storage scale unit.
- Use geo-redundant storage (GRS) to protect against region-wide outages. GRS replicates your data to a secondary region.