Design a geographically distributed data architecture
- 6 minutes
The final part of our application's architectural design to consider is the data storage tier. We want to make sure that data is both readable and writable with full functionality after a region-wide failure.
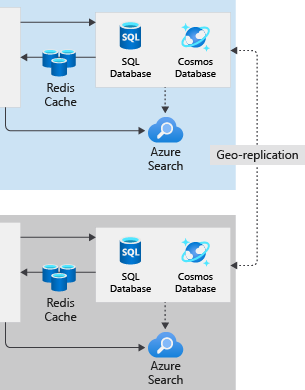
In the shipment tracking portal, we chose to use Azure Front Door to send all requests to App Services in the East US region. If the East US region fails, Front Door detects the failure, and sends requests to duplicate App Services components in the West US region. In our original, single-region architecture, we stored relational data in Azure SQL Database and semi-structured data in Cosmos DB. Now, we want to understand how we can ensure that both databases remain available if the East US region fails.
Here, we learn how to replicate data between regions, and how to ensure that failover can occur quickly, if necessary.
Azure SQL Database
To create a multi-region implementation of Azure SQL Database to store relational data, we can use either:
- Active geo-replication
- Auto failover groups
Active geo-replication
Azure SQL Database can automatically replicate a database and all its changes from one database to another with the active geo-replication feature. Only the primary logical server hosts a writable copy of the database. We can create up to four other logical servers that host read-only copies of the database.
For the shipment tracking portal, create a secondary database in the West US region and configure geo-replication from the East US region. When a regional failure occurs, Front Door redirects user requests to App Services in the West US region. App Services and Azure Functions can get access to the relational data because a copy has already been replicated to the West US region.
This change is automatic, but remember that the secondary database in West US is read-only. If a user tries to modify data, for example, by creating a new shipment, errors may arise. We can manually initiate a failover to West US as soon as we notice the problem in the Azure portal. If we want to automate this process, our developers can write code that calls the failover method in the Azure SQL Database REST API.
Note
Managed instances of Azure SQL Database do not support Active geo-replication. Managed instances are designed to make it simple to migrate data from an on-premises SQL Server while maintaining security. If your use a managed instance, consider using failover groups instead.
Auto failover groups
An auto failover group is a group of databases where data replicates automatically from a primary to one or more secondary servers. This design is like active geo-replication and uses the same data replication method. However, we can automate the response to a failure by defining a policy.
For the shipping portal, we create a secondary database in the West US region. We then add a policy that fails over the primary replica of the database to West US if a catastrophic failure occurs in the East US region. If that happens, the West US replica automatically becomes the writable primary database, and full functionality is maintained.
Consider using an auto failover group if you want to automate the failover of the writeable database without writing custom code to trigger it. Also, use auto failover groups if your database runs in a managed instance of Azure SQL Database.
Important
The replication that underlies both active geo-replication and auto failover groups are asynchronous. An acknowledgment is sent to the client when a change is applied to the primary replica. At this point, the transaction is considered complete, and replication occurs. If a failure occurs, the latest changes made in the primary database may not have replicated to the secondary. Keep in mind that, after a disaster, the most recent database changes may have been lost.
Azure Cosmos DB
Our configuration is less complex with Azure Cosmos DB because it's designed as a multi-regional cloud database system. Cosmos DB is a multi-model database, able to store relational data, semi-structured data, and other forms of data. Even if we run Cosmos DB in a single region, data is replicated to multiple instances across different fault-domains for the best availability.
When we create a Cosmos DB account multi-region, we can choose from the following modes:
Multi-region accounts with multiple write regions.
In this mode, all copies of the database are always writable. If a region fails, no failover is necessary.
Multi-region accounts with a single write region.
In this mode, only the primary region contains writable databases. The data replicated to the secondary regions are read-only. Updates are disabled by default when the primary region fails. However, we can select enable automatic failover so that Cosmos DB automatically fails over the primary, writable copy of the database to another region.
Important
In Cosmos DB, data replication is synchronous. When a change is applied, the transaction is not considered complete until replicated to a quorum of replicas. Then an acknowledgment is sent to the client. When a failure occurs, no recent changes are lost because replication has already occurred.