Exercise - Set up communication between IoT Hub and IoT Edge
This exercise uses Azure CLI in Azure Cloud Shell to issue the required commands.
Install Azure IoT extension
You need to add the Azure IoT extension to the Cloud Shell instance Azure CLI.
az extension add --name azure-iot
Note
This article uses the newest version of the Azure IoT extension, called azure-iot. The legacy version is called azure-cli-iot-ext.You should only have one version installed at a time. To see what extensions you have installed, use az extension list.
Use az extension remove --name azure-cli-iot-ext to remove the legacy version of the extension.
Use az extension add --name azure-iot to add the new version of the extension.
Create a resource group
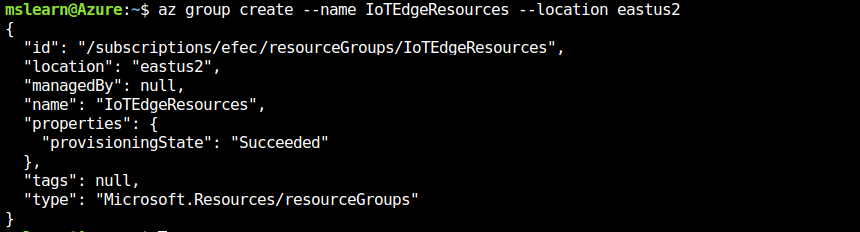
Create a resource group called "IoTEdgeResources" using the following command:
az group create --name IoTEdgeResources --location eastus2
The resulting output should be similar to this:
Create an IoT hub
The following code creates a free F1 tier hub in the resource group "IoTEdgeResources". Replace {hub_name} with a unique name for your IoT Hub.
az iot hub create --resource-group IoTEdgeResources --name {hub_name} --sku F1 --partition-count 2
Note
If you get an error because there's already one free hub in your subscription, change the SKU to S1. Each subscription can only have one free IoT hub. If you get an error that the IoT hub name isn't available, it means that someone else already has a hub with that name.
Register an IoT Edge device
In the Azure Cloud Shell, use the following instructions to create a device named "myEdgeDevice" in your hub.
Create a device identity
Since IoT Edge devices behave and can be managed differently compared to typical IoT devices, declare this identity to be for an IoT Edge device with the --edge-enabled flag.
Important
If you get an error about "iothubowner policy keys", make sure that your Cloud Shell is running the latest version of the azure-iot extension.
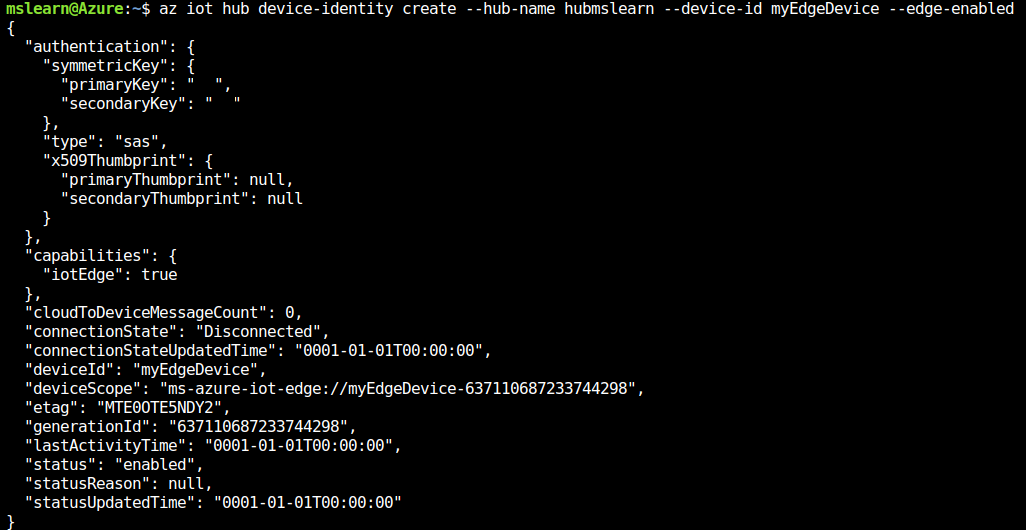
The following command creates the device identity:
az iot hub device-identity create --hub-name {hub_name} --device-id myEdgeDevice --edge-enabled
Retrieve the connection string
To retrieve the connection string for your device, which links your physical device with its identity in IoT Hub, use this command:
az iot hub device-identity connection-string show --device-id myEdgeDevice --hub-name {hub_name} --output table
The resulting output should be similar to this:
HostName={YourIoTHubName}.azure-devices.net;DeviceId=MyNodeDevice;SharedAccessKey={YourSharedAccessKey}
Copy the value of the connectionString key from the JSON output and save it. This value is the device connection string. You use this to configure the IoT Edge runtime in the next section.
Deploy the IoT Edge device
Use the following CLI command to create your IoT Edge device based on the prebuilt iotedge-vm-deploy template. Copy the following command into a text editor, replace the placeholder text with your information, then copy into your bash or Cloud Shell window:
az deployment group create \
--resource-group IoTEdgeResources \
--template-uri "https://aka.ms/iotedge-vm-deploy" \
--parameters dnsLabelPrefix='<REPLACE_WITH_VM_NAME>' \
--parameters adminUsername='azureuser' \
--parameters deviceConnectionString=$(az iot hub device-identity connection-string show --device-id myEdgeDevice --hub-name
<REPLACE_WITH_HUB_NAME> -o tsv) \
--parameters authenticationType='password' \
--parameters adminPasswordOrKey="<REPLACE_WITH_PASSWORD>"
Make sure that your password(adminPasswordOrKey) must be at least 12 characters long and have three of four of the following: lowercase characters, uppercase characters, digits, and special characters.
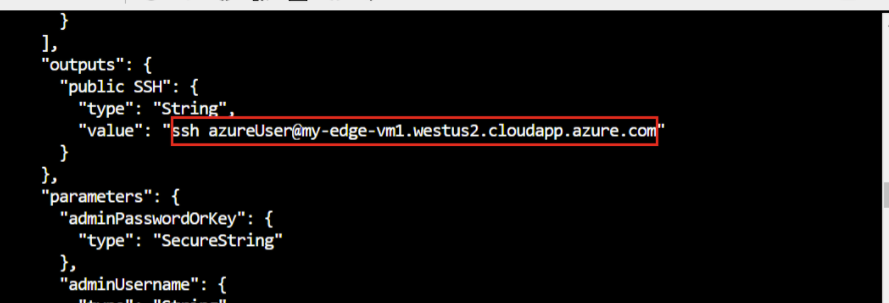
It may take a few minutes to create and start the new virtual machine. Once the deployment is complete, you should receive JSON-formatted output in the CLI that contains the SSH information to connect to the virtual machine. Copy the value of the public SSH entry of the outputs section:
View the IoT Edge runtime status
Use the following command to connect to your virtual machine. Replace azureuser if you used a different username than the one suggested during the deployment of the VM. Replace {DNS name} with your machine's DNS name.
ssh {admin username}@{DNS name}
Check if the IoT Edge device is configured
To verify that the IoT Edge security daemon is running as a system service, we use iotedge commands.
Important
You need elevated privileges to run iotedge commands.
Run the following commands to test the status of the IoT Edge device:
sudo systemctl status iotedge
The resulting output should be similar to this:
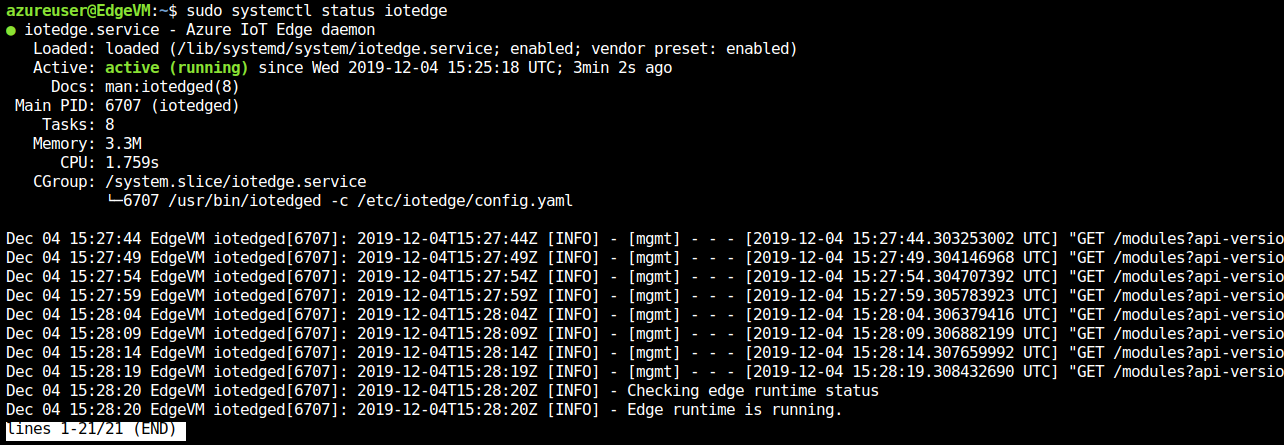

Your IoT Edge device is now configured. It's ready to run cloud-deployed modules.
If you need to troubleshoot the service, retrieve the service logs.
journalctl -u iotedge
View all the modules running on your IoT Edge device. Since the service just started for the first time, you should only see the edgeAgent module running. The edgeAgent module runs by default and helps to install and start any additional modules that you deploy to your device.
sudo iotedge list