Select DHCP high availability options
The IT manager at Contoso has told you that because DHCP is a critical component and needs to be available when clients request IP addresses, you must examine high availability options.
You learn that the options for making DHCP highly available include:
- Implementing DHCP Failover
- Using the DHCP Server role in Windows Server failover clustering
- Implementing split scopes
DHCP Failover
DHCP Failover is the preferred option for highly available DHCP service. It provides the widest variety of options for configuration. DHCP Failover is also the only high availability method in which the DHCP servers actively coordinate to provide service.
Note
The next unit describes DHCP Failover.
DHCP clustering
You can configure the DHCP Server role to run in a failover cluster. After installing the DHCP Server role on all cluster nodes and creating the failover cluster, you add the DHCP Server role to the failover cluster. As part of the configuration process, you need to provide an IP address for the DHCP server and shared storage. In this scenario, the DHCP configuration information is stored on shared storage, as displayed in the following graphic.
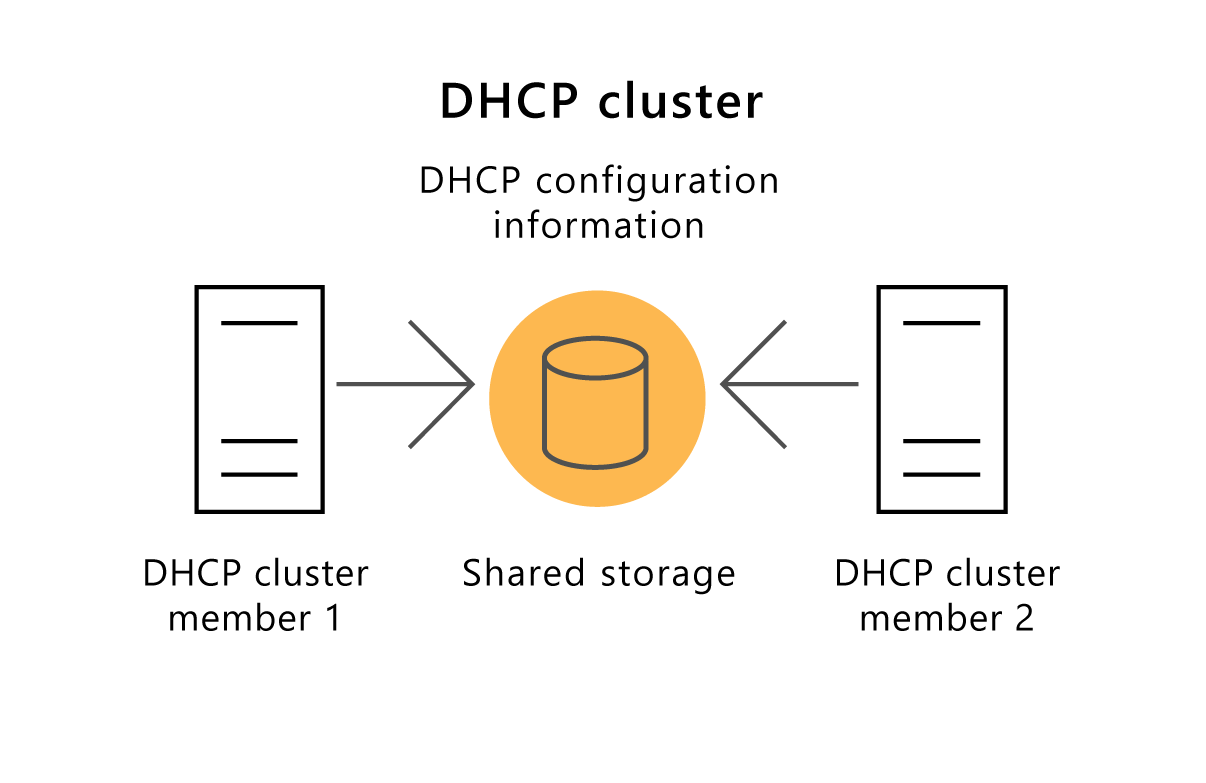
If one cluster node fails, another cluster node detects the failure and starts the DHCP service to continue providing service.
Split scopes
A split scope scenario also involves two DHCP servers. In this case, each DHCP server controls a part of the entire range of IP addresses, and both servers are active on the same network.
For example, as the following graphic illustrates, if your subnet is 192.168.0.0/24, you might assign an IP address range of 192.168.0.1 through 192.168.0.150 to the DHCP server A, the primary server, and assign 192.168.0.151 through 192.168.0.254 to DHCP server B, which acts as a DHCP secondary server.
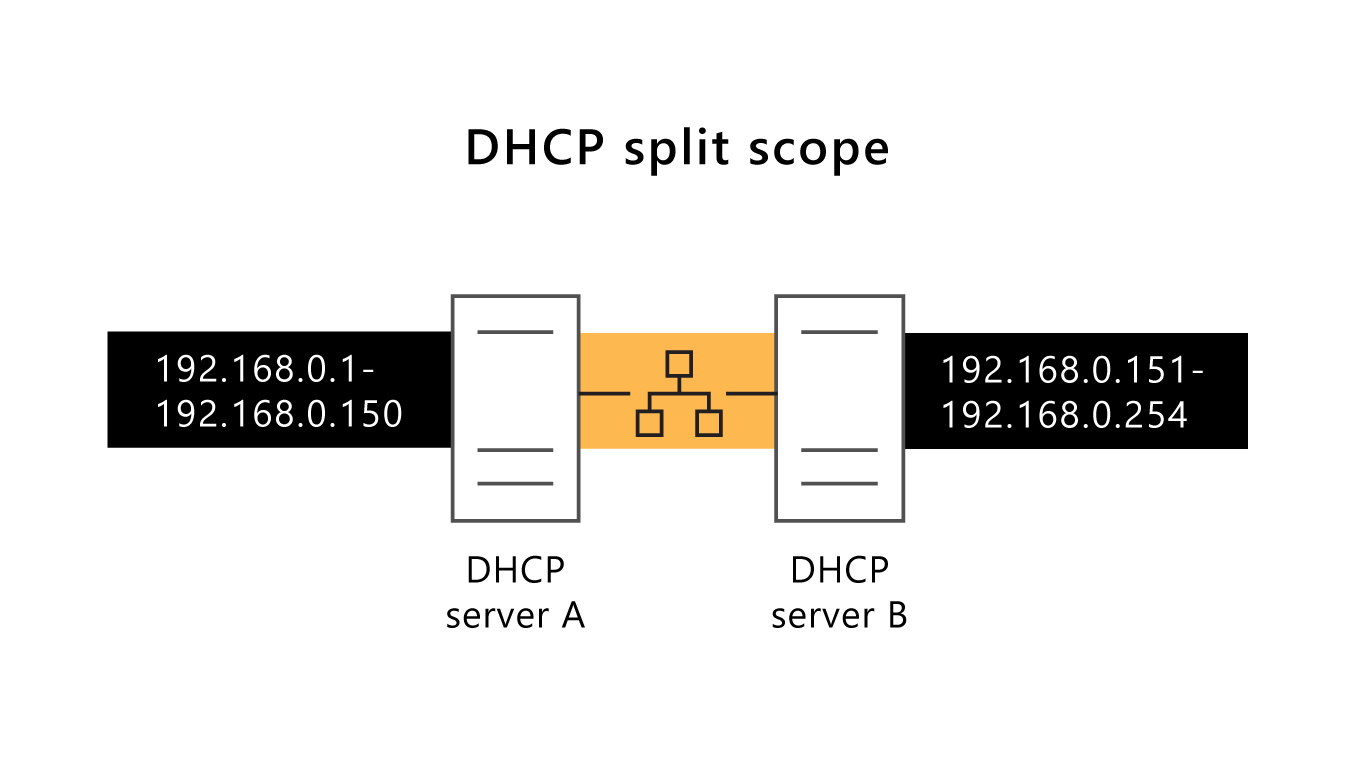
You can control which server is the primary server assigning addresses by setting the Delay configuration attribute in the properties of scope on the secondary server. This ensures that the primary server will be the first server to respond to client requests. If the primary server fails and stops responding to requests, then the secondary server’s response will be the one the client accepts.