Configure a CI/CD pipeline for your template
You've learned how to provision and deploy app resources to Azure and how to update them with new changes. However, the previous workflows relied on you manually running commands to apply changes to your environment. The Azure Developer CLI (azd) also allows you to further automate this process using a continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipeline with either GitHub Actions or Azure Pipelines. By configuring a CI/CD pipeline, you can automatically update your Azure environment with the latest changes simply by committing and pushing your changes to GitHub.
Configure the pipeline
Most azd templates have CI/CD workflow files included with them in either the .github folder for GitHub Actions or the .azdo folder for Azure Pipelines. The sample template used in this module relies on GitHub Actions, but the azd command and workflow is the same regardless of the CI/CD platform. A GitHub repository is required for you to be able to set up CI/CD. You can either create the new repository by forking the original azd template repository and setting it as a remote, or you can create a repo using azd during the pipeline configuration process, which is the approach you'll use in this example.
Complete the following steps to configure a CI/CD pipeline for your template:
In a command prompt set to your project root directory, run the following command:
azd pipeline configSelect GitHub.
If a GitHub origin isn't set for your project,
azdwill ask how you would like to configure your remote repository. Select the option Create a new private GitHub repository and then enter a name for the new repo.azdwill complete the following tasks for you:- Creates a GitHub repository and commits your project code to it.
- Creates and configures a service principal for the app on the Azure subscription.
- Configures a secure connection between Azure and your repository using the service principal and GitHub secrets.
azdwill also ask you if you want to commit and push your local changes to the configured pipeline. Enter yes and wait for it to finish.Select the output URL in the console to open a browser tab to the new GitHub repository.
Navigate to the Actions tab to find a workflow running that will authenticate, package, provision and deploy your code. The workflow uses the same
azd auth login,azd provisionandazd deploycommands you used previously. You can explore the details of this workflow in the.githubfolder of your project.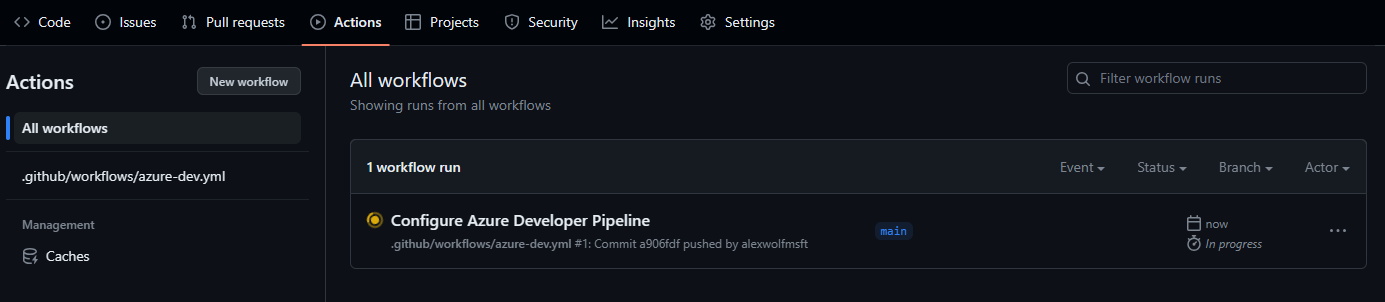
Once your pipeline is configured, you can continuously update your Azure environment and deployed app by pushing your code changes to GitHub. You can also continue to run azd commands locally like you did in the previous steps.