Create an Azure SQL Database baseline
Azure SQL Database is a cloud-based relational database family of products that support many of the same features offered in Microsoft SQL Server. Azure SQL Database provides an easy transition from an on-premises database to a cloud-based database that has built-in diagnostics, redundancy, security, and scalability.
Azure SQL Database security recommendations
The following sections describe the Azure SQL Database recommendations that are in CIS Microsoft Azure Foundations Security Benchmark v. 3.0.0. Included with each recommendation are the basic steps to complete in the Azure portal. You should complete these steps for your own subscription and by using your own resources to validate each security recommendation.
Enable auditing - Level 1
Auditing for Azure SQL Database and Azure Synapse Analytics tracks database events and writes them to an audit log in your Azure storage account, Azure Log Analytics workspace, or in Azure Event Hubs. Auditing also:
- Helps you maintain regulatory compliance, understand database activity, and gain insight into discrepancies and anomalies that might alert you to business concerns or suspected security violations.
- Enables and facilitates adherence to compliance standards, although it doesn't guarantee compliance.
To turn on auditing, complete the following steps for each database in your Azure subscription.
Sign in to the Azure portal. Search for and select SQL databases.
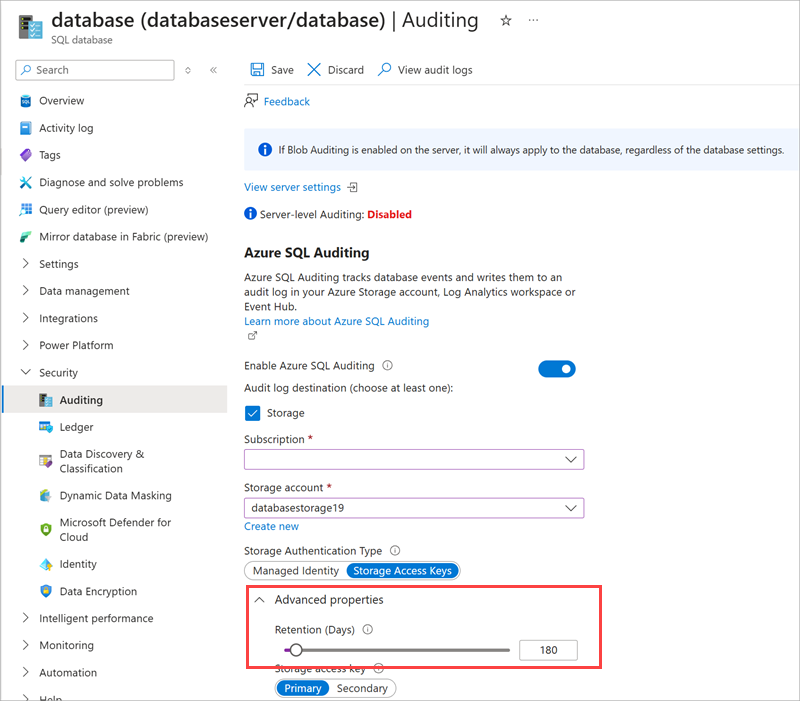
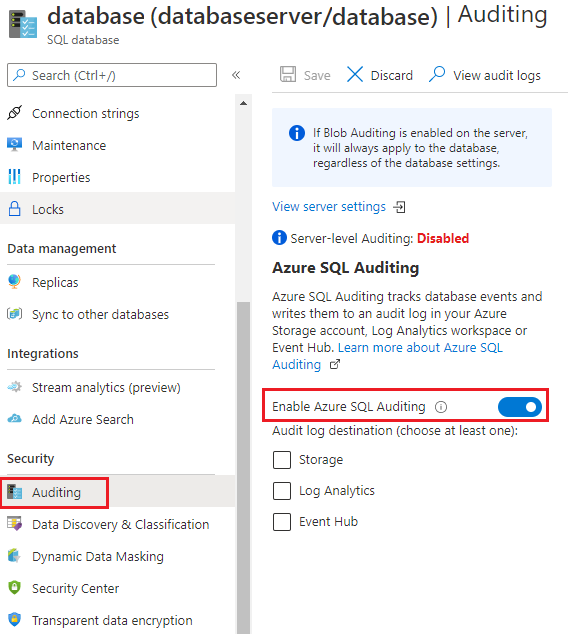
In the left menu under Security, select Auditing.
In the Auditing pane, enable Enable Azure SQL Auditing, and then select at least one audit log destination.
If you change any settings, select Save in the menu bar.
For more information about auditing, see Auditing for Azure SQL Database and Azure Synapse Analytics.
Enable SQL protections in Microsoft Defender for Cloud - Level 1
Microsoft Defender for Cloud detects anomalous activities that indicate unusual and potentially harmful attempts to access or exploit databases. Defender for Cloud can identify:
- Potential SQL injection.
- Access from an unusual location or datacenter.
- Access from an unfamiliar principal or from a potentially harmful application.
- Brute-force SQL credentials.
You can access and manage SQL threats in the Defender for Cloud menu.
Sign in to the Azure portal. Search for and select Microsoft Defender for Cloud.
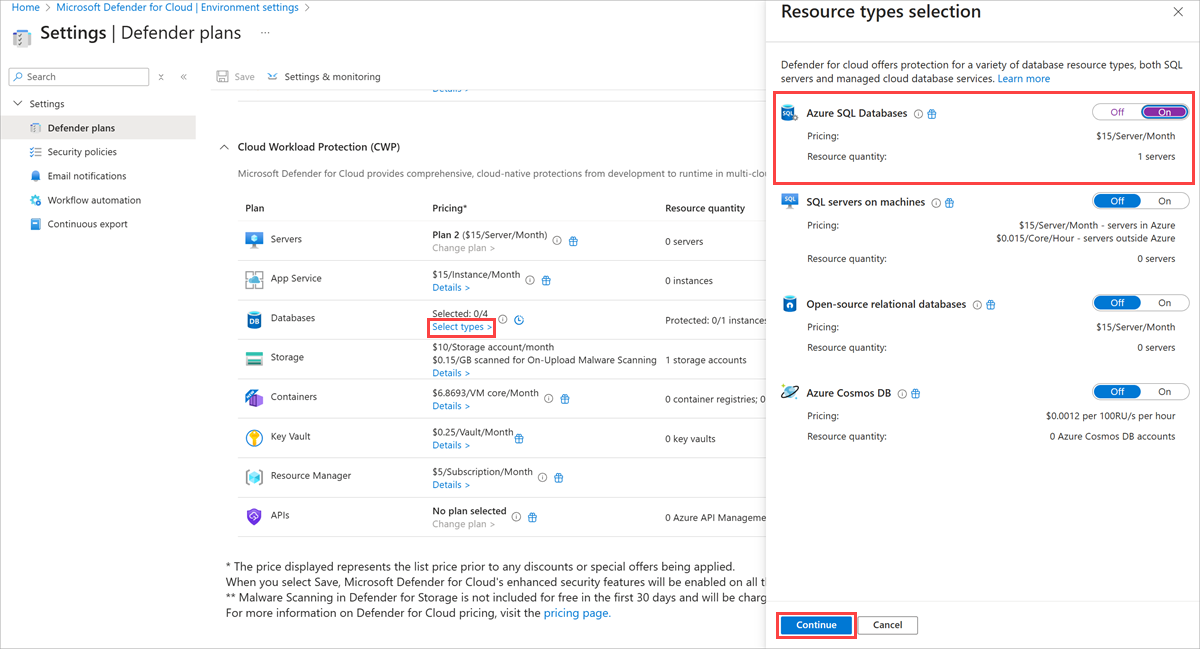
In the left menu under Management, select Environment settings.
Select your subscription.
In the Defender plans pane, select Select types in the Databases row, then set Azure SQL Databases to On.
Select Continue.
Return to Azure Home. Search for and select SQL databases, then select the database you want to view.
For each database instance, in the left menu under Security, select Microsoft Defender for Cloud. View security recommendations, alerts, and vulnerability assessment findings for your SQL Database instance.
Configure audit retention for more than 90 days - Level 1
Audit logs should be preserved for security and discovery, and to meet legal and regulatory compliance requirements. Complete the following steps for each Azure SQL Database instance in your Azure subscription.
Sign in to the Azure portal. Search for and select SQL databases, then select a database.
In the left menu under Security, select Auditing.
Select your Audit log destination, and then expand Advanced properties.
Ensure that Retention (Days) is greater than 90 days.
If you change any settings, select Save in the menu bar.