Exercise - Ensure secure access with access control list
In this exercise, you update the code responsible for importing local markdowns files with configuring ACLs on selected items.
Before you start
Before you do this exercise, be sure to complete the previous exercise in this module.
Import content that's available to everyone in the organization
When you implemented the code for importing external content in the previous exercise, you configured it to be available to everyone in the organization. Here's the code that you used:
static IEnumerable<ExternalItem> Transform(IEnumerable<DocsArticle> content)
{
var baseUrl = new Uri("https://learn.microsoft.com/graph/");
return content.Select(a =>
{
var docId = GetDocId(a.RelativePath ?? "");
return new ExternalItem
{
Id = docId,
Properties = new()
{
AdditionalData = new Dictionary<string, object> {
{ "title", a.Title ?? "" },
{ "description", a.Description ?? "" },
{ "url", new Uri(baseUrl, a.RelativePath!.Replace(".md", "")).ToString() }
}
},
Content = new()
{
Value = a.Content ?? "",
Type = ExternalItemContentType.Html
},
Acl = new()
{
new()
{
Type = AclType.Everyone,
Value = "everyone",
AccessType = AccessType.Grant
}
}
};
});
}
You configured the ACL to grant access to everyone. Let's adjust it for selected markdown pages that you're importing.
Import content available to select users
First, configure one of the pages that you're importing to be accessible only to a specific user.
In the web browser:
Navigate to the Azure portal at https://portal.azure.com and sign in with your work or school account.
From the sidebar, select Microsoft Entra ID.
From the navigation, select Users.
From the list of users, open one of the users by selecting their name.
Copy the value of the Object ID property.
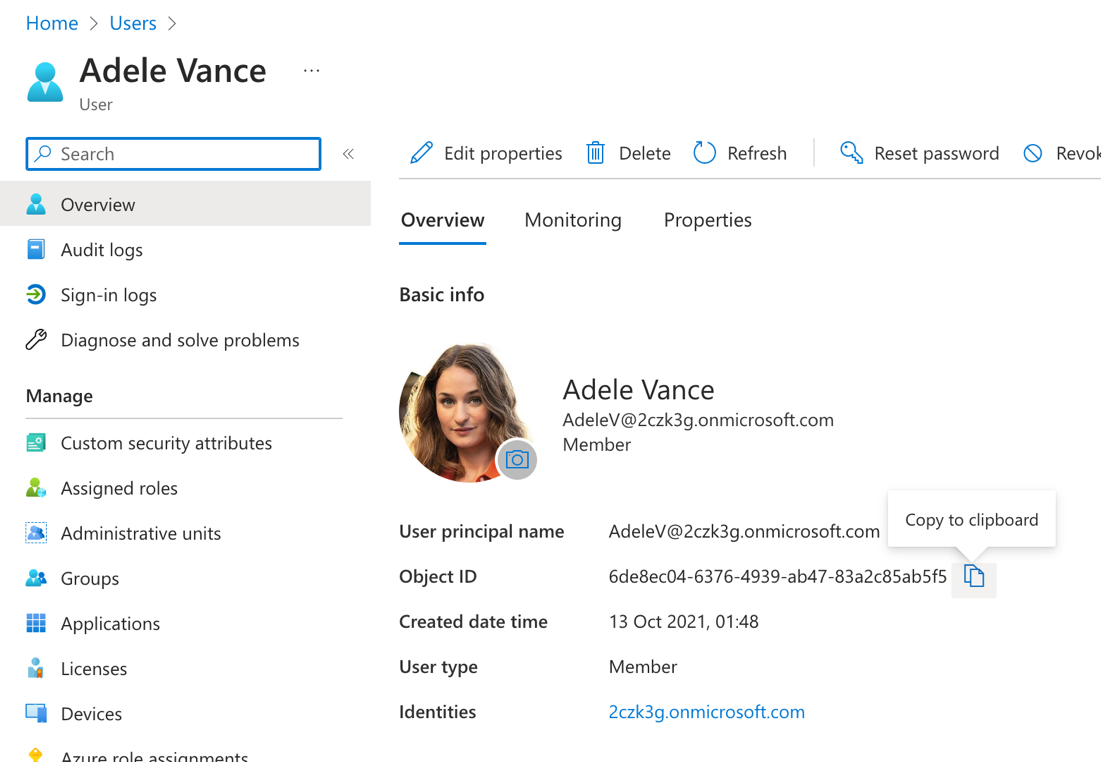
Use this value to define a new ACL for a specific markdown page.
In the code editor:
Open the ContentService.cs file, and locate the
Transformmethod.Inside the
Selectdelegate, define the default ACL that applies to all imported items:var acl = new Acl { Type = AclType.Everyone, Value = "everyone", AccessType = AccessType.Grant };Next, override the default ACL for the markdown file with name ending in
use-the-api.md:if (a.RelativePath!.EndsWith("use-the-api.md")) { acl = new() { Type = AclType.User, // AdeleV Value = "6de8ec04-6376-4939-ab47-83a2c85ab5f5", AccessType = AccessType.Grant }; }Finally, update the code that returns the external item to use the defined ACL:
return new ExternalItem { Id = docId, Properties = new() { AdditionalData = new Dictionary<string, object> { { "title", a.Title ?? "" }, { "description", a.Description ?? "" }, { "url", new Uri(baseUrl, a.RelativePath!.Replace(".md", "")). ToString() } } }, Content = new() { Value = a.Content ?? "", Type = ExternalItemContentType.Html }, Acl = new() { acl } };The updated
Transformmethod looks as follows:static IEnumerable<ExternalItem> Transform(IEnumerable<DocsArticle> content) { var baseUrl = new Uri("https://learn.microsoft.com/graph/"); return content.Select(a => { var acl = new Acl { Type = AclType.Everyone, Value = "everyone", AccessType = AccessType.Grant }; if (a.RelativePath!.EndsWith("use-the-api.md")) { acl = new() { Type = AclType.User, // AdeleV Value = "6de8ec04-6376-4939-ab47-83a2c85ab5f5", AccessType = AccessType.Grant }; } var docId = GetDocId(a.RelativePath ?? ""); return new ExternalItem { Id = docId, Properties = new() { AdditionalData = new Dictionary<string, object> { { "title", a.Title ?? "" }, { "description", a.Description ?? "" }, { "url", new Uri(baseUrl, a.RelativePath!.Replace(".md", "")). ToString() } } }, Content = new() { Value = a.Content ?? "", Type = ExternalItemContentType.Html }, Acl = new() { acl } }; }); }Save your changes.
Import content available to a select group
Now, let's extend the code so that another page is only accessible by a select group of users.
In the web browser:
- Navigate to the Azure portal at https://portal.azure.com and sign in with your work or school account.
- From the sidebar, select Microsoft Entra ID.
- From the navigation, select Groups.
- From the list of groups, open one of the groups by selecting their name.
- Copy the value of the Object Id property.
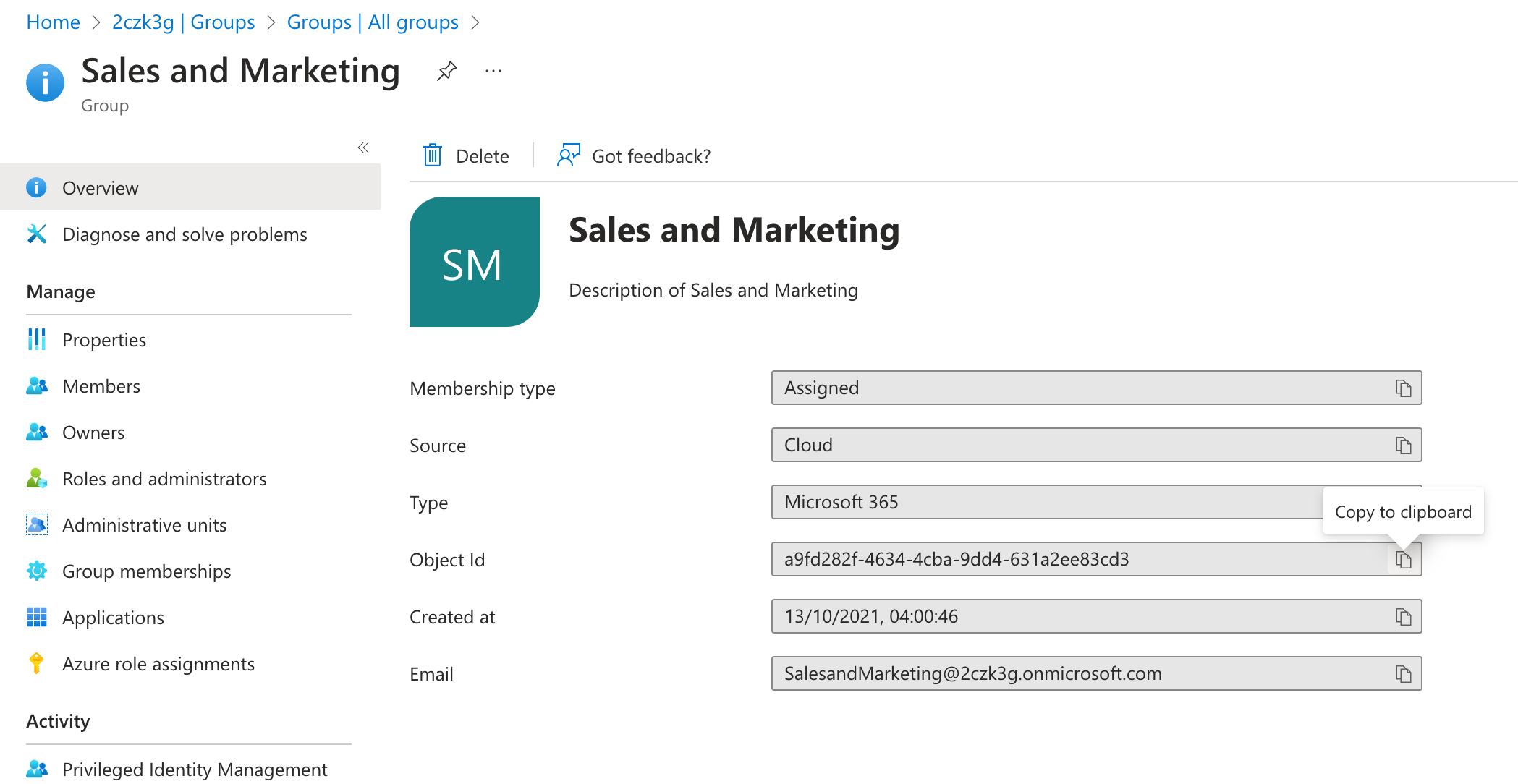
Use this value to define a new ACL for a specific markdown page.
In the code editor:
Open the ContentService.cs file, and locate the
TransformmethodExtend the previously defined
ifclause, with an extra condition to define the ACL for the markdown file with name ending intraverse-the-graph.md:if (a.RelativePath!.EndsWith("use-the-api.md")) { acl = new() { Type = AclType.User, // AdeleV Value = "6de8ec04-6376-4939-ab47-83a2c85ab5f5", AccessType = AccessType.Grant }; } else if (a.RelativePath.EndsWith("traverse-the-graph.md")) { acl = new() { Type = AclType.Group, // Sales and marketing Value = "a9fd282f-4634-4cba-9dd4-631a2ee83cd3", AccessType = AccessType.Grant }; }The updated
Transformmethod looks as follows:static IEnumerable<ExternalItem> Transform(IEnumerable<DocsArticle> content) { var baseUrl = new Uri("https://learn.microsoft.com/graph/"); return content.Select(a => { var acl = new Acl { Type = AclType.Everyone, Value = "everyone", AccessType = AccessType.Grant }; if (a.RelativePath!.EndsWith("use-the-api.md")) { acl = new() { Type = AclType.User, // AdeleV Value = "6de8ec04-6376-4939-ab47-83a2c85ab5f5", AccessType = AccessType.Grant }; } else if (a.RelativePath.EndsWith("traverse-the-graph.md")) { acl = new() { Type = AclType.Group, // Sales and marketing Value = "a9fd282f-4634-4cba-9dd4-631a2ee83cd3", AccessType = AccessType.Grant }; } var docId = GetDocId(a.RelativePath ?? ""); return new ExternalItem { Id = docId, Properties = new() { AdditionalData = new Dictionary<string, object> { { "title", a.Title ?? "" }, { "description", a.Description ?? "" }, { "url", new Uri(baseUrl, a.RelativePath!.Replace(".md", "")).ToString() } } }, Content = new() { Value = a.Content ?? "", Type = ExternalItemContentType.Html }, Acl = new() { acl } }; }); }Save your changes.
Apply the new ACLs
The final step is to apply the newly configured ACLs.
- Open a terminal and change the working directory to your project.
- Build the project by running the
dotnet buildcommand. - Start loading the content by running the
dotnet run -- load-contentcommand.